Access Control Overview
A VPC is your private network on the cloud. You can configure security groups and network ACL rules to ensure the security of instances, such as ECSs, databases, and containers, running in a VPC.
- A security group protects the instances in it.
- A network ACL protects associated subnets and all the resources in the subnets.
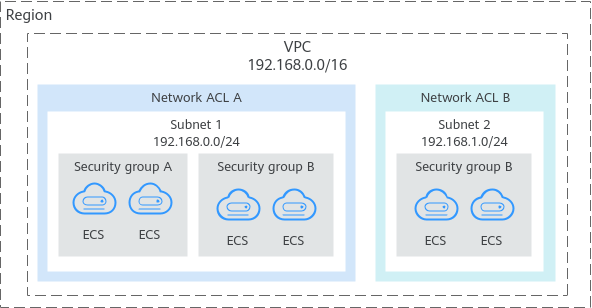
Figure 1 shows how security groups and network ACLs are used. Security groups A and B protect the network security of ECSs. Network ACLs A and B add an additional layer of defense to subnets 1 and 2.
Figure 1 Security groups and network ACLs
Differences Between Access Control Options
Table 1 provides differences between access control options. You can select one or more as needed.
Item | Security Group | Network ACL |
|---|---|---|
Protection Scope | Protects instances in a security group, such as ECSs, databases, and containers. | Protects subnets and all the instances in the subnets. |
Mandatory or Optional | Mandatory. Instances must be added to at least one security group. | Optional. You can determine whether to associate a subnet with a network ACL based on service requirements. |
Stateful | Stateful. The response traffic of inbound and outbound requests is allowed to flow to and out of an instance. | Stateful. The response traffic of inbound and outbound requests is allowed to flow to and out of a subnet. |
Action | Supports both Allow and Deny rules.
| Supports both Allow and Deny rules.
|
Rule Packets | Packet filtering based on 3-tuple (protocol, port, and source/destination) | Packet filtering based on 5-tuple (protocol, source port, destination port, source, and destination) |
Matching Rule | If an instance is associated with multiple security groups that have multiple rules:
| A subnet can have only one network ACL associated. If there are multiple rules, traffic is matched based on the rule priority. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. |
Usage |
| Selecting a network ACL is not allowed when you create a subnet. You must create a network ACL, add inbound and outbound rules, associate subnets with the network ACL, and enable the network ACL. The network ACL then protects the associated subnets and instances in the subnets. |
- Differences Between Access Control Options