What Should I Do If a Pod Fails to Pull the Image?
Fault Locating
When a workload's status shows "Pod not ready: Back-off pulling image "xxxxx", a Kubernetes event of PodsFailed to pull image or Failed to re-pull image will be reported. For details about how to view Kubernetes events, see Viewing Pod Events.
Troubleshooting
Determine the cause based on the events, as listed in Table 1.
Event | Cause and Solution |
|---|---|
Failed to pull image "xxx": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = Error response from daemon: Get xxx: denied: You may not login yet | You have not logged in to the image repository. |
Failed to pull image "nginx:v1.1": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = Error response from daemon: Get https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/: dial tcp: lookup registry-1.docker.io: no such host | The image address is incorrectly configured. |
Failed create pod sandbox: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to create a sandbox for pod "nginx-6dc48bf8b6-l8xrw": Error response from daemon: mkdir xxxxx: no space left on device | The disk space is insufficient. |
Failed to pull image "xxx": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = error pulling image configuration: xxx x509: certificate signed by unknown authority | An unknown or insecure certificate is used by the third-party image repository from which the image is pulled. |
Failed to pull image "xxx": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = context canceled | The image size is too large. |
Failed to pull image "docker.io/bitnami/nginx:1.22.0-debian-11-r3": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = Error response from daemon: Get https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/: net/http: request canceled while waiting for connection (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers) | |
ERROR: toomanyrequests: Too Many Requests. Or you have reached your pull rate limit, you may increase the limit by authenticating an upgrading | The rate is limited because the number of image pull times reaches the upper limit. |
Check Item 1: Whether imagePullSecret Is Specified When You Use kubectl to Create a Workload
If the workload is abnormal and a Kubernetes event that indicates the pod fails to pull the image is displayed, you can check whether the imagePullSecrets field exists in the YAML file.
Items to Check
- If an image needs to be pulled from SWR, the name parameter must be set to default-secret.apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1kind: Deploymentmetadata:name: nginxspec:replicas: 1selector:matchLabels:app: nginxstrategy:type: RollingUpdatetemplate:metadata:labels:app: nginxspec:containers:- image: nginximagePullPolicy: Alwaysname: nginximagePullSecrets:- name: default-secret
- If an image needs to be pulled from a third-party image repository, the name parameter must be set to the created secret name.
When you use kubectl to create a workload from a third-party image, specify the imagePullSecret field, in which name indicates the name of the secret used to pull the image.
Check Item 2: Whether the Image Address Is Correct When a Third-Party Image Is Used
CCE allows you to create workloads using images pulled from third-party image repositories.
You need to enter the third-party image addresses based on specific requirements. The image addresses must be in the format of ip:port/path/name:version or name:version. If no version is specified, latest is used by default.
- For a private repository, enter an image address in the format of ip:port/path/name:version.
- For an open source Docker repository, enter an image address in the format of name:version, for example, nginx:latest.
When you fail to pull an image due to incorrect image address provided, information similar to the following information is displayed in the Kubernetes events:
Failed to pull image "nginx:v1.1": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = Error response from daemon: Get https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/: dial tcp: lookup registry-1.docker.io: no such host
Solution
Change the image address by editing your YAML file or log in to the CCE console and replace the image on the Upgrade tab on the workload details page.
Check Item 3: Whether an Incorrect Secret Is Used When a Third-Party Image Is Used
Typically, a third-party image repository can be accessed only after authentication (using your account and password). CCE uses the secret authentication mode to pull images, so you need to create a secret for an image repository before pulling images from the repository.
Solution
If your secret is incorrect, images will fail to be pulled. In this case, create a new secret.
Check Item 4: Whether the Node Disk Space Is Insufficient
If information similar to the following is displayed in the Kubernetes events, it means that there is no disk space left for storing the image. As a result, the image will fail to be pulled. In this case, clear the image or expand the disk space to resolve this issue.
Failed create pod sandbox: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to create a sandbox for pod "nginx-6dc48bf8b6-l8xrw": Error response from daemon: mkdir xxxxx: no space left on device
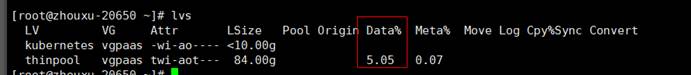
You can obtain the disk space for storing images on a node by running the following command:
lvs
Solution 1: Clearing images
Perform the following operations to clear unused images:
- Nodes that use containerd
- Obtain local images on the node.crictl images -v
- Delete the unnecessary images by image ID.crictl rmi {Image ID}
- Obtain local images on the node.
- Nodes that use Docker
- Obtain local images on the node.docker images
- Delete the unnecessary images by image ID.docker rmi {}Image ID}
- Obtain local images on the node.
Do not delete system images such as the cce-pause image. Otherwise, the pod creation may fail.
Solution 2: Expanding the disk capacity
To expand a disk capacity, perform the following operations:
- Expand the capacity of a data disk on the EVS console.
Only the storage capacity of EVS disks can be expanded. You need to perform the following operations to expand the capacity of logical volumes and file systems.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Nodes. In the right pane, click the Nodes tab, locate the row containing the target node, and choose More > Sync Server Data in the Operation column.
- Log in to the target node.
- Run lsblk to view the block device information of the node.
A data disk is divided depending on the container storage Rootfs:
Overlayfs: No independent thin pool is allocated. Image data is stored in dockersys.
- Check the disk and partition space of the device.# lsblkNAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTsda 8:0 0 50G 0 disk└─sda1 8:1 0 50G 0 part /sdb 8:16 0 150G 0 disk # The data disk has been expanded to 150 GiB, but 50 GiB space is free.├─vgpaas-dockersys 253:0 0 90G 0 lvm /var/lib/containerd└─vgpaas-kubernetes 253:1 0 10G 0 lvm /mnt/paas/kubernetes/kubelet
- Expand the disk capacity.
Add the new disk capacity to the dockersys logical volume used by the container engine.
- Expand the PV capacity so that LVM can identify the new EVS capacity. /dev/sdb specifies the physical volume where dockersys is located.pvresize /dev/sdb
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Physical volume "/dev/sdb" changed1 physical volume(s) resized or updated / 0 physical volume(s) not resized - Expand 100% of the free capacity to the logical volume. vgpaas/dockersys specifies the logical volume used by the container engine.lvextend -l+100%FREE -n vgpaas/dockersys
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Size of logical volume vgpaas/dockersys changed from <90.00 GiB (23039 extents) to 140.00 GiB (35840 extents).Logical volume vgpaas/dockersys successfully resized. - Adjust the size of the file system. /dev/vgpaas/dockersys specifies the file system path of the container engine.resize2fs /dev/vgpaas/dockersys
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Filesystem at /dev/vgpaas/dockersys is mounted on /var/lib/containerd; on-line resizing requiredold_desc_blocks = 12, new_desc_blocks = 18The filesystem on /dev/vgpaas/dockersys is now 36700160 blocks long.
- Expand the PV capacity so that LVM can identify the new EVS capacity. /dev/sdb specifies the physical volume where dockersys is located.
- Check whether the capacity has been expanded.# lsblkNAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTsda 8:0 0 50G 0 disk└─sda1 8:1 0 50G 0 part /sdb 8:16 0 150G 0 disk├─vgpaas-dockersys 253:0 0 140G 0 lvm /var/lib/containerd└─vgpaas-kubernetes 253:1 0 10G 0 lvm /mnt/paas/kubernetes/kubelet
- Check the disk and partition space of the device.
Check Item 5: Whether the Remote Image Repository Uses an Unknown or Insecure Certificate
If a pod tries to pull an image from a third-party repository with an unknown or insecure certificate, the image pulling will fail on the node. The pod events contain "Failed to pull the image" with the cause "x509: certificate signed by unknown authority".
The security of EulerOS 2.9 images has been improved by removing insecure or expired certificates from the system. While some third-party images on certain nodes may not report any errors, it is common for this type of error to occur in EulerOS 2.9. To fix the issue, you can perform the following operations.
Solution
- Check the IP address and port number of the third-party image server for which the error message "unknown authority" is displayed.
You can see the IP address and port number of the third-party image server for which the error is reported in the event "Failed to pull image".
Failed to pull image "bitnami/redis-cluster:latest": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = error pulling image configuration: Get https://production.cloudflare.docker.com/registry-v2/docker/registry/v2/blobs/sha256/e8/e83853f03a2e792614e7c1e6de75d63e2d6d633b4e7c39b9d700792ee50f7b56/data?verify=1636972064-AQbl5RActnudDZV%2F3EShZwnqOe8%3D: x509: certificate signed by unknown authorityThe IP address of the third-party image server is production.cloudflare.docker.com, and the default HTTPS port number is 443.
- Load the root certificate of the third-party image server to the node where the third-party image is to be pulled.
Run the following command on an EulerOS or CentOS node with {server_url}:{server_port} replaced with the IP address and port number obtained in the previous step, for example, production.cloudflare.docker.com:443.
If the container engine of the node is containerd, replace systemctl restart docker with systemctl restart containerd.
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect {server_url}:{server_port} < /dev/null | sed -ne '/-BEGIN CERTIFICATE-/,/-END CERTIFICATE-/p' > /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/tmp_ca.crtupdate-ca-trustsystemctl restart dockerRun the following command on an Ubuntu node:
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect {server_url}:{server_port} < /dev/null | sed -ne '/-BEGIN CERTIFICATE-/,/-END CERTIFICATE-/p' > /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/tmp_ca.crtupdate-ca-trustsystemctl restart docker
Check Item 6: Whether the Image Size Is Too Large
The pod events contain "Failed to pull image". This may be caused by a large image size.
Failed to pull image "XXX": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = context canceled
However, the image can be manually pulled by running the docker pull command on the node.
Possible cause
In Kubernetes clusters, there is a default timeout period for pulling images. If the image pulling progress is not updated within a certain period of time, the pulling will be canceled. If the node performance is poor or the image size is too large, the image may fail to be pulled and the workload may fail to be started.
Solution
- (Recommended) Solution 1:
- Log in to the node and manually pull the image.
- Nodes that use containerd:crictl pull <image-address>
- Nodes that use Docker:docker pull <image-address>
- Nodes that use containerd:
- When creating a workload, ensure that imagePullPolicy is set to IfNotPresent (the default configuration). In this case, the workload can use the image that has been pulled to the local host.
- Log in to the node and manually pull the image.
- (For clusters of v1.25 or later) Solution 2: Modify the configuration parameters of the node pool. The configuration parameters for nodes in the DefaultPool node pool cannot be modified.
- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Nodes. In the right pane, click the Node Pools tab.
- Locate the row containing the target node pool and click Manage.
- In the window that slides out from the right, modify the image-pull-progress-timeout parameter under Docker/containerd. This image-pull-progress-timeout parameter specifies the timeout interval for pulling an image.
- Click OK.
Check Item 7: Whether the Image Repository Can Be Accessed
Symptom
An error message similar to the following is displayed during workload creation:
Failed to pull image "docker.io/bitnami/nginx:1.22.0-debian-11-r3": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = Error response from daemon: Get https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/: net/http: request canceled while waiting for connection (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)
Possible cause
The image repository cannot be accessed due to the network problems. SWR allows you to pull images only from the official Docker repository. To pull images from other repositories, you need to access the Internet.
Solution
- Bind a public IP address to the node to which the image needs to be pulled.
- Push images to SWR and then pull them from SWR to your nodes.
Check Item 8: Whether the Number of Public Image Pulls Reaches the Upper Limit
Symptom
An error message similar to the following is displayed during workload creation:
ERROR: toomanyrequests: Too Many Requests.
Or
you have reached your pull rate limit, you may increase the limit by authenticating an upgrading: https://www.docker.com/increase-rate-limits.
Possible cause
Docker Hub sets limits for the maximum number of container image pull requests. For details, see Docker Hub pull usage and limits.
Solution
Push the frequently used images to SWR and then pull them from SWR to your nodes.
- Fault Locating
- Troubleshooting
- Check Item 1: Whether imagePullSecret Is Specified When You Use kubectl to Create a Workload
- Check Item 2: Whether the Image Address Is Correct When a Third-Party Image Is Used
- Check Item 3: Whether an Incorrect Secret Is Used When a Third-Party Image Is Used
- Check Item 4: Whether the Node Disk Space Is Insufficient
- Check Item 5: Whether the Remote Image Repository Uses an Unknown or Insecure Certificate
- Check Item 6: Whether the Image Size Is Too Large
- Check Item 7: Whether the Image Repository Can Be Accessed
- Check Item 8: Whether the Number of Public Image Pulls Reaches the Upper Limit