Using NAT Gateway and Direct Connect to Accelerate Internet Access
Scenarios
Connect your on-premises data center to a VPC using Direct Connect and then configure SNAT rules of a NAT gateway to enable servers to access the Internet in a secure, reliable, and high-speed way, or configure DNAT rules to enable servers to provide services accessible from the Internet. Typical scenarios include Internet, games, e-commerce, and finance.
Solution Advantages
With Direct Connect, you can access a VPC with high-performance, low-latency, and secure networks. A Direct Connect connection supports a maximum of 10 Gbit/s bandwidth, meeting various bandwidth requirements.
With the SNAT and DNAT functions of the NAT gateway, multiple servers can share an EIP, effectively reducing costs. The NAT gateway specifications and bound EIPs can be adjusted at any time. The configuration is simple and will take effect immediately.
Typical Topology
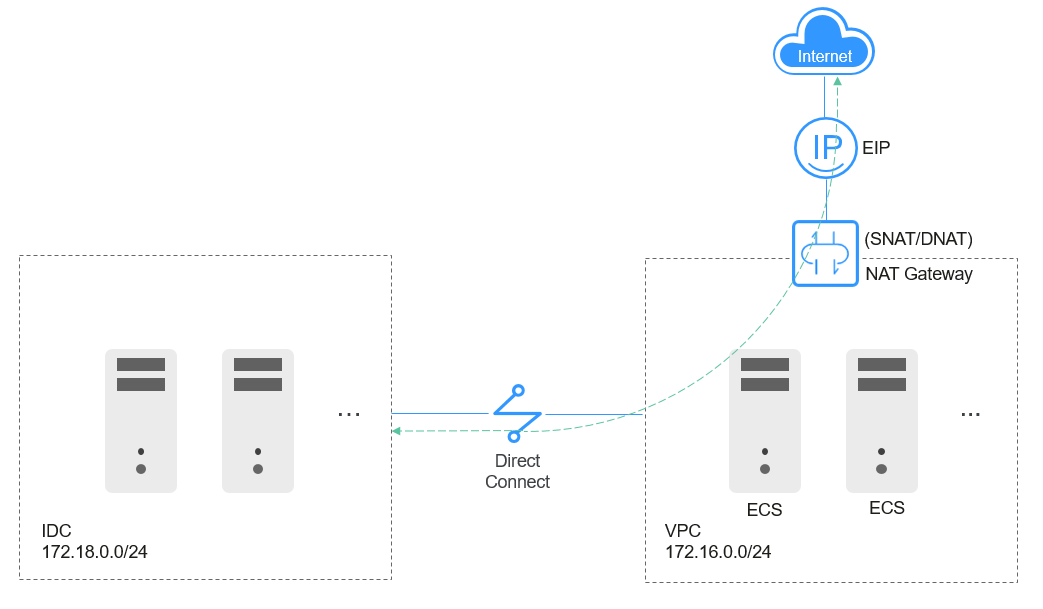
Assume that the IDC network is 172.18.0.0/24 and the VPC subnet is 172.16.0.0/24.
Implementation methods:
- Use Direct Connect to connect your IDC to your VPC.
- Create a NAT gateway in the VPC to connect to the Internet.
Figure 1 Network topology
Prerequisites
- The default route of the IDC is available for configuring Direct Connect.
- The network CIDR block of the IDC does not overlap with the subnet CIDR block of the VPC on the cloud. Otherwise, the communication between the IDC and the VPC will fail.
Procedure
- Create a VPC.
For details, see section "Creating a VPC" in the Virtual Private Cloud User Guide.
- Configure a Direct Connect connection.
Create a Direct Connect connection to connect the IDC to the VPC. For details, see section "Getting Started" in the Direct Connect User Guide
NoteAdd the 0.0.0.0/0 CIDR block as the local subnet on the cloud when configuring the route for the Direct Connect connection.
- Static: Add the default route with 0.0.0.0/0 as the destination in the on-premises data center and set the next hop to the connection.
- BGP: The on-premises network can learn the default route using BGP.
- Assign an EIP and configure a NAT gateway.
- For details, see section "Assigning an EIP" in the Elastic IP User Guide.
- Create a NAT gateway. For details, see Creating a NAT Gateway.
- Add an SNAT rule with the CIDR block set to that of the Direct Connect connection. For more information, see Adding an SNAT Rule.
Set CIDR Block to 172.18.0.0/24 and select an EIP.
- Add a DNAT rule. For more information, see Adding a DNAT Rule.
Configure the protocol and port type. All ports is used as an example. Set Private IP Address to 172.18.0.100 and select an EIP.
NoteSNAT and DNAT rules are designed for different functions. If SNAT and DNAT rules use the same EIP, resource preemption will occur. An SNAT rule cannot share an EIP with a DNAT rule with Port Type set to All ports.
Verification
After the configuration is complete, test the network connectivity.
Ping an external IP address, for example, 114.114.114.114, from a server in the IDC.
- Scenarios
- Solution Advantages
- Typical Topology
- Prerequisites
- Procedure
- Verification