Using Custom Storage Classes
Background
When using storage resources in CCE, the most common method is to specify storageClassName to define the type of storage resources to be created when creating a PVC. The following configuration shows how to use a PVC to apply for an SAS (high I/O) EVS disk (block storage).
apiVersion: v1kind: PersistentVolumeClaimmetadata:name: pvc-evs-examplenamespace: defaultannotations:everest.io/disk-volume-type: SASspec:accessModes:- ReadWriteOnceresources:requests:storage: 10GistorageClassName: csi-disk
To specify the EVS disk type, you can configure the everest.io/disk-volume-type field. The value SAS is used as an example here, indicating the high I/O EVS disk type. Or you can choose SSD (ultra-high I/O).
This configuration method may not work if you want to:
- Set storageClassName only, which is simpler than specifying the EVS disk type by using everest.io/disk-volume-type.
- Avoid modifying YAML files or Helm charts. Some users switch from self-built or other Kubernetes services to CCE and have written YAML files of many applications. In these YAML files, different types of storage resources are specified by different StorageClassNames. When using CCE, they need to modify a large number of YAML files or Helm charts to use storage resources, which is labor-consuming and error-prone.
- Set the default storageClassName for all applications to use the default storage class. In this way, you can create storage resources of the default type without needing to specify storageClassName in the YAML file.
Solution
This section describes how to set a custom storage class in CCE and how to set the default storage class. You can specify different types of storage resources by setting storageClassName.
- For the first scenario, you can define custom storageClassNames for SAS and SSD EVS disks. For example, define a storage class named csi-disk-sas for creating SAS disks. The following figure shows the differences before and after you use a custom storage class.
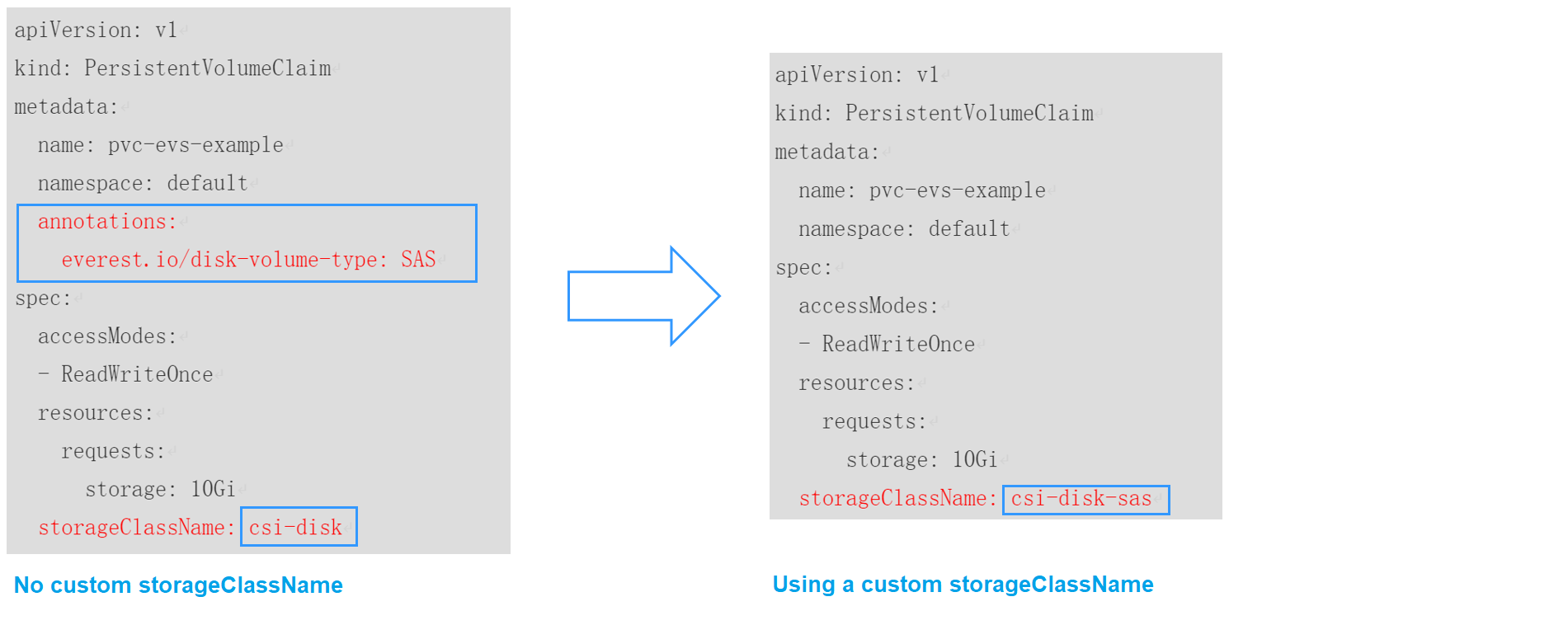
- For the second scenario, you can define a storage class with the same name as that in the existing YAML file without needing to modify storageClassName in the YAML file.
- For the third scenario, you can set the default storage class as described below to create storage resources without specifying storageClassName in YAML files.apiVersion: v1kind: PersistentVolumeClaimmetadata:name: pvc-evs-examplenamespace: defaultspec:accessModes:- ReadWriteOnceresources:requests:storage: 10Gi
Creating a StorageClass Using a YAML File
As of now, CCE provides StorageClasses such as csi-disk, csi-nas, and csi-obs by default. When defining a PVC, you can use a StorageClassName to automatically create a PV of the corresponding type and automatically create underlying storage resources.
Run the following kubectl command to obtain the StorageClasses that CCE supports. Use the CSI add-on provided by CCE to create a StorageClass.
# kubectl get scNAME PROVISIONER AGEcsi-disk everest-csi-provisioner 17d # EVS diskcsi-disk-topology everest-csi-provisioner 17d # EVS disks created with delaycsi-nas everest-csi-provisioner 17d # SFS 1.0csi-obs everest-csi-provisioner 17d # OBScsi-sfsturbo everest-csi-provisioner 17d # SFS Turbocsi-local-topology everest-csi-provisioner 17d # Local PV created with delay
Each StorageClass contains the default parameters used for dynamically creating a PV. The following is an example of StorageClass for EVS disks:
kind: StorageClassapiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1metadata:name: csi-diskprovisioner: everest-csi-provisionerparameters:csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: disk.csi.everest.iocsi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4everest.io/disk-volume-type: SASeverest.io/passthrough: 'true'reclaimPolicy: DeleteallowVolumeExpansion: truevolumeBindingMode: Immediate
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
provisioner | Specifies the storage resource provider, which is the Everest add-on for CCE. Set this parameter to everest-csi-provisioner. |
parameters | Specifies the storage parameters, which vary with storage types. For details, see Table 2. |
reclaimPolicy | Specifies the value of persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy for creating a PV. The value can be Delete or Retain. If reclaimPolicy is not specified when a StorageClass object is created, the value defaults to Delete.
|
allowVolumeExpansion | Specifies whether the PV of this StorageClass supports dynamic capacity expansion. The default value is false. Dynamic capacity expansion is implemented by the underlying storage add-on. This is only a switch. |
volumeBindingMode | Specifies the volume binding mode, which is the time when a PV is dynamically created. The value can be Immediate or WaitForFirstConsumer.
|
mountOptions | This field must be supported by the underlying storage. If this field is not supported but is specified, the PV creation will fail. |
Volume Type | Parameter | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
EVS | csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name | Yes | Driver type. If an EVS disk is used, the parameter value is fixed at disk.csi.everest.io. |
EVS | csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype | Yes | If an EVS disk is used, the parameter value can be ext4. |
EVS | everest.io/disk-volume-type | Yes | EVS disk type. All letters are in uppercase.
|
EVS | everest.io/passthrough | Yes | The parameter value is fixed at true, which indicates that the EVS device type is SCSI. No other parameter values are allowed. |
SFS | csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name | Yes | Driver type. If SFS is used, the parameter value is fixed at nas.csi.everest.io. |
SFS | csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype | Yes | If SFS is used, the value can be nfs. |
SFS | everest.io/share-access-level | Yes | The parameter value is fixed at rw, indicating that the SFS data is readable and writable. |
SFS | everest.io/share-access-to | Yes | VPC ID of the cluster. |
SFS | everest.io/share-is-public | No | The parameter value is fixed at false, indicating that the file is shared to private. When you use SFS 3.0, there is no need to configure this parameter. |
SFS | everest.io/sfs-version | No | This parameter is only required for SFS 3.0 and its value is fixed at sfs3.0. |
SFS Turbo | csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name | Yes | Driver type. If SFS Turbo is used, the parameter value is fixed at sfsturbo.csi.everest.io. |
SFS Turbo | csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype | Yes | If SFS Turbo is used, the value can be nfs. |
SFS Turbo | everest.io/share-access-to | Yes | VPC ID of the cluster. |
SFS Turbo | everest.io/share-expand-type | No | Extension type. The default value is bandwidth, indicating an enhanced file system. This parameter does not take effect. |
SFS Turbo | everest.io/share-source | Yes | The parameter value is fixed at sfs-turbo. |
SFS Turbo | everest.io/share-volume-type | No | SFS Turbo StorageClass. The default value is STANDARD, indicating standard and standard enhanced editions. This parameter does not take effect. |
SFS Turbo | everest.io/reclaim-policy | No | Whether to retain subdirectories when deleting a PVC. This parameter must be used with reclaim policies. This parameter is available only when the PV reclaim policy is Delete. Options:
|
OBS | csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name | Yes | Driver type. If OBS is used, the parameter value is fixed at obs.csi.everest.io. |
OBS | csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype | Yes | Instance type, which can be obsfs or s3fs.
|
OBS | everest.io/obs-volume-type | Yes | OBS StorageClass.
|
Local PV | csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name | Yes | Driver type. If a local PV is used, the parameter value is fixed at local.csi.everest.io. |
Local PV | csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype | Yes | File system type. The value can only be ext4. |
Local PV | volume-type | Yes | Volume type. The value can only be persistent. |
Custom Storage Classes
You can customize a high I/O storage class in a YAML file. For example, the name csi-disk-sas indicates that the disk type is SAS (high I/O).
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1kind: StorageClassmetadata:name: csi-disk-sas # Name of the high I/O storage class, which can be customized.parameters:csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: disk.csi.everest.iocsi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4everest.io/disk-volume-type: SAS # High I/O EVS disk type, which cannot be customized.everest.io/passthrough: "true"provisioner: everest-csi-provisionerreclaimPolicy: DeletevolumeBindingMode: ImmediateallowVolumeExpansion: true # true indicates that capacity expansion is allowed.
For an ultra-high I/O storage class, you can set the class name to csi-disk-ssd to create SSD EVS disk (ultra-high I/O).
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1kind: StorageClassmetadata:name: csi-disk-ssd # Name of the ultra-high I/O storage class, which can be customized.parameters:csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: disk.csi.everest.iocsi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4everest.io/disk-volume-type: SSD # Ultra-high I/O EVS disk type, which cannot be customized.everest.io/passthrough: "true"provisioner: everest-csi-provisionerreclaimPolicy: DeletevolumeBindingMode: ImmediateallowVolumeExpansion: true
reclaimPolicy: indicates the recycling policies of the underlying cloud storage. The value can be Delete or Retain.
- Delete: When a PVC is deleted, both the PV and the EVS disk are deleted.
- Retain: When a PVC is deleted, the PV and underlying storage resources are not deleted. Instead, you must manually delete these resources. After that, the PV resource is in the Released state and cannot be bound to the PVC again.
The reclamation policy configured here has no impact on the SFS Turbo storage.
If high data security is required, you are advised to select Retain to prevent data from being deleted by mistake.
After the definition is complete, run the kubectl create commands to create storage resources.
# kubectl create -f sas.yamlstorageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-disk-sas created# kubectl create -f ssd.yamlstorageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-disk-ssd created
Query the storage class again. Two more types of storage classes are displayed in the command output, as shown below.
# kubectl get scNAME PROVISIONER AGEcsi-disk everest-csi-provisioner 17dcsi-disk-sas everest-csi-provisioner 2m28scsi-disk-ssd everest-csi-provisioner 16scsi-disk-topology everest-csi-provisioner 17dcsi-nas everest-csi-provisioner 17dcsi-obs everest-csi-provisioner 17dcsi-sfsturbo everest-csi-provisioner 17d
Other types of storage resources can be defined in the similar way. You can use kubectl to obtain the YAML file and modify it as required.
- File storage# kubectl get sc csi-nas -oyamlkind: StorageClassapiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1metadata:name: csi-nasprovisioner: everest-csi-provisionerparameters:csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: nas.csi.everest.iocsi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: nfseverest.io/share-access-level: rweverest.io/share-access-to: 5e3864c6-e78d-4d00-b6fd-de09d432c632 # ID of the VPC to which the cluster belongseverest.io/share-is-public: 'false'everest.io/zone: xxxxx # AZreclaimPolicy: DeleteallowVolumeExpansion: truevolumeBindingMode: Immediate
- Object storage# kubectl get sc csi-obs -oyamlkind: StorageClassapiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1metadata:name: csi-obsprovisioner: everest-csi-provisionerparameters:csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: obs.csi.everest.iocsi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: s3fs # Object storage type. s3fs indicates an object bucket, and obsfs indicates a parallel file system.everest.io/obs-volume-type: STANDARD # Storage class of the OBS bucketreclaimPolicy: DeletevolumeBindingMode: Immediate
Specifying an Enterprise Project for Storage Classes
CCE allows you to specify an enterprise project when creating EVS disks and OBS PVCs. The created storage resources (EVS disks and OBS) belong to the specified enterprise project. The enterprise project can be the enterprise project to which the cluster belongs or the default enterprise project.
If you do not specify any enterprise project, the enterprise project in StorageClass is used by default. The created storage resources by using the csi-disk and csi-obs storage classes of CCE belong to the default enterprise project.
If you want the storage resources created from the storage classes to be in the same enterprise project as the cluster, you can customize a storage class and specify the enterprise project ID, as shown below.
To use this function, the everest add-on must be upgraded to 1.2.33 or later.
kind: StorageClassapiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1metadata:name: csi-disk-epid #Customize a storage class name.provisioner: everest-csi-provisionerparameters:csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: disk.csi.everest.iocsi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4everest.io/disk-volume-type: SASeverest.io/enterprise-project-id: 86bfc701-9d9e-4871-a318-6385aa368183 #Specify the enterprise project ID.everest.io/passthrough: 'true'reclaimPolicy: DeleteallowVolumeExpansion: truevolumeBindingMode: Immediate
Specifying a Default Storage Class
You can specify a storage class as the default class. In this way, if you do not specify storageClassName when creating a PVC, the PVC is created using the default storage class.
For example, to specify csi-disk-ssd as the default storage class, edit your YAML file as follows:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1kind: StorageClassmetadata:name: csi-disk-ssdannotations:storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true" # Specifies the default storage class in a cluster. A cluster can have only one default storage class.parameters:csi.storage.k8s.io/csi-driver-name: disk.csi.everest.iocsi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4everest.io/disk-volume-type: SSDeverest.io/passthrough: "true"provisioner: everest-csi-provisionerreclaimPolicy: DeletevolumeBindingMode: ImmediateallowVolumeExpansion: true
Delete the created csi-disk-ssd disk, run the kubectl create command to create a csi-disk-ssd disk again, and then query the storage class. The following information is displayed.
# kubectl delete sc csi-disk-ssdstorageclass.storage.k8s.io "csi-disk-ssd" deleted# kubectl create -f ssd.yamlstorageclass.storage.k8s.io/csi-disk-ssd created# kubectl get scNAME PROVISIONER AGEcsi-disk everest-csi-provisioner 17dcsi-disk-sas everest-csi-provisioner 114mcsi-disk-ssd (default) everest-csi-provisioner 9scsi-disk-topology everest-csi-provisioner 17dcsi-nas everest-csi-provisioner 17dcsi-obs everest-csi-provisioner 17dcsi-sfsturbo everest-csi-provisioner 17d
Verification
When creating a PVC, you have the following configuration methods:
- Specify a storage class explicitly.
- Use the default storage class set up in the cluster if you do not specify a storage class.
Below are the steps to check the results of both configuration methods.
The following steps are used to verify whether the storage class csi-disk-sas defined in Custom Storage Classes can be used to create a PVC.
- Create a YAML file named sas-disk.yaml. You can change the file name as needed. This file uses csi-disk-sas to create a PVC.vim sas-disk.yaml
The file content is as follows:
apiVersion: v1kind: PersistentVolumeClaimmetadata:name: sas-diskspec:accessModes:- ReadWriteOnceresources:requests:storage: 10GistorageClassName: csi-disk-sas - Create a PVC.kubectl create -f sas-disk.yaml
Information similar to the following is displayed:
persistentvolumeclaim/sas-disk created - Check the PVC information.kubectl get pvc
If information similar to the following is displayed, a PV has been associated with the PVC and the storage class is csi-disk-sas.
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGEsas-disk Bound pvc-6e2f37f9-7346-4419-82f7-b42e79f7964c 10Gi RWO csi-disk-sas 24s - Check the PV information.kubectl get pv
If information similar to the following is displayed, the PV has been automatically created.
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGEpvc-6e2f37f9-7346-4419-82f7-b42e79f7964c 10Gi RWO Delete Bound default/sas-disk csi-disk-sas 30sThe result shows that the custom storage class csi-disk-sas can be used properly.
- Background
- Solution
- Creating a StorageClass Using a YAML File
- Custom Storage Classes
- Specifying an Enterprise Project for Storage Classes
- Specifying a Default Storage Class
- Verification