Checking and Handling Intrusion Events
HSS displays alarm and event statistics and their summary all on one page. You can have a quick overview of alarms, including the numbers of servers with alarms, handled alarms, unhandled alarms, blocked IP addresses, and isolated files.
The Events page displays the alarm events generated in the last 30 days.
The status of a handled event changes from Unhandled to Handled.
Constraints and Limitations
- To skip the checks on high-risk command execution, privilege escalation, reverse shells, abnormal shells, or web shells, manually disable the corresponding policies in the policy groups on the Policies page. HSS will not check the servers associated with disabled policies.
- Other detection items cannot be manually disabled.
Checking Alarm Events
- Log in to the management console.
- In the upper left corner of the page, select a region, click
 , and choose .
, and choose . - In the navigation pane, choose Intrusions > Events, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Events page
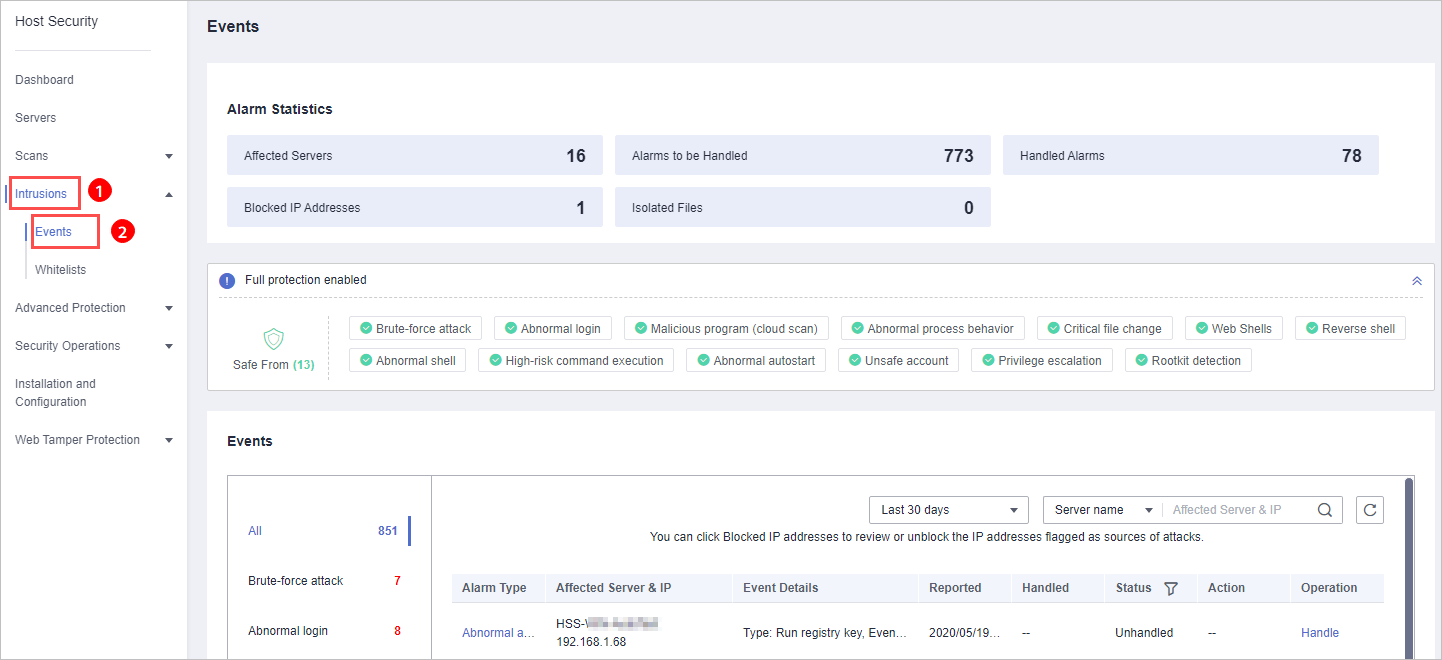
Table 1 Alarm events Alarm Event
Description
Affected Servers
Number of servers for which alarms are generated.
Alarms to be Handled
Number of alarms to be handled.
By default, all unhandled alarms are displayed on the Events page. For more information, see Handling Alarm Events.
Handled Alarms
Number of handled alarms.
Blocked IP Addresses
Number of blocked IP addresses. You can click the number to check blocked IP address list.
If a valid IP address is blocked by mistake (for example, after O&M personnel enter incorrect passwords for multiple times), you can manually unblock it. If a server is frequently attacked, you are advised to fix its vulnerabilities in a timely manner and eliminate risks.
NOTICE:After a blocked IP address is unblocked, HSS will no longer block the operations performed by the IP address.
Isolated Files
HSS can isolate detected threat files. Files that have been isolated are displayed on a slide-out panel on the Events page. You can click Isolated Files on the upper right corner to check them.
You can recover isolated files. For details, see Managing Isolated Files.
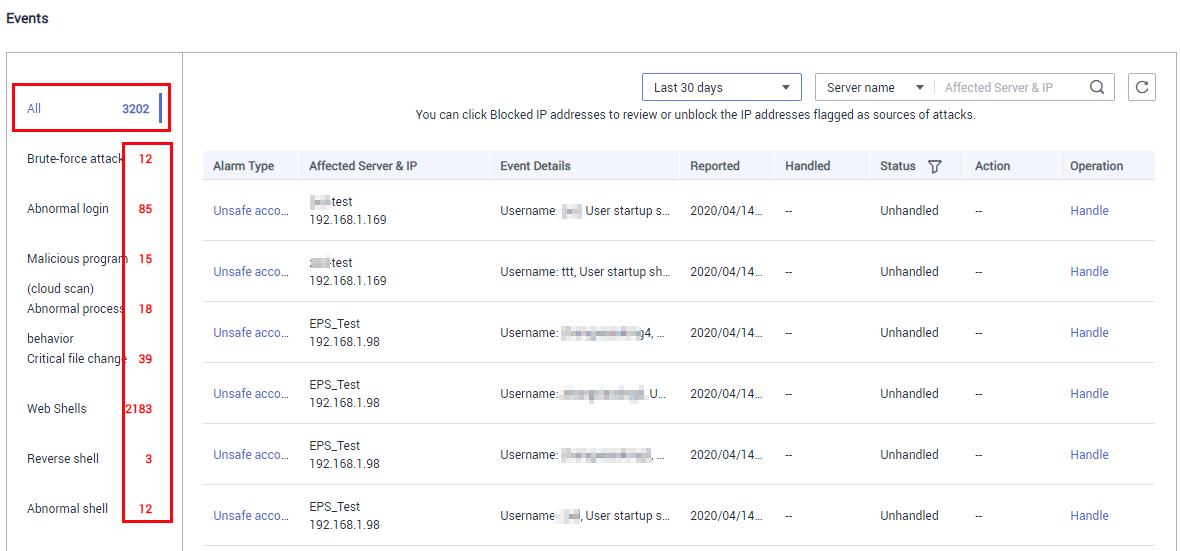
- Click an alarm event in the list to view the affected servers and occurrence time of the event, as shown in Figure 2. The following information is displayed:
- Total number of alarms
- Number of each type of alarms
Figure 2 Alarm event statistics
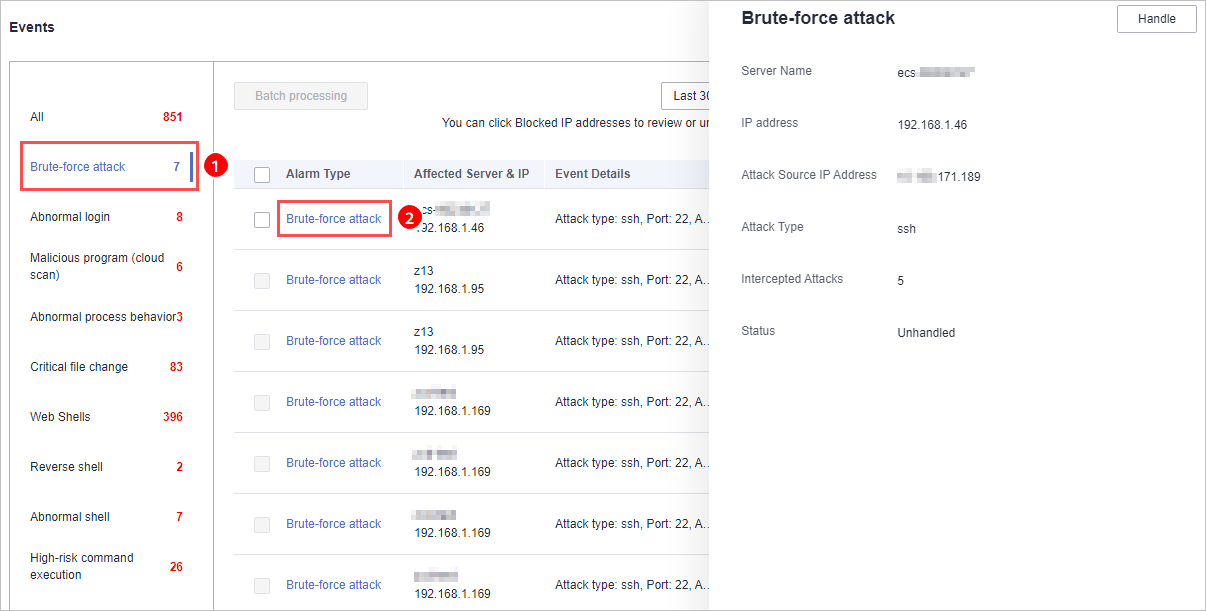
- Click an alarm name to view its details, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Alarm details
Handling Alarm Events
This section describes how you should handle alarm events to ensure server security.
Do not fully rely on alarms to defend against attacks, because not every issue can be detected in a timely manner. You are advised to take more measures to prevent threats, such as checking for and fixing vulnerabilities and unsafe settings.
- Log in to the management console.
- In the upper left corner of the page, select a region, click
 , and choose .
, and choose . - In the navigation pane, choose Intrusions > Events.
Figure 4 Events page

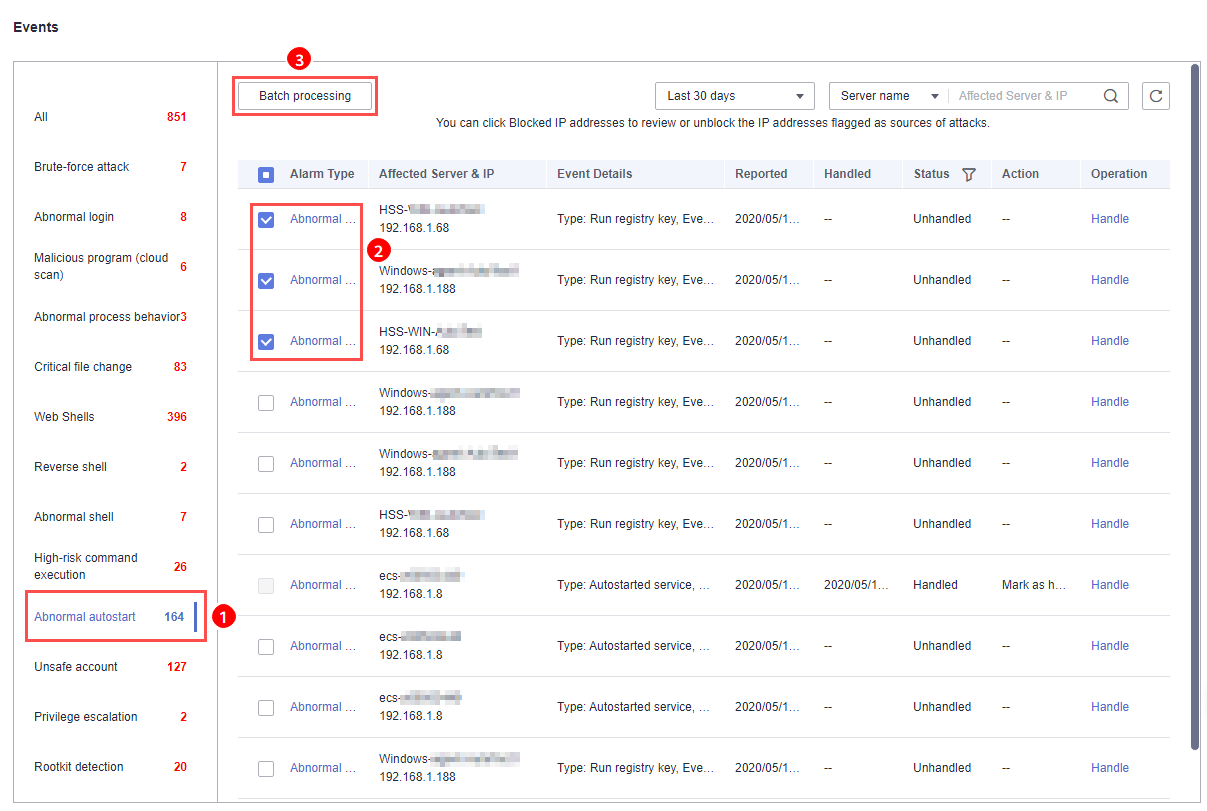
- Click an event type, select events, and click Handle, as shown in Figure 5. Table 2 describes the processing methods you can choose from.Note
You can also click Handle in the row where an alarm resides.
Figure 5 Handling alarm events
Alarm events are displayed on the Events page. Here you can check up to 30 days of historical events.
Check and handle alarm events as needed. The status of a handled event changes from Unhandled to Handled. HSS will no longer collect its statistics or display them on the Dashboard page.
Table 2 Event handling methods Method
Description
Ignore
Ignore the current alarm. Any new alarms of the same type will still be reported by HSS.
Isolate and kill
If a program is isolated and killed, it will be terminated immediately and no longer able to perform read or write operations. Isolated source files of programs or processes are displayed on the Isolated Files slide-out panel and cannot harm your servers.
You can click Isolated Files on the upper right corner to check the files. For details, see Managing Isolated Files.
The following types of alarm events support online isolation and killing:
- Malicious program (cloud scan)
- Abnormal process behavior
NOTE:When a program is isolated and killed, the process of the program is terminated immediately. To avoid impact on services, check the detection result, and cancel the isolation of or unignore misreported malicious programs (if any).
Mark as handled
Mark the event as handled. You can add remarks for the event to record more details.
Add to whitelist
Add false alarmed items of the Brute-force attack and Abnormal login types to the login whitelist.
HSS will no longer report alarm on the whitelisted items.
Add to alarm whitelist
Add false alarmed items of the following types to the login whitelist.
HSS will no longer report alarm on the whitelisted items.
- Reverse shell
- Web shell
- Abnormal process behavior
- Process privilege escalation
- File privilege escalation
- High-risk command
- Malicious program
Handling Suggestion
Alarm Name | Suggestion |
|---|---|
Brute-force attack | Pay special attention to such events. If you receive a brute-force attack alarm, detected events will probably be but are not limited to:
You are advised to check whether the alarmed login IP address is valid.
|
Abnormal login | If an abnormal login is detected, you are advised to immediately check whether the source IP address is valid.
|
Malicious program (cloud scan) | Common methods to handle the event are as follows:
|
Abnormal process behavior | If abnormal process behaviors are detected, you are advised to check processes immediately.
|
Critical file change | If a key file change is detected, you are advised to check the change immediately.
|
Web shell | If a web shell is detected, you are advised to immediately check whether the file is valid.
|
Reverse/Abnormal shell | If a reverse or abnormal shell is detected, you are advised to check whether executed commands are valid.
|
High-risk command execution | If a high-risk command is detected, you are advised to immediately check whether the command is valid.
|
Auto-startup check | If a new auto-started item is detected, you need to check whether the auto-startup item is valid.
|
Unsafe account | If an unsafe account is detected, you are advised to immediately check whether the account is valid.
|
Privilege escalation | If a privilege escalation operation is detected, you are advised to immediately check whether the operation is valid.
|
Rootkit | If Rootkit installation is detected, you are advised to immediately check whether the installation is valid.
|
- Constraints and Limitations
- Checking Alarm Events
- Handling Alarm Events
- Handling Suggestion