SQL Statement Concurrency Control
Scenarios
SQL statement concurrency control aims to keep MySQL DB instances running stably in the case of high SQL statement concurrency.
Procedure
- Log in to the DAS console using your username and password.
- On the Overview page, click Go to CloudDBA.
- Locate your desired instance and click Details to go to the Cloud DBA overview page.
- Choose SQL > SQL Statement Concurrency Control.
- On the displayed page, enable SQL Statement Concurrency Control.
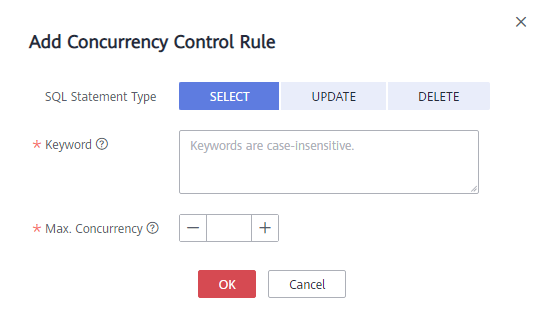
- Click Add Concurrency Control Rule. On the displayed page, select the SQL statement type and set the keyword and maximum concurrency.
Figure 1 Add Concurrency Control Rule
 Note
NoteKeyword: Take SELECT~a>1 as an example. SELECT and a>1 are the two keywords contained in the concurrency control rule. The keywords are separated by ~. In this example, to trigger this concurrency rule, keywords SELECT and a>1 must be contained in the SQL command.
Max. Concurrency: Maximum number of concurrent statements meeting the same rule. If the concurrent statements exceed the upper limit, they will not be executed.
- Confirm the settings and click OK.
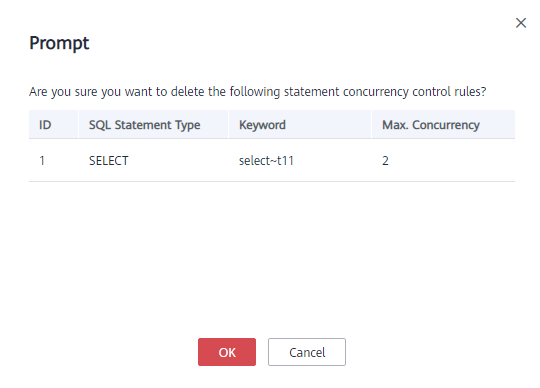
- If a rule is no longer needed, click Delete to delete the rule. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
Figure 2 Prompt
Parent topic: SQL
- Scenarios
- Procedure