How Do I View Logs of All SQL Statements Executed by My RDS for MySQL Instance?
You can use the SQL audit function of RDS to query all SQL operation records.
Querying SQL Logs Through RDS
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - Click Service List. Under Database, click Relational Database Service.
- On the Instances page, click the DB instance name.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose SQL Audits.
- On the displayed page, select a time range in the upper right corner, select SQL audit logs to be downloaded in the list, and click Download above the list to download SQL audit logs in batches.
Alternatively, select an audit log and click Download in the Operation column to download an individual SQL audit log.
NoteYou are advised to download no more than six audit log files at a time. Too many files can fail to be downloaded completely due to the limit on the number of concurrent requests of the browser.
- Check that the SQL audit log content is as follows. For field descriptions, see Table 1.
Figure 1 RDS for MySQL audit logs
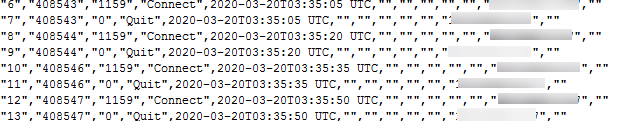
Table 1 Audit log field description Parameter
Description
record_id
ID of a single record, which is the unique global ID of each SQL statement recorded in the audit log.
connection_id
ID of the session executed for the record, which is the same as the ID in the show processlist command output.
connection_status
Session status, which is usually the returned error code of a statement. If the statement is successfully executed, the value 0 is returned.
name
Recorded type name. Generally, DML and DDL operations are QUERY, connection and disconnection operations are CONNECT and QUIT, respectively.
timestamp
UTC time for the record.
command_class
SQL command type. The value is the parsed SQL type, for example, select or update. (This field does not exist if the connection is disconnected.)
sqltext
Executed SQL statement content. (This field does not exist if the connection is disconnected.)
user
Login account.
host
Login host. The value is localhost for local login and is empty for remote login.
external_user
External username.
ip
IP address of the remotely-connected client. For local connection, the field is empty.
default_db
Default database on which SQL statements are executed.
- Querying SQL Logs Through RDS