Enabling the WTP Edition
The premium edition will be enabled when you enable WTP.
How WTP Prevents Web Page Tampering
Type | Mechanism |
|---|---|
Static web page protection |
|
Dynamic web page protection |
|
Restrictions
The Windows firewall must be enabled when you enable protection for a Windows server. Do not disable the Windows firewall during the HSS in-service period.
Prerequisites
- On the Server Protection page of the WTP console, the Agent Status of the target server is Online, and the Protection Status of the server is Disabled.
- In the server list on the Servers page of the HSS console, the Agent Status of the target server is Online, and the Protection Status of the server is Disabled.
Setting Protected Directories
You can set:
- Directories
You can add a maximum of 50 protected directories to a host. For details, see Adding a Protected Directory or File System.
To record the running status of the server in real time, exclude the log files in the protected directory. You can grant high read and write permissions for log files to prevent attackers from viewing or tampering with the log files.
- File systems
You can add a maximum of five file systems. For details, see Adding a Protected Directory or File System.
OS partitions are not allowed.
Enabling WTP
- Log in to the management console.
- In the upper left corner of the page, select a region, click
 , and choose .
, and choose . - In the navigation pane, choose Web Tamper Protection > Server Protection. Click Enable in the Operation column of a server.
Figure 1 Web Tamper Protection
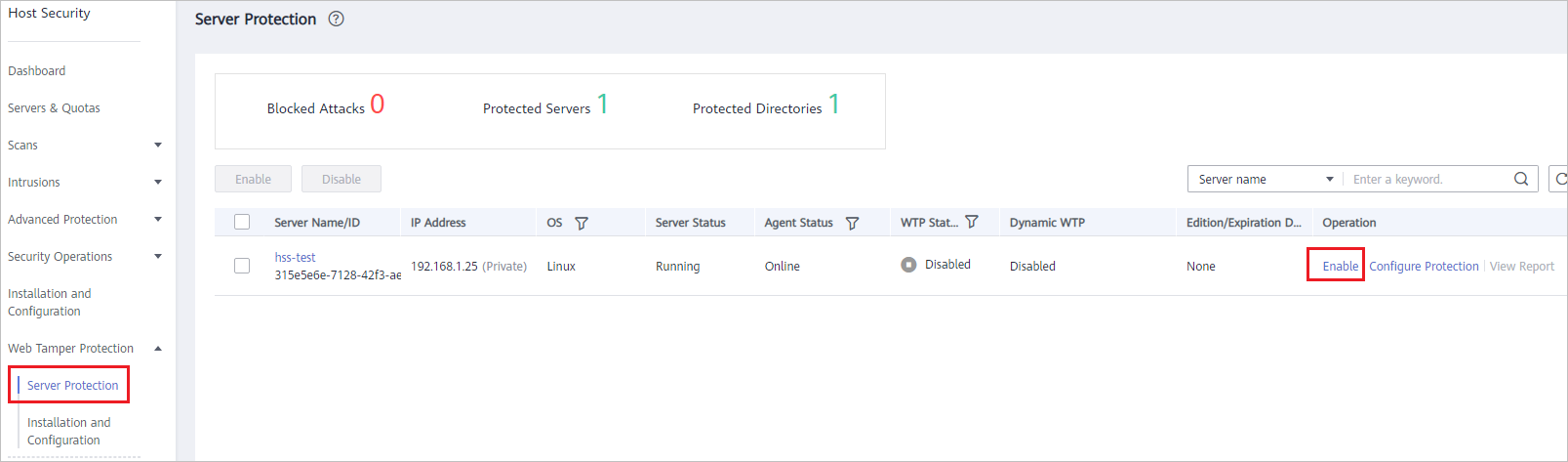
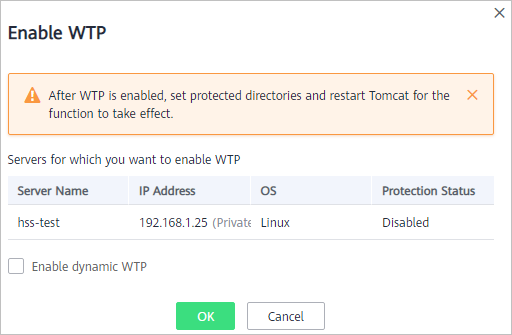
- In the Enable WTP dialog box, click OK, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Enabling WTP
- View the server status on the Web Tamper Protection page.
- Disable WTP before updating a website and enable it after the update is complete. Otherwise, the website will fail to be updated.
- Your website is not protected while WTP is disabled. Enable it immediately after updating your website.
Follow-Up Procedure
Disabling WTP
Choose Web Tamper Protection > Server Protection and click Disable in the Operation column of a server.
- Before disabling WTP, perform a comprehensive detection on the server, handle known risks, and record operation information to prevent O&M errors and attacks on the server.
- If WTP is disabled, web applications are more likely to be tampered with. Therefore, you need to delete important data on the server, stop important services on the server, and disconnect the server from the external network in a timely manner to avoid unnecessary losses caused by attacks on the server.
- After you or disable WTP, files in the protected directory are no longer protected. You are advised to process files in the protected directory before performing these operations.
- If you find some files missing after disabling WTP, search for them in the local or remote backup path.
- How WTP Prevents Web Page Tampering
- Restrictions
- Prerequisites
- Setting Protected Directories
- Enabling WTP
- Follow-Up Procedure