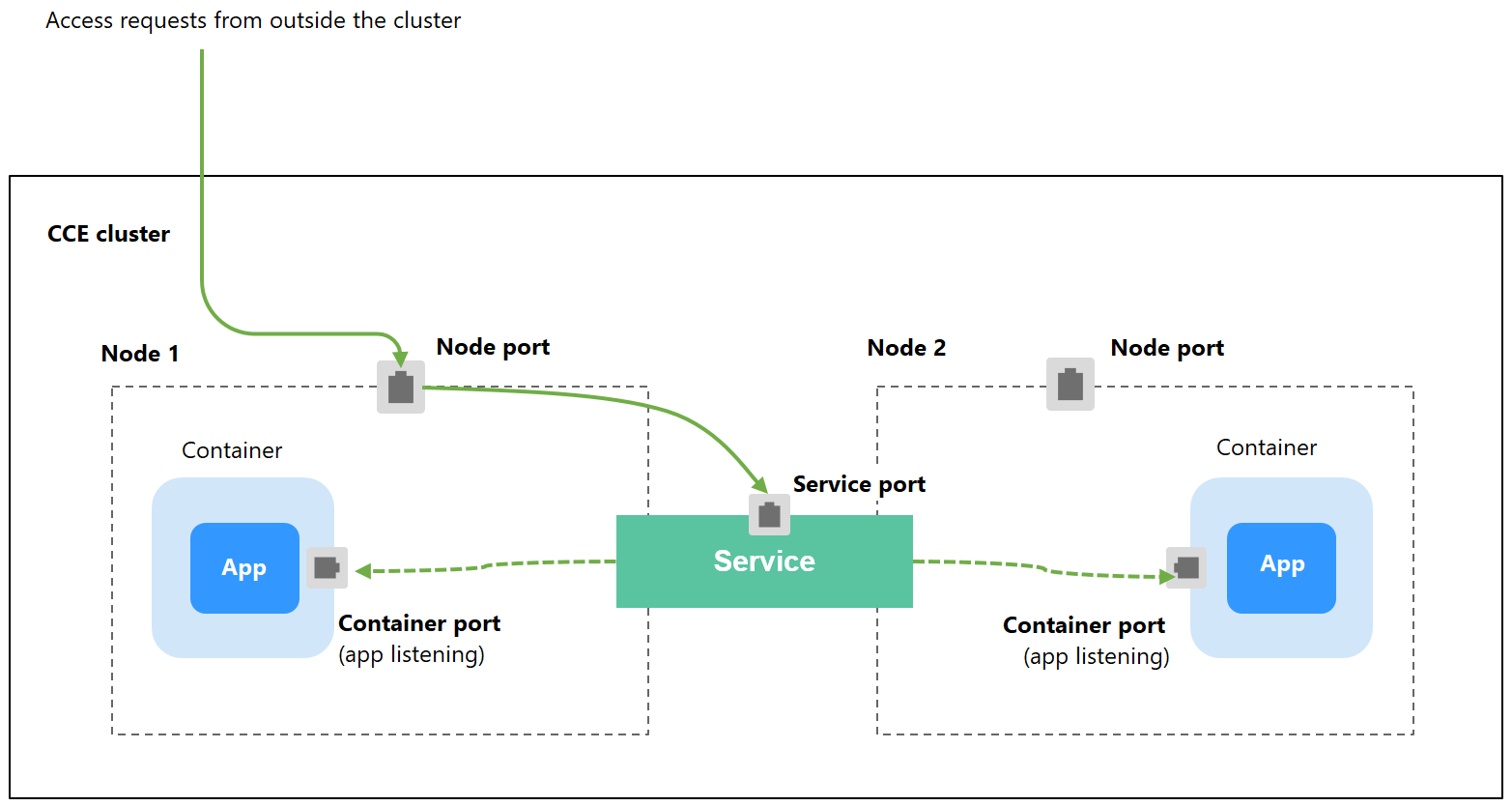
NodePort is a basic Service type in Kubernetes. It adds node port mapping to intra-cluster access. This means the Service is exposed on each node's IP address at a static port. When you create a NodePort Service, Kubernetes automatically allocates a cluster-scoped IP address (ClusterIP). When clients outside the cluster access <node-IP>:<node-port>, the traffic will be forwarded to the target pod through the ClusterIP of the NodePort Service.
If pods require temporary access or the traffic is low, you can create a NodePort Service. For example, in a testing environment, you can use a NodePort Service when deploying and debugging a web application.
Figure 1 NodePort Service access
Constraints
- By default, a NodePort Service is accessed within a VPC. To use an EIP to access a NodePort Service through public networks, bind an EIP to the node in the cluster in advance.
- After a Service is created, if the affinity setting is switched from the cluster level to the node level, the connection tracing table will not be cleared. Do not modify the Service affinity setting after the Service is created. To modify it, create a Service again.
- In a CCE Turbo cluster, node-level affinity is supported only when the Service backend is connected to a hostNetwork pod.
- In VPC network mode, when container A is published through a NodePort service and the service affinity is set to the node level (that is, externalTrafficPolicy is set to local), container B deployed on the same node cannot access container A through the node IP address and NodePort service.
- When a NodePort service is created in a cluster of v1.21.7 or later, the port on the node is not displayed using netstat by default. If the cluster forwarding mode is iptables, run the iptables -t nat -L command to view the port. If the cluster forwarding mode is IPVS, run the ipvsadm -Ln command to view the port.
Using the CCE Console
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Services & Ingresses. In the upper right corner, click Create Service.
- Configure the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Service Name
Enter a name, which can be the same as the workload name.
Service Type
Select NodePort.
Namespace
Select the namespace that the workload belongs to.
Service Affinity
Whether to route external traffic to a local node or a cluster-wide endpoint. For details, see Service Affinity (externalTrafficPolicy).
- Cluster-level: The IP addresses and ports of all nodes in a cluster can access the workload associated with the Service. However, accessing the Service may result in a performance decrease due to route redirection, and the client's source IP address may not be obtainable.
- Node-level: Only the IP address and port of the node where the workload is located can access the workload associated with the Service. Accessing the Service will not result in a performance decrease due to route redirection, and the client's source IP address can be obtained.
Selector
The Service will be associated with the workload pods based on the label and direct traffic to the pods with this label.
You can add a key and value for the pod label and click Confirm.
You can also click Reference Workload Label to use the label of an existing workload. In the dialog box displayed, select a workload and click OK.
IPv6
This function is disabled by default. After this function is enabled, the cluster IP address of the Service changes to an IPv6 address. This function is available only in clusters of v1.15 or later with IPv6 enabled (set during cluster creation).
Port
- Protocol: the protocol supported by the Service.
- Container Port: the listening port of the service containers. The port ranges from 1 to 65535. You need to determine the port based on the container image. For example, the default port of Nginx is 80, and the default port of MySQL is 3306.
- Service Port: the port used to access the ClusterIP Service. You can customize the port as required. The port ranges from 1 to 65535.
- Node Port: the port used for accessing the node using the node IP address. You are advised to select Auto. You can also specify a port. The default port range is 30000 to 32767.
- Click OK. After creating the Service, access it through <node-IP-address>:<node-port>. Cloud servers within the same VPC as the cluster or containers within the cluster can access this IP address. If an EIP is bound to a node, you can also use the EIP for access.
Using kubectl
You can configure Service access using kubectl. This section uses an Nginx workload as an example to describe how to configure a NodePort Service using kubectl.
- Use kubectl to access the cluster. For details, see Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl.
- Create and edit the nginx-deployment.yaml file to configure the sample workload. For details, see Creating a Deployment. nginx-deployment.yaml is an example file name. You can rename it as needed.vi nginx-deployment.yaml
File content:
apiVersion: apps/v1kind: Deploymentmetadata:name: nginxspec:replicas: 1selector:matchLabels:app: nginxtemplate:metadata:labels:app: nginxspec:containers:- image: nginx:latestname: nginximagePullSecrets:- name: default-secret - Create and edit the nginx-nodeport-svc.yaml file to configure Service parameters. nginx-nodeport-svc.yaml is an example file name. You can rename it as needed.vi nginx-nodeport-svc.yaml
File content:
apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata:labels:app: nginxname: nginx-nodeportspec:ports:- name: servicenodePort: 30000 # Node port. The value ranges from 30000 to 32767.port: 8080 # Port for accessing a Serviceprotocol: TCP # Protocol used for accessing a Service. The value can be TCPTCP or UDPUDP.targetPort: 80 # Port used by a Service to access the target container. This port is closely related to the applications running in a container. In this example, the Nginx image uses port 80 by default.selector: # Label selector. A Service selects a pod based on the label and forwards the requests for accessing the Service to the pod. In this example, select the pod with the app:nginxapp:nginx label.app: nginxtype: NodePort # Service type. NodePortNodePort indicates that the Service is accessed through a node port. - Create a workload.kubectl create -f nginx-deployment.yaml
If information similar to the following is displayed, the workload has been created:
deployment/nginx createdCheck the created workload.
kubectl get podIf information similar to the following is displayed, the workload is running:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEnginx-2601814895-znhbr 1/1 Running 0 15snginx-2601814895-znhbr 1/1 Running 0 15s - Create a Service.kubectl create -f nginx-nodeport-svc.yaml
If information similar to the following is displayed, the Service is being created:
service/nginx-nodeport createdCheck the created Service.
kubectl get svcIf information similar to the following is displayed, the Service has been created:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEkubernetes ClusterIP 10.247.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 4d8hnginx-nodeport NodePort 10.247.30.40 <none> 8080:30000/TCP 18s - Access the Service. By default, a NodePort Service can be accessed using IP-address-of-any-node:node-port. Cloud servers within the same VPC or containers within the cluster can access the Service. If an EIP is bound to a node, you can also use the EIP to access the Service.
Create a container in the cluster and access it using IP-address-of-the-node:node-port.
- Obtain the node's IP address.kubectl get node -owide
Command output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME10.100.0.136 Ready <none> 152m 10.100.0.136 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.25.1.el7.x86_64 docker://18.9.010.100.0.5 Ready <none> 152m 10.100.0.5 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.25.1.el7.x86_64 docker://18.9.0 - Create a pod and access its container.kubectl run -i --tty --image nginx:alpine test --rm /bin/sh
- Run the curl command to access the Service.curl 10.100.0.136:30000
Command output:
/ # <!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>Welcome to nginx!</title><style>body {width: 35em;margin: 0 auto;font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;}</style></head><body><h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1><p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed andworking. Further configuration is required.</p><p>For online documentation and support please refer to<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>Commercial support is available at<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p><p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p></body></html>/ #
- Obtain the node's IP address.