What Is SFS?
Overview
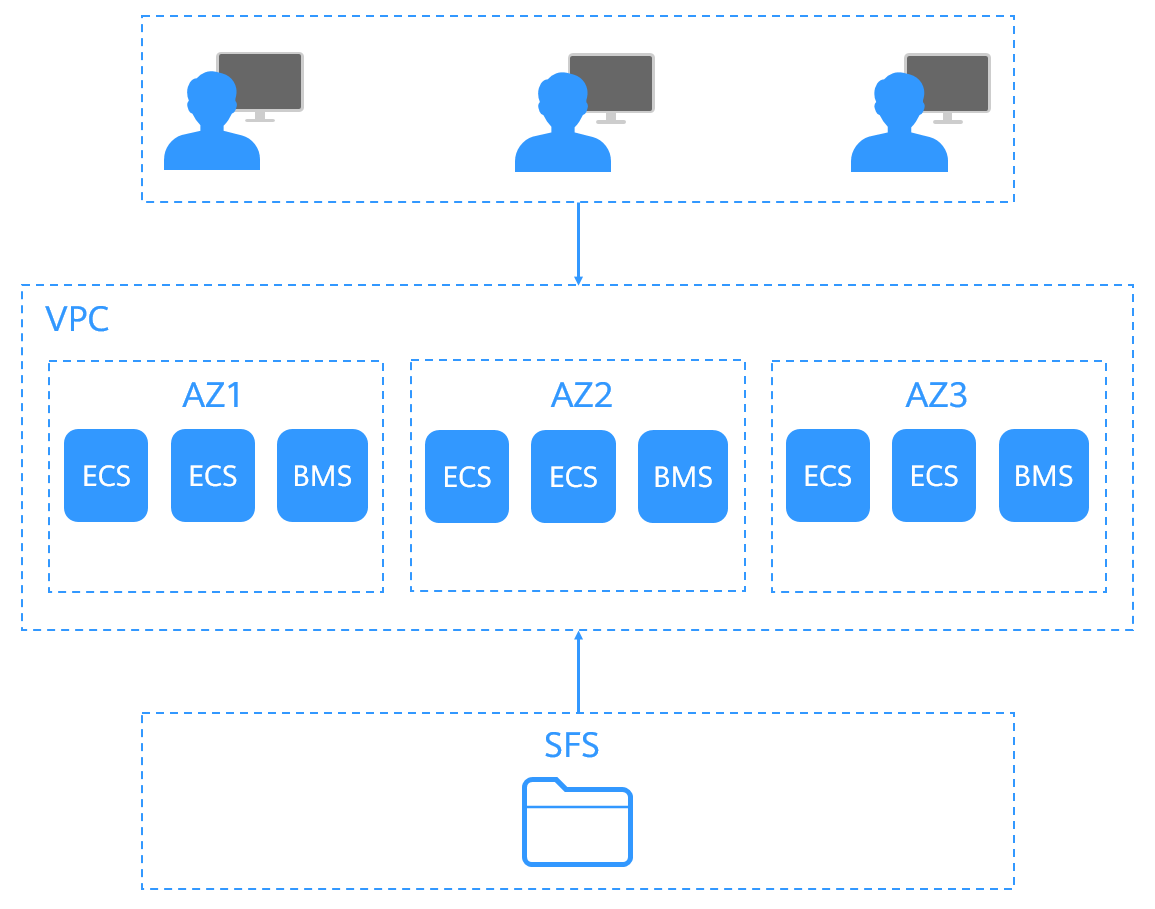
Scalable File Service (SFS) provides scalable, high-performance (NAS) file storage. With SFS, you can enjoy shared file access spanning multiple Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs), Bare Metal Servers (BMSs), and containers created on Cloud Container Engine (CCE). See Figure 1.
Figure 1 Accessing SFS
Compared with traditional file sharing storage, SFS has the following advantages:
- File sharing
Servers in multiple availability zones (AZs) of a same region can access the same file system concurrently and share files.
- Elastic scaling
Storage can be scaled up or down on demand to dynamically adapt to service changes without interrupting applications. You can complete resizing with a few clicks.
- Superior performance and reliability
SFS enables file system performance to increase as capacity grows, and it delivers a high data durability to support rapid service growth.
The backend storage system supports both HDD and SSD storage media. It adopts a distributed architecture and uses full redundant design for modules, which eliminate single-node faults.
- Seamless integration
SFS supports NFS and CIFS protocols. With these standard protocols, a broad range of mainstream applications can read data from and write data to the file system. In addition, the service is compatible with SMB 2.0, SMB 2.1, and SMB 3.0, facilitating Windows clients to access the shared space.
- Easy operation
In an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI), you can create and manage file systems with ease.
Accessing SFS
You can access SFS on the management console or via APIs by sending HTTPS requests.
- APIs
Use APIs if you need to integrate SFS into a third-party system for secondary development. For detailed operations, see Scalable File Service API Reference.
- Management console
Use the console if you prefer a web-based UI to perform operations.
- Overview
- Accessing SFS