Record Set
Overview
A record set provides information about a domain name, including the IP addresses associated with and how to handle requests for the domain name and its subdomains.
If you have created a zone on the DNS console, you can add record sets to define how you want to route traffic for the domain name or its subdomains.
Table 1 describes the record set types and their application scenarios.
Type | Description |
|---|---|
A | Maps domains to IPv4 addresses. |
CNAME | Maps one domain name to another domain name or multiple domain names to one domain name. |
MX | Maps domain names to email servers. |
AAAA | Maps domain names to IPv6 addresses. |
TXT | Creates text records for domain names. TXT record sets are usually used in the following scenarios:
|
SRV | Records servers providing specific services. |
NS | Delegates subdomains to other name servers. This type of record set is created by default and cannot be added manually. |
SOA | Identifies the base information about a domain name. The SOA record set is automatically generated by the DNS service and cannot be added manually. |
PTR | Maps IP addresses to domain names. |
Usage
Record sets are used in following scenarios:
- Private domain name resolution
On a private network, A and AAAA record sets translate private domain names into private IP addresses.
Figure 1 Private domain name resolution
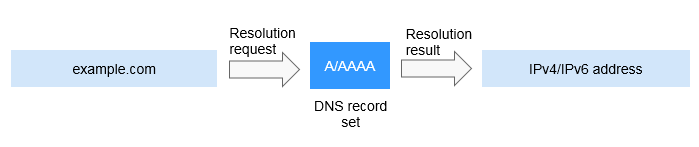
- Reverse resolution on a private network
PTR records translate private IP addresses into private domain names.
Figure 2 Reverse resolution on a private network

Helpful Links
For details, see Record Set Overview.
- Overview
- Usage
- Helpful Links