Modifying a Policy
You can modify policies in a policy group.
Modifications on a policy take effect only in the group it belongs to.
Accessing the Policies Page
- Log in to the management console.
- In the upper left corner of the page, select a region, click
 , and choose .
, and choose . - In the navigation pane, choose Security Operations > Policies.
Asset
- In the policy group list, click the name of the group that contains the required policy.
- Click Assets.
- In the Policy Settings area, modify the settings as required, as shown in Figure 1. For more information, see Table 1.
Figure 1 Assets
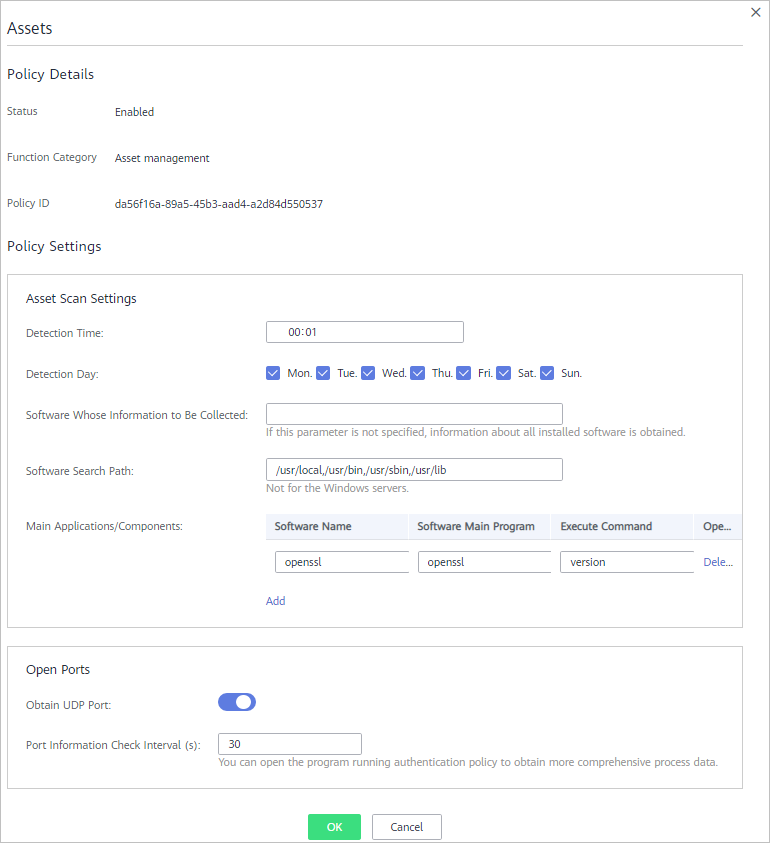
Table 1 Assets parameters Parameter
Description
Detection Time
Time point when scans are performed. It can be accurate to the minute.
Detection Day
Days in a week when assets are scanned. You can select one or more days.
Software Whose Information to Be Collected
- Software name. A name can contain a maximum of 5000 characters without any space. Use commas (,) to separate software names.
- If this parameter is not specified, information about all installed software will be retrieved as its value.
Software Search Path
Software search path. This parameter is not required for a Windows server.
Main Applications/Components
- Software Name
- Software Main Program
- Execute Command
- Operation: You can click Add or Remove to modify operations.
Obtain UDP Port
Obtains UDP port information and check the web directories.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Port Information Check Interval (s)
Interval between two consecutive port checks. The value range is 30s to 86,400s.
- Click OK.
System Configuration Detection
- In the policy group list, click the name of the group that contains the required policy.
- Click System Configuration Detection.
- In the Policy Settings area, modify the settings as required, as shown in Figure 2. For more information, see Table 2.
Figure 2 System Configuration Detection
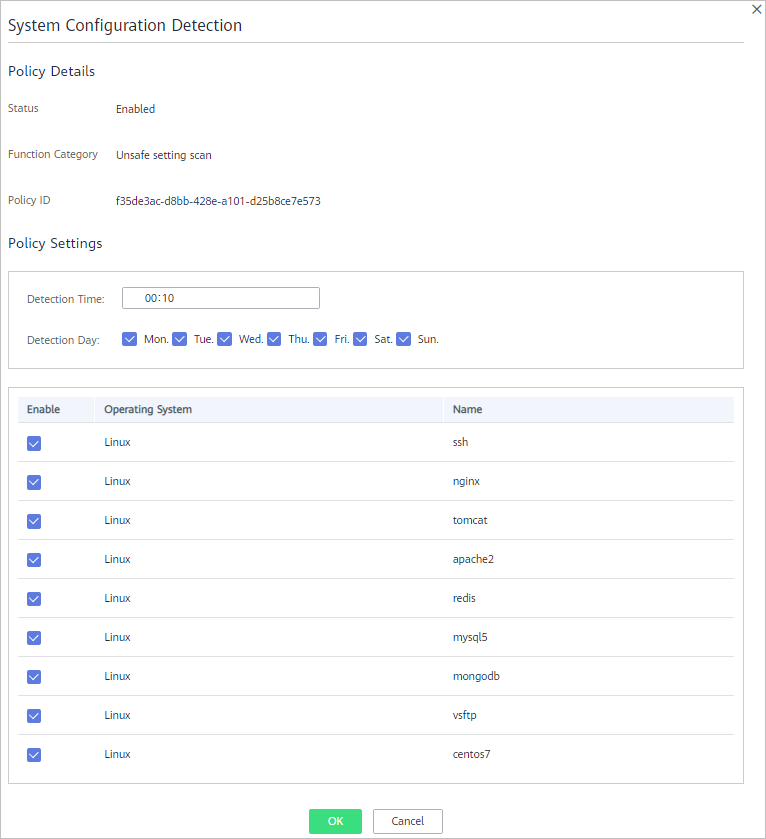
Table 2 System configuration detection parameters Parameter
Description
Detection Time
Time point when detections are performed. It can be accurate to the minute.
Detection Day
Day in a week when a detection is performed. You can select any days from Monday to Sunday.
- Select the OSs to be checked.
- Click OK.
Weak Password Detection
Weak passwords are not attributed to a certain type of vulnerabilities, but they bring no less security risks than any type of vulnerabilities. Data and programs will become insecure if their passwords are cracked.
HSS proactively detects the accounts using weak passwords and generates alarms for the accounts. You can also add a password that may have been leaked to the weak password list to prevent server accounts from using the password.
- In the policy group list, click the name of the group that contains the required policy.
- In the policy group list, click Weak Password Detection.
- In the Policy Settings area, modify the settings as required, as shown in Figure 3. For more information, see Table 3.
Figure 3 Weak password detection
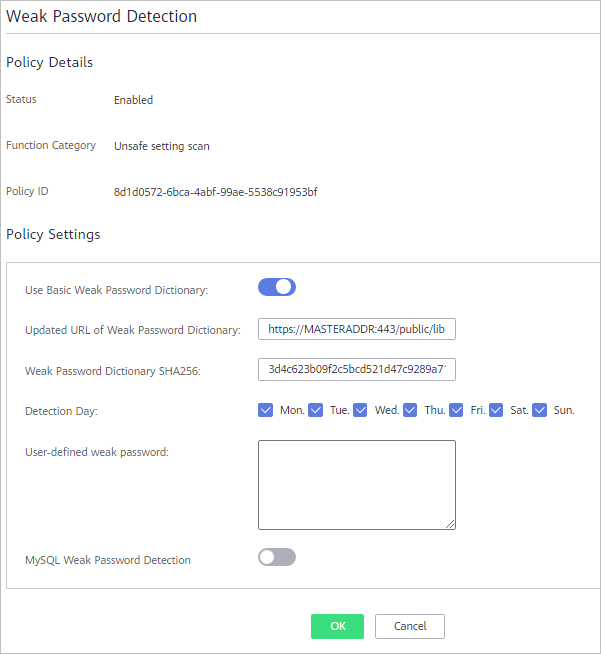
Table 3 Weak password detection parameters Parameter
Description
Use Basic Weak Password Dictionary
Whether to enable the weak password dictionary.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Updated URL of Weak Password Dictionary
URL of the website that the weak password dictionary gets updates from
Weak Password Dictionary SHA256
SHA256 of the weak password dictionary
Detection Day
Days in a week when weak passwords are scanned. You can select one or more days.
User-defined weak password
You can add a password that may have been leaked to this weak password text box to prevent server accounts from using the password.
MySQL Weak Password Detection
Scans MySQL login passwords for weak passwords.
- Click OK.
High-risk Command Detection
- In the policy group list, click the name of the group that contains the required policy.
- Click High-risk command detection.
- In the Policy Settings area, modify the settings as required, as shown in Figure 4. For more information, see Table 4.
Figure 4 High-risk command detection
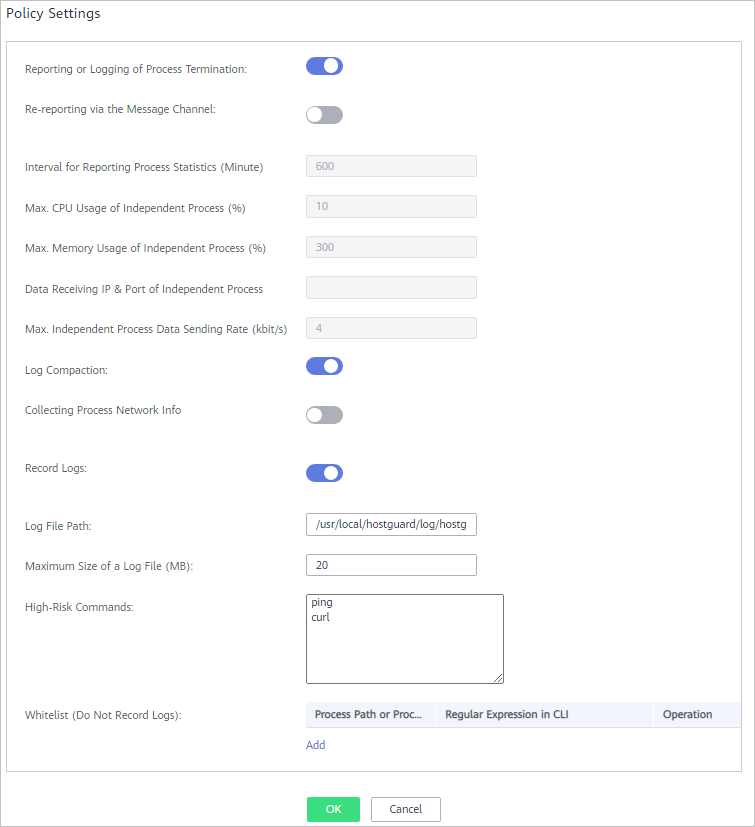
Table 4 High-risk command detection parameters Parameter
Description
Reporting or Logging of Process Termination
Reports or records process termination.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Re-reporting via the Message Channel
De-duplicates messages reported through the message channel.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Interval for Reporting Process Statistics (Minute)
This parameter takes effect only if Re-reporting via the Message Channel has been enabled.
This parameter specifies the interval for reporting process statistics. Set it to a valid number.
Max. CPU usage of Independent Process (%)
This parameter takes effect only if Re-reporting via the Message Channel has been enabled.
This parameter specifies the maximum CPU usage of an independent process. The value range is 5 to 99.
Max. Memory Usage of Independent Process (MB)
This parameter takes effect only if Re-reporting via the Message Channel has been enabled.
This parameter specifies the maximum memory usage of an independent process. The value range is 50 to 1024.
Data Receiving IP & Port of Independent Process
This parameter takes effect only if Re-reporting via the Message Channel has been enabled.
This parameter specifies the data receiving IP address and port of an independent process.
Max. Independent Process Data Sending Rate (kbit/s)
This parameter takes effect only if Re-reporting via the Message Channel has been enabled.
This parameter specifies the maximum data sending rate of an independent process. The value range is 1 to 100.
Log Compaction
Compacts logs.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Collecting Process Network Info
Collects network connection information of processes.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Record Logs
Records logs.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Log File Path
Log file path
Maximum Size of a Log File (MB)
Maximum size of a log file. The value range is 10 to 1024.
- If the size of a .log file exceeds the allowed maximum size, the system automatically renames the file as .log.0, creates a .log file, and writes logs to the .log file.
- There can be a maximum of two log files. If the .log file exceeds the allowed maximum size, the system deletes the .log.0 file, renames the .log file as .log.0, creates a .log file, and writes logs to the .log file.
High-Risk Commands
High-risk commands you want HSS to detect. Each command occupies a line.
Whitelist (Do Not Record Logs)
- Process Path or Process Name: full path of a process or full name of a program
- Regular Expression in CLI: regular expression of a command
- Operation: You can click Add or Delete to modify the list of processes and programs.
- Click OK.
Privilege Escalation Detection
- In the policy group list, click the name of the group that contains the required policy.
- Click Privilege escalation detection.
- In the Policy Settings area, modify the settings as required, as shown in Figure 5. For more information, see Table 5.
Figure 5 Privilege escalation detection
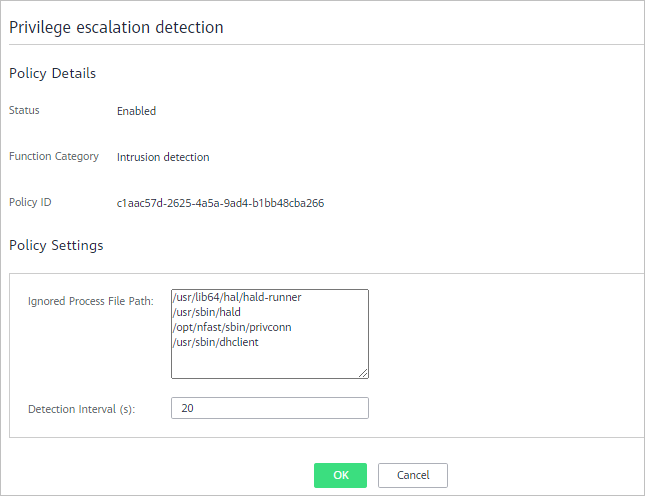
Table 5 Privilege escalation detection parameters Parameter
Description
Ignored Process File Path
Ignored process file path
Detection Interval (s)
Interval for checking process files. The value range is 5 to 3600.
- Click OK.
Abnormal or Reverse Shell Detection
- In the policy group list, click the name of the group that contains the required policy.
- Click Abnormal shell detection.
- In the Policy Settings area, modify the settings as required, as shown in Figure 6. For more information, see Figure 6.
Figure 6 Abnormal or reverse shell detection
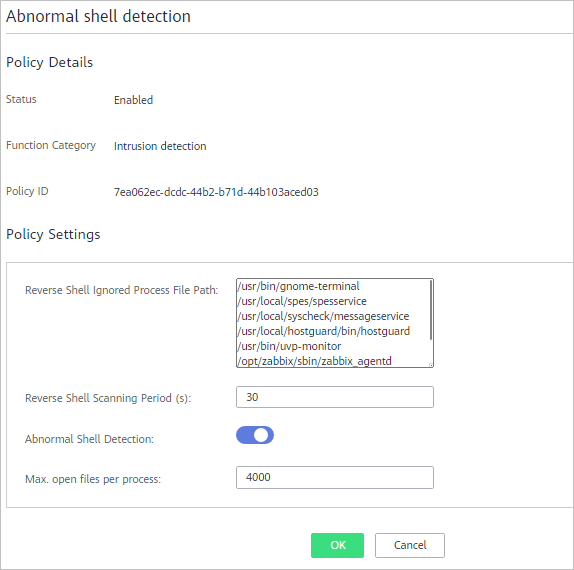
Table 6 Abnormal or reverse shell detection parameters Parameter
Description
Reverse Shell Ignored Process File Path
Process file path to be ignored in reverse shell detection
Reverse Shell Scanning Period (s):
Reverse shell scanning period. The value range is 30 to 86,400.
Abnormal Shell Detection
Detects abnormal shells. You are advised to enable it.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Max. open files per process
Maximum number of files that can be opened by a process. The value range is 10 to 300,000.
- Click OK.
File Integrity Monitoring
- In the policy group list, click the name of the group that contains the required policy.
- Click Integrity check on critical files.
- In the Policy Settings area, modify the settings as required, as shown in Figure 7. For more information, see Table 7.
Figure 7 Integrity check on critical files
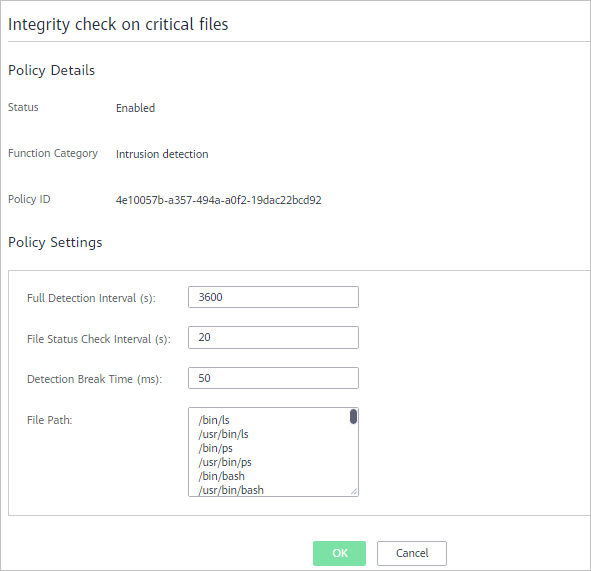
Table 7 File integrity monitoring parameters Parameter
Description
Full Detection Interval (s)
Interval between two consecutive full scans on specified files. The value range is 3,600 to 100,000.
For example, setting it to 3600 means the full scan is performed every hour.
File Status Check Interval (s)
Interval for checking file status. The value range is 10 to 600.
Detection Break Time (ms)
Interval between the checks of two files. The value range is 0 to 1000.
For example, if this parameter is set to 50, the system checks /usr/bin/ls 50 milliseconds after it checks /bin/ls.
File Path
Path of the files to be checked
NOTE:- Exercise caution when modifying its settings. Its default values are all critical files and you are not advised to delete any of them.
- HSS does not monitor changes on the files that are not specified here.
- Click OK.
Web Shell Detection
Web shell detection takes effect only after a web path is set.
- In the policy group list, click the name of the group that contains the required policy.
- Click Web Shell Detection.
- In the Policy Settings area, modify the settings as required, as shown in Figure 8. For more information, see Table 8.
Figure 8 Web shell detection
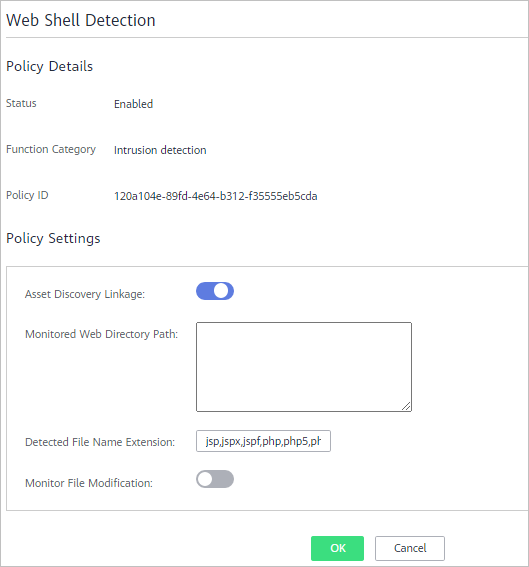 Note
NoteTo prevent the software in web paths from affecting the HSS agent, do not set web paths under /usr/local.
Table 8 Web shell detection parameters Parameter
Description
Asset Discovery Linkage
Automatically scans the web paths you specified.
 : enable
: enable : disable
: disable
Monitored Web Directory Path
Web paths to be scanned. A file path must:
- Start with a slash (/) and end with no slashes (/).
- End with a port number.
- Occupy a separate line and cannot contain spaces.
Detected File Name Extension
Extensions of files to be checked. Valid values include jsp, jspx, jspf, php, php5, php4.
Monitor File Modification
Monitors modifications on files.
- Click OK.
- Accessing the Policies Page
- Asset
- System Configuration Detection
- Weak Password Detection
- High-risk Command Detection
- Privilege Escalation Detection
- Abnormal or Reverse Shell Detection
- File Integrity Monitoring
- Web Shell Detection