Mounting a File System
Scenarios
You can mount file systems to your function to provide scalable file storage. The function can then read and write data in the file systems as it would do in local file systems. Each file system can be shared by different functions and instances. You only need to specify information such as file systems and function access paths.
Before mounting file systems, enable access over the following ports:
- 111, 445, 2049, 2051, 2052, and 20048
- Another three ports for Ubuntu. To obtain the port numbers, run the following command:rpcinfo -p|grep mountd|grep tcp
For details, see What Resources Does SFS Occupy?
FunctionGraph supports the following types of file systems:
- SFS
Scalable File Service (SFS) is a network-attached storage (NAS) service that provides scalable high-performance file storage. With SFS, shared access can be achieved among multiple ECSs, Bare Metal Servers (BMSs), and Cloud Container Engine (CCE) and Cloud Container Instance (CCI) containers. SFS is expandable to petabytes, and provides fully hosted shared file storage. It features high availability and durability, and seamlessly handles data-intensive and bandwidth-intensive applications. SFS is suitable for high-performance computing (HPC), media processing, file sharing, content management, and web services.
- SFS Turbo
SFS Turbo is expandable to 320 TB, and provides fully hosted shared file storage. It features high availability and durability, and supports massive quantities of small files and applications requiring low latency and high input/output operations per second (IOPS). SFS Turbo is suitable for high-performance websites, log storage, compression and decompression, DevOps, enterprise offices, and containerized applications.
- ECS
A directory on an ECS is specified as a shared file system (see Creating an NFS Shared Directory on ECS) by using the network file system (NFS) service. The directory can then be mounted to a function in the same VPC as the ECS so that the function can read and write data in the directory. ECS file systems make it possible for dynamic expansion of compute resources. This type of file system is suitable for low service demand scenarios.
Benefits from using these file systems:
- The execution space of each function can be expanded in addition to the /tmp directory (512 MB).
- A file system can be shared by multiple functions.
- ECS compute resources can be dynamically expanded and existing ECS storage capability can be used to achieve stronger computing performance.Note
You can write temporary files in the /tmp directory. The total size of these files cannot exceed 10,240 MB.
Creating an Agency
Before adding file systems to a function, specify an agency with permissions for accessing the file system services for the function.
There is a limit on the maximum number of agencies you can create, and cloud service agencies cannot be modified. Therefore, you are advised to create an agency with high-level permissions, for example, Tenant Administrator, to allow a function to access all resources in the selected region. For more information, see Creating an Agency.
Mounting an SFS File System
Setting an Agency
On the Configuration tab page, select an agency that has been granted SFS Administrator or Tenant Administrator permissions in the selected region.
If no agencies are available, create one in IAM.
Mounting a File System
On the function details page, choose Configuration > Disk Mounting, and click Mount File System. When you mount a file system to the target function for the first time, you need to set the user ID and group ID.
User ID and group ID (just like uid and gid in Linux) let the function access a specific file system.
User ID: Enter –1 or an integer from 1 to 65,534, except 1000 and 1002. The default value –1 indicates that the FunctionGraph backend automatically allocates an ID.
Group ID: Enter –1 or an integer from 1 to 65,534, except 1000 and 1002. The default value –1 indicates that the FunctionGraph backend automatically allocates an ID.
For example, an ECS has been mounted with an SFS file system, and the owner of a directory in the file system is test-user. Then you can run the id test-user command to query the uid and gid.
Select an SFS file system and set the access path.
The function access path can contain a maximum of two levels. /mnt and /home are existing paths. You are advised to set an access path starting with /mnt or /home. If you set the path to /mnt or /home, message "failed to mount exist system path" will be displayed.
Mounting an SFS Turbo File System
Setting an Agency
Before mounting an SFS Turbo file system to a function, specify an agency that has been granted SFS Administrator and VPC Administrator permissions for the function. If no agencies are available, create one in IAM. For details, see Creating an Agency.
Configuring VPC Access
An SFS Turbo file system is accessible only in the VPC where it has been created. Before mounting such a file system to a function, enable VPC access for the function.
- On the SFS console, obtain the information about the VPC and subnet where a file system is to be mounted to your function. For details, see File System Management.
- Enable VPC access by referring to Configuring VPC Access and enter the VPC and subnet obtained in 1.
Mounting an SFS Turbo File System
SFS Turbo file systems can be mounted in the same way as SFS file systems. Select a file system and set the access path.
Mounting an ECS Shared Directory
Specifying an Agency
Before mounting an ECS shared directory to a function, specify an agency that has been granted Tenant Guest and VPC Administrator permissions for the function. If no agencies are available, create one in IAM. For details, see Creating an Agency.
Configuring VPC Access
Before adding an ECS shared directory, specify the VPC where the ECS is deployed. View the VPC information on the details page of the ECS. Click the VPC name to go to the VPC details page, and view the subnet.
Set the acquired VPC and subnet for the function.
Mounting an ECS Directory
Enter a shared directory and function access path.
Follow-up Operations
A function can read and write data in an access path in the same way as in the mounted file system.
Function logs can be persisted by configuring the log path as a subdirectory in the access path.
The following uses SFS Turbo and template Web-Server-Access-Log-Statistics as an example to describe how to analyze logs of servers running on the cloud.
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console. In the navigation pane, choose Templates.
- In the upper right corner of the Templates page, enter Web-Server-Access-Log-Statistics in the search box and press Enter.
- In the search result, click Configure. The configuration page is displayed, as shown in Figure 1. Set the parameters as follows:
Figure 1 Function template
- Region: Select the same region as the created VPC and file system. For details about how to create a VPC and file system, see Configuring VPC Access and Creating a File System.
- Project: Use default.
- Function Name: Enter a custom name.
- Agency: Select an agency with the file system, VPC, and APIG permissions. For details about how to create an agency, see Creating an Agency.
- Enterprise Project: Select an enterprise project as required.
- Environment Variables: access_log_path indicates the log file address. Set this parameter to /home/test/access_log.log.Note
To specify file paths in the file system, use absolute paths starting with a slash (/). However, if no file system is mounted, you can skip adding the slash (/) and simply set the parameter to code/access_log.log.
- Trigger Type: The default value is API Gateway (APIG). For details about how to configure APIG, see Using an APIG (Dedicated) Trigger.
- API Name: Enter a custom name.
- API Group: Select a group based on the actual service.
- Environment: Select RELEASE.
- Security Authentication: Select None.
- Protocol and Timeout (ms): Retain the default values.
- After parameter configuration is complete, click Create Function.
- On the function details page, click the Code tab, add the following code to the index.py file, and click Deploy.import shutilshutil.copyfile('/opt/function/code/access_log.log', '/home/test/access_log.log')
Figure 2 Adding code
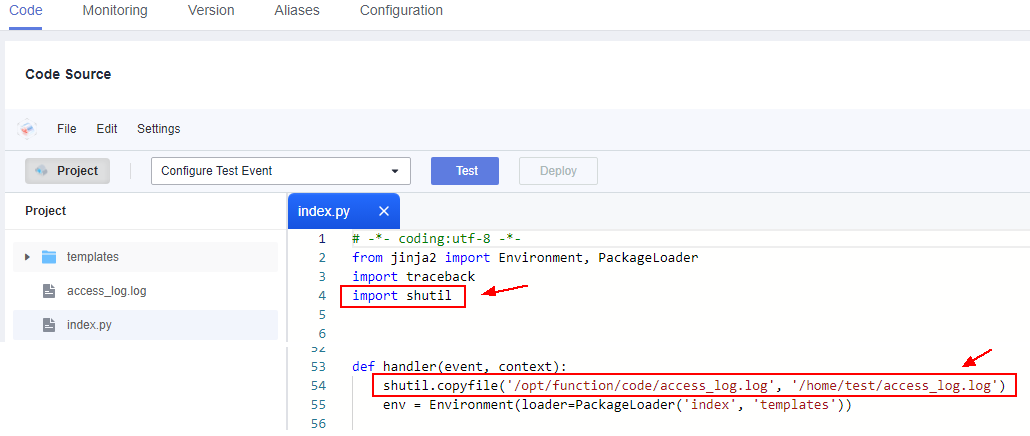
In addition, add the public dependency Jinja2-2.10. For details, see How Do I Add a Dependency to a Function?
NoteIf no file system is mounted, you do not need to add the preceding code.
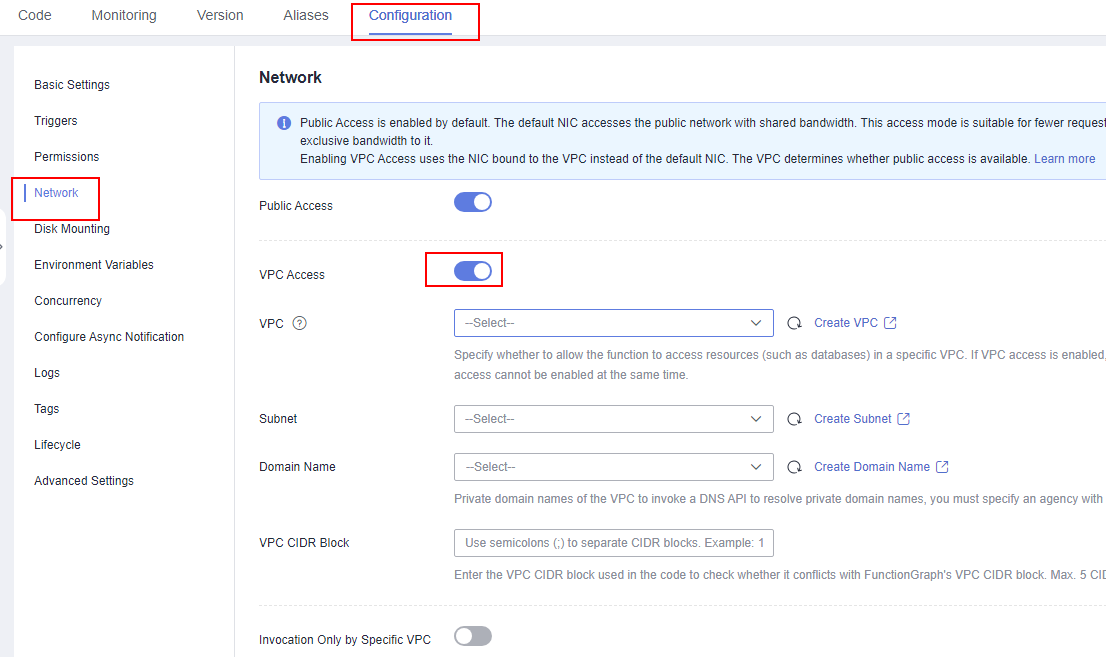
- On the function details page, choose Configuration > Network and enable VPC Access. Set VPC and Subnet to the created VPC and subnet, and click Save.
Figure 3 VPC access
- Choose Disk Mounting, click Mount File System, and select SFS Turbo.
- File System: Select an existing SFS Turbo file system.
- Access Path: Set this parameter to /home/test.
- Shared Directory: shared directory path of the file system. If this parameter is left blank by default, the function can access all directories of the file system. If a specific directory path is configured, the function can access only the directory path.
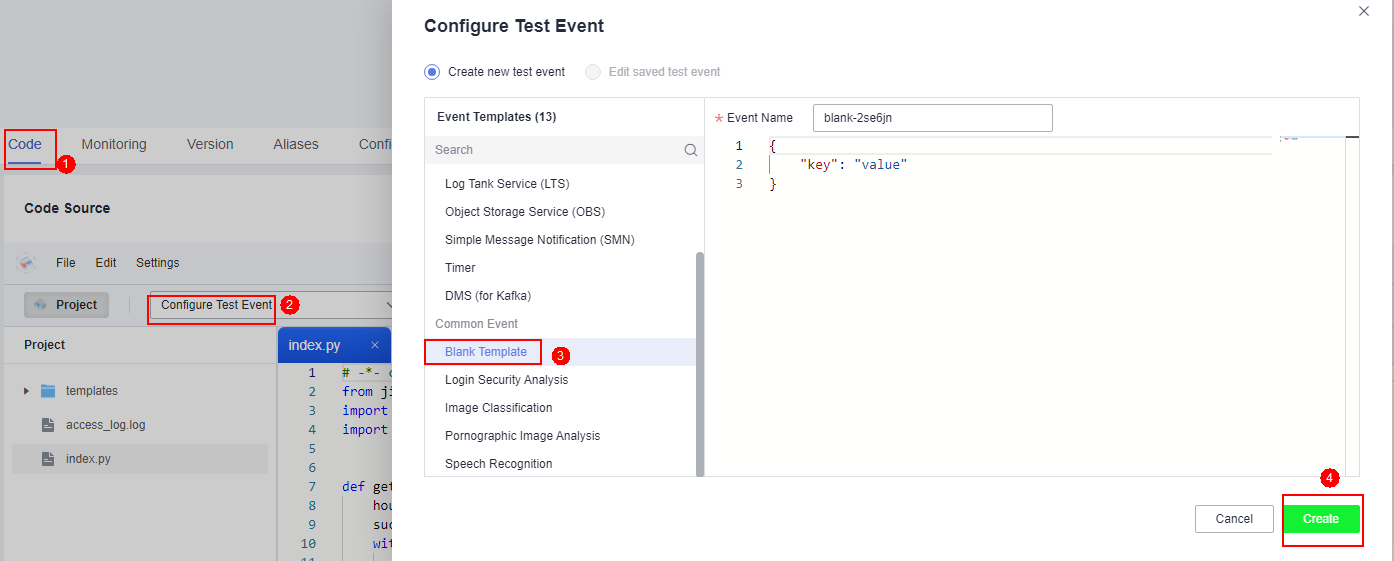
- Click the Code tab, select Configure Test Event, create a Blank Template, and click Create.
Figure 4 Configuring a test event
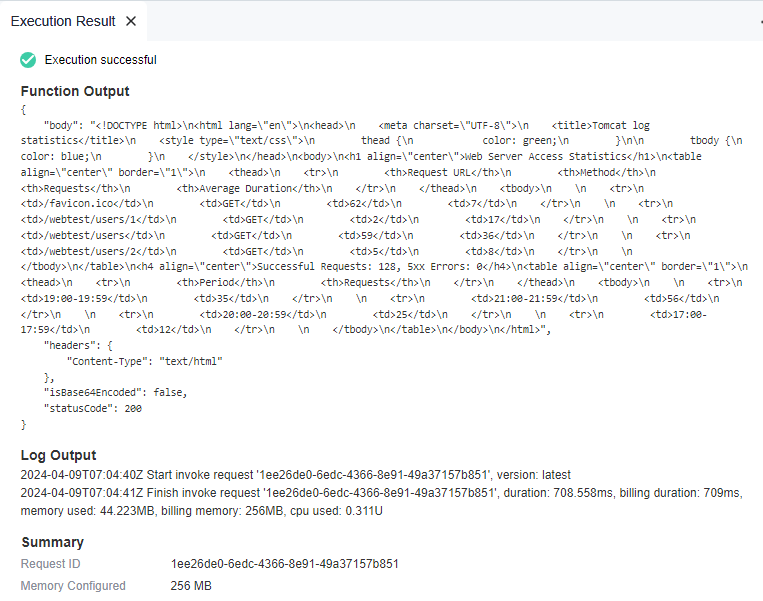
- Select the created test event and click Test.
Figure 5 Test result
- Choose Configuration > Triggers, copy the URL of the APIG trigger, and open the URL using a browser.
Figure 6 Copying a URL
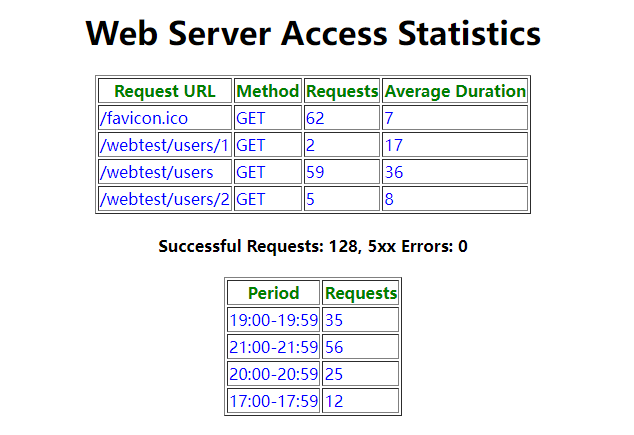
Figure 7 Results display
- Scenarios
- Creating an Agency
- Mounting an SFS File System
- Mounting an SFS Turbo File System
- Mounting an ECS Shared Directory
- Follow-up Operations