A DNS server is used to resolve domain names of file systems.
Scenarios
By default, the IP address of the DNS server used to resolve domain names of file systems is automatically configured on ECSs when they are created. No manual configuration is needed except when the resolution fails due to a change in the DNS server IP address.
Procedure
- Log in to the ECS as user root.
- Run the vi /etc/resolv.conf command to edit the /etc/resolv.conf file. Add the DNS server IP address above the existing nameserver information. See Figure 1.
Figure 1 Configuring DNS
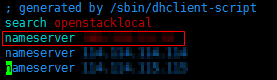
The format is as follows:
nameserver DNS server IP address - Press Esc, input :wq, and press Enter to save the changes and exit the vi editor.
- Run the following command to check whether the IP address is successfully added:
cat /etc/resolv.conf
- Run the following command to check whether an IP address can be resolved from the file system domain name:
nslookup File system domain name
NoteObtain the file system domain name from the file system mount point.
- (Optional) In a network environment that uses the DHCP server, edit the /etc/resolv.conf file to prevent the file from being automatically modified upon an ECS restart, and prevent the DNS server IP address added in 2 from being reset.
- Run the following command to lock the file:chattr +i /etc/resolv.confNote
Run the chattr -i /etc/resolv.conf command to unlock the file if needed.
- Run the following command to check whether the editing is successful:
lsattr /etc/resolv.conf
If the information shown in Figure 2 is displayed, the file is locked.
Figure 2 A locked file

- Run the following command to lock the file:
Parent topic: Network Configuration