Using ELB to Distribute Traffic to a Web Application Across ECSs
Scenarios
ELB distributes traffic across ECSs, which eliminates single points of failure (SPOFs) and makes your application more available.
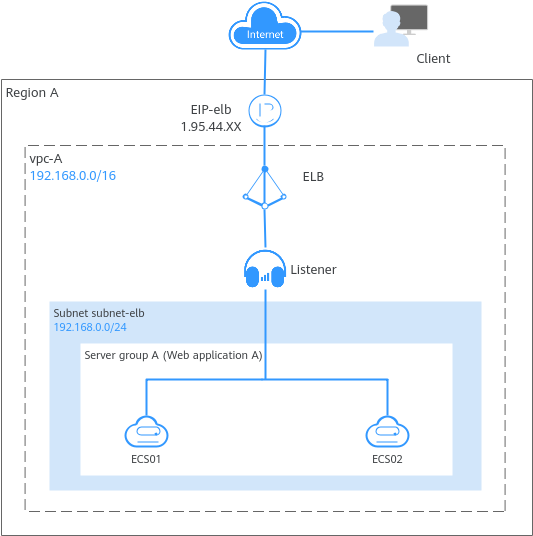
If you have a web application that needs to handle heavy traffic, you can deploy your application on two ECSs (ECS01 and ECS02 in this example) and create a load balancer to distribute traffic across these ECSs.
Figure 1 Using ELB to distribute traffic to an application
Procedure
You can follow the process in Figure 2 to use a load balancer to distribute traffic to a web application.
Figure 2 Distributing traffic to a web application deployed in multiple ECSs

Procedure | What to Do |
|---|---|
| |
Deploy Nginx on the two ECSs. | |
Create a load balancer with elastic specifications to receive requests from clients and distribute the requests to backend servers. | |
Configure security group rules to allow traffic from the backend subnet where the load balancer works to the backend servers. | |
Add a listener to the load balancer to check requests from clients and route requests to backend servers in the backend server group. | |
Access the domain name of the load balancer to check whether different backend servers can be accessed. |
Step 1: Create a VPC and Two ECSs
You need to plan the region for your load balancer, and create a VPC and two ECSs. Ensure that the ECSs and load balancer are in the same AZ and VPC.
- Create a VPC.
- Configuring a VPC
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Name
vpc-A
The VPC name. Set it to vpc-A.
IPv4 CIDR Block
192.168.0.0/16
The IPv4 CIDR block of vpc-A.
Enterprise Project
default
The enterprise project by which VPCs are centrally managed. Select an existing enterprise project for vpc-A.
Advanced Settings (Optional)
N/A
In this example, retain the default value.
- Configuring a VPC subnet
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Subnet Name
subnet-elb
The subnet name. Set it to subnet-elb.
IPv4 CIDR Block
192.168.0.0/24
The IPv4 CIDR block of subnet-elb, which is a unique CIDR block with a range of IP addresses in vpc-A.
IPv6 CIDR Block (Optional)
Do not enable
Whether to assign IPv6 addresses.
Associated Route Table
Default
The default route table that subnet-elb is associated with. The default route table has a preset system route that allows subnets in a VPC to communicate with each other.
Advanced Settings (Optional)
N/A
In this example, retain the default value.
- Configuring a VPC
- Create two ECSs.
- Configuring the network parameters for the two ECSs
Parameter
Example Value
Description
ECS Name
- ECS01
- ECS02
Names of the two ECSs. Set them to ECS01 and ECS02.
Network
- vpc-A
- subnet-elb
The VPC subnet where the ECSs work. Select vpc-A and subnet-elb for the two ECSs.
EIP
- EIP01
- EIP02
The EIP bound to each ECS for Internet access.
- Configuring the network parameters for the two ECSs
Step 2: Deploy the Application
Deploy Nginx on the two ECSs and edit two HTML pages so that a page with message "Welcome to ELB test page one!" is returned when ECS01 is accessed, and the other page with message "Welcome to ELB test page two!" is returned when ECS02 is accessed.
- Log in to the ECSs.
- Install and start Nginx.
- Modify the HTML page of ECS01.
Modify the index.html file in the default root directory of Nginx /usr/share/nginx/html to identify access to ECS01.
- Run the following command to open the index.html file:vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
- Press i to enter editing mode.
- Modify the index.html file.
Modify the following content:
...<body><h1>Welcome to <strong>ELB</strong> test page one!</h1><div class="content"><p>This page is used to test the <strong>ELB</strong>!</p><div class="alert"><h2>ELB01</h2><div class="content"><p><strong>ELB test (page one)!</strong></p><p><strong>ELB test (page one)!</strong></p><p><strong>ELB test (page one)!</strong></p></div></div></div></body> - Press Esc to exit the editing mode. Then, enter :wq to save the settings and exit the file.
- Run the following command to open the index.html file:
- Modify the HTML page of ECS02 by referring to step 3 to identify the access to ECS02.
Modifying the HTML Page of ECS02
- Run the following command to open the index.html file:vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
- Press i to enter editing mode.
- Modify the index.html file.
Modify the following content:
...<body><h1>Welcome to <strong>ELB</strong> test page two!</h1><div class="content"><p>This page is used to test the <strong>ELB</strong>!</p><div class="alert"><h2>ELB02</h2><div class="content"><p><strong>ELB test (page two)!</strong></p><p><strong>ELB test (page two)!</strong></p><p><strong>ELB test (page two)!</strong></p></div></div></div></body> - Press Esc to exit the editing mode. Then, enter :wq to save the settings and exit the file.
- Run the following command to open the index.html file:
- Use your browser to access http://ECS01 EIP and http://ECS02 EIP to verify that Nginx has been deployed.
If the modified HTML pages are displayed, Nginx has been deployed.
- HTML page of ECS01
Figure 4 Nginx successfully deployed on ECS01

- HTML page of ECS02
Figure 5 Nginx successfully deployed on ECS02

- HTML page of ECS01
Step 3: Create a Load Balancer
The load balancer needs an EIP to access the application deployed on the ECSs over the Internet. You can determine whether to bind an EIP to the load balancer based on your requirements.
- In the upper left corner of the page, click
 and select the desired region.
and select the desired region.Select the same region as the two ECSs.
- Click
 in the upper left corner to display Service List and choose Network > Elastic Load Balance.
in the upper left corner to display Service List and choose Network > Elastic Load Balance. - On the Load Balancers page, click Create Elastic Load Balancer.
- On the displayed page, set the parameters as required.
- Configuring the basic information
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Type
Dedicated load balancer
Specifies the type of the load balancer. Select Dedicated load balancer. A dedicated load balancer uses dedicated resources. Its performance is not affected by other load balancers.
Region
-
Specifies the desired region. Resources in different regions cannot communicate with each other over internal networks. Select the same region as the ECSs.
AZ
- AZ1
- AZ2
Specifies the AZ of the load balancer. Select multiple AZs if you need DR capability. The load balancer performance multiplies as the number of AZs increases.
Name
elb-test
Specifies the name of the load balancer.
Enterprise Project
default
Specifies an enterprise project by which cloud resources and members are centrally managed.
- Configuring the basic information
- Set Specifications to Elastic.
- Configure the network parameters and EIP information.
- Configuring network parameters
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Network Type
Private IPv4 network
Specifies the network where the load balancer works. In this example, select Private IPv4 network.
The load balancer uses the private IPv4 address to process private network requests.
To let the load balancer route requests over the Internet, bind an EIP to it.
VPC
N/A
Specifies the VPC where the load balancer works. In this example, select vpc-A.
Frontend Subnet
N/A
Specifies the frontend subnet from which an IPv4 address will be assigned to the load balancer to receive client requests. If IPv6 is enabled, an IPv6 address will also be assigned to the load balancer.
IPv4 Address
Automatically assign IP address
Specifies how you want the IPv4 address to be assigned.
Backend Subnet
Subnet of the load balancer
Specifies the backend subnet from which an IP address will be assigned to the load balancer to forward requests to backend servers.
IP as a Backend
N/A
Specifies whether to add IP addresses as backend servers that are not in the VPC of the load balancer. In this example, leave this feature disabled.
Elastic IPs
EIP
New EIP
Specifies the public IP address that will be bound to the load balancer for receiving and forwarding requests over the Internet. This parameter is mandatory when Network Type is set to IPv4 public network.
EIP Type
Dynamic BGP
Specifies the link type (BGP) when a new EIP is used.
Billed By
Traffic
Specifies how the bandwidth will be billed. In this example, select Traffic. You need to specify a maximum bandwidth and pay for the outbound traffic you use.
Bandwidth (Mbit/s)
100
Specifies the maximum bandwidth when a new EIP is used, in Mbit/s. The value ranges from 1 Mbit/s to 300 Mbit/s.
- Configuring network parameters
- Specifies the maximum bandwidth. Click
 to expand the advanced settings and add a description and tags to the load balancer.
to expand the advanced settings and add a description and tags to the load balancer. - Click Create Now.
- Confirm the configuration and submit your request.
- View the newly created load balancer in the load balancer list.
Step 4: Configure Security Group Rules
To ensure normal communications between the load balancer and backend servers, you need to check the security group and network ACL rules.
- The security groups configured for backend servers must have inbound rules to allow health check and service traffic from backend subnet of the load balancer to backend servers. By default, the backend subnet of a load balancer is the same as the subnet where the load balancer works.
- Network ACL rules are optional for subnets. If network ACL rules are configured for the subnet where backend servers are running, the inbound rules must allow traffic from the backend subnet of the load balancer to the subnet of backend servers.
For details about how to configure security group and network ACL rules, see Security Group and Network ACL RulesSecurity Group and Network ACL Rules.
You can configure security group rules based on Table 1.
Direction | Action | Type | Protocol & Port | Source/Destination | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Inbound | Allow | IPv4 | TCP: 80 | Source: 192.168.0.0/24 | Allows outbound traffic to ECSs in the security group. |
Outbound | Allow | IPv4 | All | Destination: 0.0.0.0/0 | Allows the ECSs in the security group to access the Internet. |
Step 5: Add a Listener
Add a listener to the created load balancer. When you add the listener, create a backend server group, configure a health check, and add the two ECSs to this backend server group. If a backend server is detected unhealthy, the load balancer will stop routing traffic to it until the backend server recovers.
- On the load balancer list page, locate load balancer elb-test and click its name.
- On the Listeners tab, click Add Listener and configure parameters based on Table 2.
Table 2 Parameters for configuring a listener Parameter
Example Value
Description
Name
listener
Specifies the listener name.
Frontend Protocol
HTTP
Specifies the protocol that will be used by the load balancer to receive requests from clients.
Frontend Port
80
Specifies the port that will be used by the load balancer to receive requests from clients.
Redirect
N/A
Specifies whether to redirect requests from the HTTP listener to an HTTPS listener.
Disable it in this example.
Access Control
All IP addresses
Specifies how access to the listener is controlled.
Transfer Client IP Address
N/A
Specifies whether to transmit IP addresses of the clients to backend servers.
This feature is enabled for dedicated load balancers by default and cannot be disabled.
Advanced Forwarding
N/A
Specifies whether to enable the advanced forwarding policy. Once it is enabled, more forwarding rules and actions are supported.
Enable it in this example.
- Retain the default values for Advanced Settings. Click Next: Configure Request Routing Policy. On the Configure Routing Policy page, select Create new for Backend Server Group.
Set Load Balancing Algorithm to Weighted round robin and retain the default values for other parameters.
- Click Next: Add Backend Server.
- Backend servers: Click Add Backend Server and select ECS01 and ECS02 from the server list.
- Backend ports: Set them to 80. ECS01 and ECS02 will use this port to communicate with the load balancer.
- Configure health check parameters. In this example, retain the default settings.
- Click Next: Confirm, confirm the settings, and click Submit.
Step 6: Verify Load Balancing
After the load balancer is configured, you can access the domain name to check whether the two ECSs are accessible.
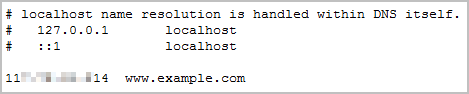
- Modify the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts file on your PC to map the domain name to the EIP bound to the load balancer.
View the EIP on the Summary page of the load balancer.
Figure 6 hosts file on your PC
- Choose Start and enter cmd to open the CLI.
- Run the following command to check whether the domain name is mapped to the load balancer EIP:ping www.example.com
If data packets are returned, the domain name has been mapped to the load balancer EIP.
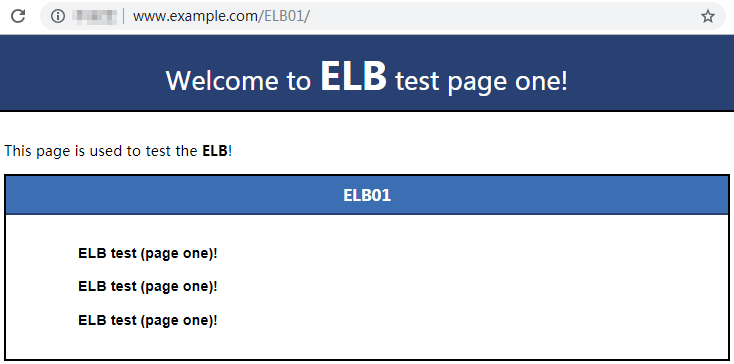
- Use your browser to access http://www.example.com.
If the following page is displayed, the load balancer has routed the request to ECS01.
Figure 7 Accessing ECS01
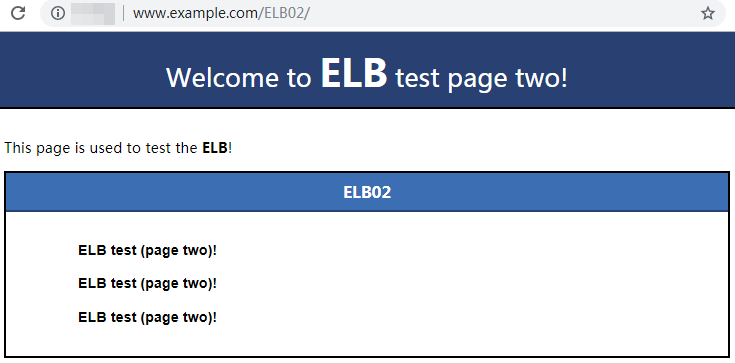
- Use your browser to access http://www.example.com again.
If the following page is displayed, the load balancer has routed the request to ECS02.
Figure 8 Accessing ECS02
- Scenarios
- Procedure
- Step 1: Create a VPC and Two ECSs
- Step 2: Deploy the Application
- Step 3: Create a Load Balancer
- Step 4: Configure Security Group Rules
- Step 5: Add a Listener
- Step 6: Verify Load Balancing