Basic Concepts
Execution Node
An execution node is the target machine that a pressure test will be performed on and can provide performance data during testing.
Management Node
A management node is used to manage execution nodes.
Test Project
CPTS manages test projects created by users. Test transactions, pressure test tasks, and test reports are shared in a test project. Users can create test projects for different test programs.
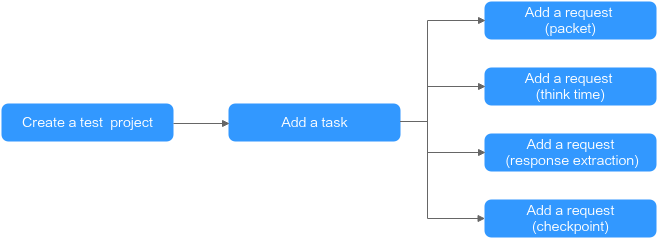
Figure 1 Creating a test project
Transaction
A transaction is a user-defined test operation model, which includes four parts: think time, packet, response extraction, and checkpoint. HTTP, HTTPS, TCP, and UDP packets are supported.
Packet
Packets are data blocks transmitted between HTTP-based applications. These data blocks start with text metadata that describes the packet content and meaning. Optional packet data follows the text metadata. Packets are transmitted between the client, server, and agent.
Think Time
To better simulate user behavior, insert a waiting time between different operations. For example, when a user receives data from the server, the user may wait several seconds before viewing data and providing responses. This period of time is called think time.
Response Extraction
If a transaction contains multiple packets, the output of the previous packet, which is extracted by a regular expression, is used as the input of the next packet.
Checkpoint
Checkpoints are where you define the verification information to determine whether the contents returned by the server are correct.
Test Task
A test task initiates a performance test based on a defined test model.
Test Report
When a test task is complete, a test report will be generated to present the test results.
Number of Concurrent Users
The number of concurrent users refers to the number of users performing operations on a system at the same time. In CPTS, it is the number of virtual users you define when you configure a test phase.
RPS
RPS is the number of requests that CPTS sends to the tested server per second.
Bandwidth
Records the real-time bandwidth usage during the running of the pressure test task. Uplink bandwidth refers to the speed at which the CPTS execution node sends out data. Downlink bandwidth refers to the speed at which the CPTS execution node receives data.
Response Time
Response time indicates the duration from the time when a client sends a request to the time when the client receives a response from the server.
Response Timeout
If the corresponding TCP connection does not return the response data within the set response timeout (5 seconds by default), the transaction request is considered a response timeout. Possible causes are: the tested server is busy, in crashes, or the network bandwidth is fully occupied.
Verification Failure
The response packet content and response code returned from the server do not meet the expectation (the default expected response code of HTTP/HTTPS is 200), such as code 404 or 502. A possible cause is that the tested service cannot be processed normally in scenarios with a large number of concurrent users. For example, a database bottleneck occurs in the distributed system or the backend application returns an error.
Resolution Failure
All response packets are received, but some packets are lost. As a result, the entire transaction response is incomplete. In this case, network packet loss may be the cause.
- Execution Node
- Management Node
- Test Project
- Transaction
- Packet
- Think Time
- Response Extraction
- Checkpoint
- Test Task
- Test Report
- Number of Concurrent Users
- RPS
- Bandwidth
- Response Time
- Response Timeout
- Verification Failure
- Resolution Failure