Symptom
After a VPC peering connection is created, the local and peer VPCs cannot communicate with each other.
Troubleshooting
The issues here are described in order of how likely they are to occur.
Figure 1 Troubleshooting process
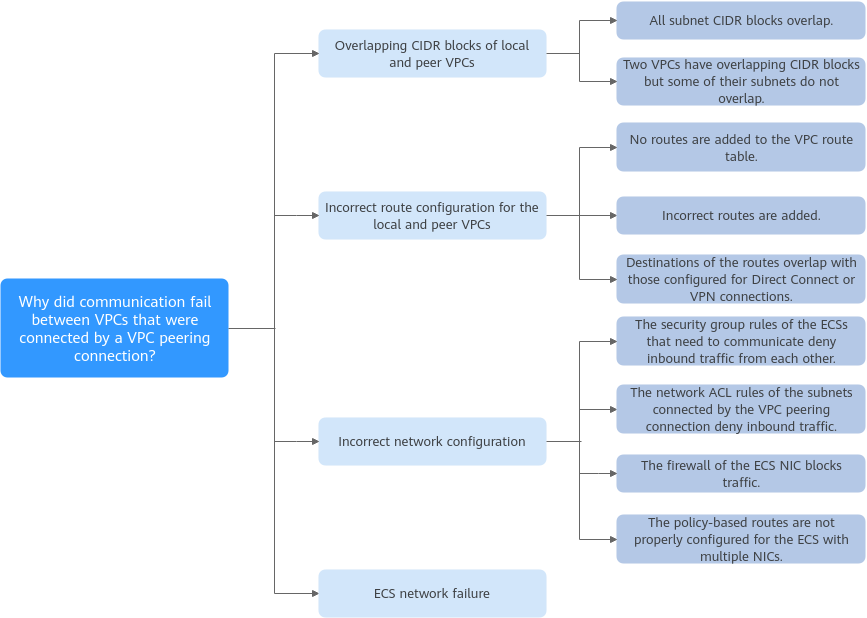
No. | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
1 | Overlapping CIDR blocks of local and peer VPCs
| |
2 | Incorrect route configuration for the local and peer VPCs
| |
3 | Incorrect network configuration
| Refer to Incorrect Network Configuration. |
4 | ECS network failure | Refer to ECS Network Failure. |
Overlapping CIDR Blocks of Local and Peer VPCs
If the CIDR blocks of VPCs connected by a VPC peering connection overlap, the connection may not take effect due to route conflicts.
Scenario | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
VPCs with overlapping CIDR blocks also include subnets that overlap. | As shown in Figure 2, the CIDR blocks of VPC-A and VPC-B overlap, and all their subnets overlap.
| VPC-A and VPC-B cannot be connected using a VPC peering connection. Replan the network. |
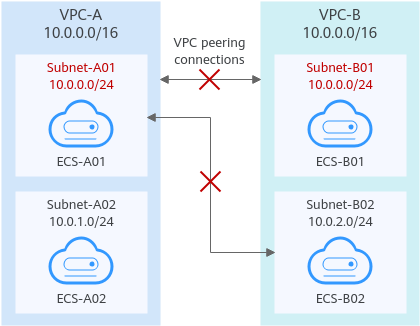
Two VPCs have overlapping CIDR blocks but some of their subnets do not overlap. | As shown in Figure 3, the CIDR blocks of VPC-A and VPC-B overlap, and some of their subnets overlap.
|
|
Figure 2 Networking diagram (IPv4)
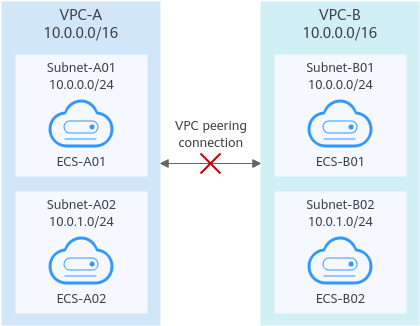
Figure 3 Networking diagram (IPv4)
If CIDR blocks of VPCs overlap and some of their subnets overlap, you can create a VPC peering connection between their subnets with non-overlapping CIDR blocks. Figure 4 shows the networking diagram of connecting Subnet-A02 and Subnet-B02. Table 3 describes the routes required.
Figure 4 Networking diagram (IPv4)
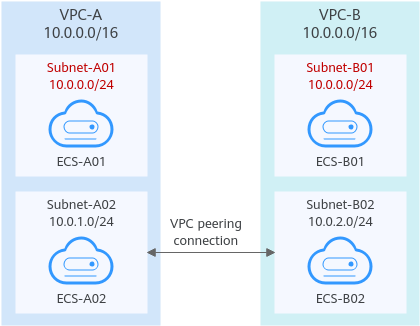
Route Table | Destination | Next Hop | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
VPC-A route table | 10.0.2.0/24 | Peering-AB | Add a route with the CIDR block of Subnet-B02 as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. |
VPC-B route table | 10.0.1.0/24 | Peering-AB | Add a route with the CIDR block of Subnet-A02 as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. |
Incorrect Route Configuration for Local and Peer VPCs
After a VPC peering connection is created, check whether routes are added to the route tables of the local and peer VPCs by referring to Viewing Routes Configured for a VPC Peering Connection. Table 4 lists the items that you need to check.
Item | Solution |
|---|---|
Check whether routes are added to the route tables of the local and peer VPCs. | If routes are not added, add routes by referring to: |
Check the destinations of routes added to the route tables of the local and peer VPCs.
| If the route destination is incorrect, change it. For details, see Modifying Routes Configured for a VPC Peering Connection. |
Destinations of the routes overlap with that configured for Direct Connect or VPN connections. | Check whether any of the VPCs connected by the VPC peering connection also has a VPN or Direct Connect connection connected. If they do, check the destinations of their routes. If the destinations of the routes overlap, the VPC peering connection does not take effect. In this case, replan the network connection. |
Incorrect Network Configuration
- Check whether the security group rules of the ECSs that need to communicate with each other allow inbound traffic from each other.
- If the ECSs are associated with the same security group, you do not need to check their rules.
- If the ECSs are associated with different security groups, add inbound rules to allow access from each other. For details, see Security Group Examples.
- Check whether the firewall of the ECS's network interface blocks traffic.
If the firewall blocks traffic, configure the firewall to allow inbound traffic.
- Check whether network ACL rules of the subnets connected by the VPC peering connection deny inbound traffic.
If the network ACL rules deny inbound traffic, configure rules to allow the traffic.
- If an ECS has more than one network interface, check whether correct policy-based routes have been configured for the ECS and packets with different source IP addresses match their own routes from each network interface.
If an ECS has two network interfaces (eth0 and eth1):
- IP address of eth0: 192.168.1.10; subnet gateway: 192.168.1.1
- IP address of eth1: 192.168.2.10; subnet gateway: 192.168.2.1
Command format:
- ping -l IP address of eth0 Subnet gateway address of eth0
- ping -l IP address of eth1 Subnet gateway address of eth1
Run the following commands:
- ping -I 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.1
- ping -I 192.168.2.10 192.168.2.1
If the network communication is normal, the routes of the network interfaces are correctly configured.
Otherwise, you need to configure policy-based routing for the ECS with multiple network interfaces by referring to How Do I Configure Policy-Based Routes for an ECS with Multiple Network Interfaces?
ECS Network Failure
- Log in to the ECS.
- Check whether the ECS's network interface has an IP address assigned.
- Linux ECS: Use the ifconfig or ip address command to view the IP address of the network interface.
- Windows ECS: In the search box, enter cmd and press Enter. In the displayed command prompt, run the ipconfig command.
- Check whether the subnet gateway of the ECS can be pinged.
- In the ECS list, click the ECS name.
The ECS details page is displayed.
- On the ECS details page, click the hyperlink of VPC.
The Virtual Private Cloud page is displayed.
- In the VPC list, locate the target VPC and click the number in the Subnets column.
The Subnets page is displayed.
- In the subnet list, click the subnet name.
The subnet details page is displayed.
- Click the IP Addresses tab and view the gateway address of the subnet.
- Check whether the gateway communication is normal:
ping Subnet gateway address
Example command: ping 172.17.0.1
- In the ECS list, click the ECS name.