Advanced Forwarding
Overview
Advanced forwarding policies are available only for dedicated load balancers. If you have enabled Advanced Forwarding, you can configure advanced forwarding policies for HTTP and HTTPS listeners of dedicated load balancers.
You can configure advanced forwarding policies for HTTP or HTTPS listeners to forward requests to different backend server groups based on a wide range of forwarding rules and actions. Table 1 describes the rules and actions that you can configure for request forwarding.
Figure 1 How advanced forwarding works
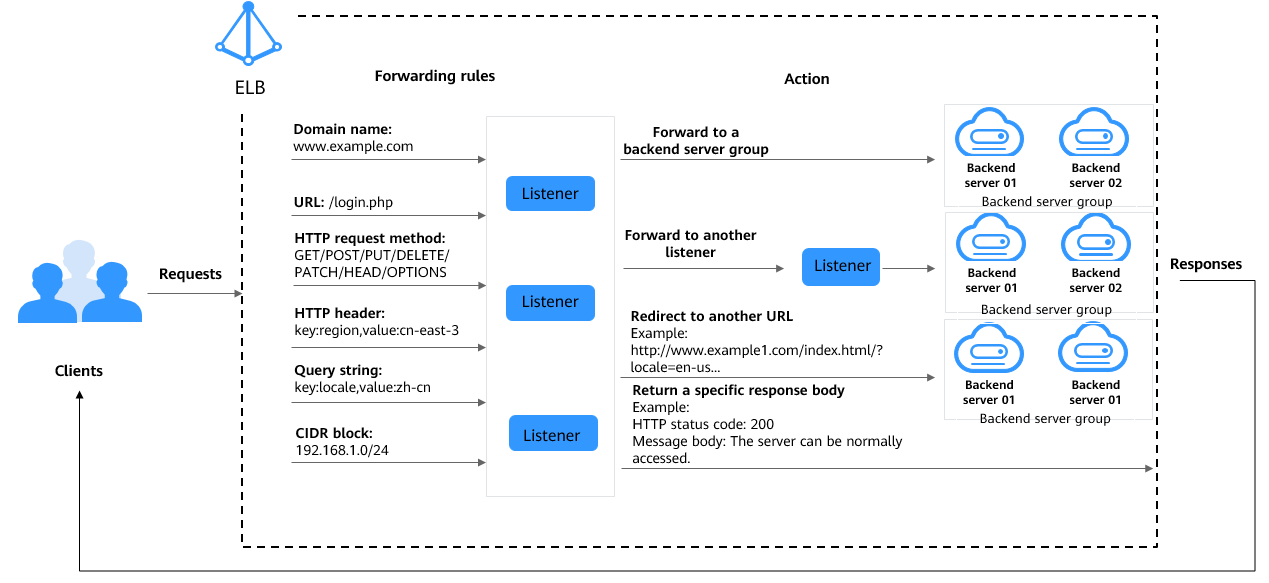
The following describes how an advanced forwarding policy works:
- The client sends a request to the load balancer.
- The load balancer matches the request based on the forwarding rule you configure.
- The load balancer forwards the request to the corresponding backend server or returns a fixed response to the client based on the action you configure.
- The load balancer sends a response to the client.
Forwarding Policy | Description |
|---|---|
Forwarding rule | The following forwarding rules are supported: domain name, path, HTTP request method, HTTP header, query string, and CIDR block. For details, see Forwarding Rule. |
Action | The following actions are supported: forward to a backend server group, redirect to another listener, redirect to another URL, rewrite, and return a specific response body. For details, see Action Types. NOTE: If Action is set to Forward to a backend server group, you can also select Rewrite. For details, see Table 4. |
How Requests Are Matched
After you add an HTTP or HTTPS listener to a load balancer, a default forwarding policy is generated. This policy uses the protocol and port specified for the listener to match requests and forward the requests to the backend server group you specified when adding the listener.
The default forwarding policy has the lowest priority and is not included when you sort forwarding policies. It can be edited but cannot be deleted.
Each request is matched based on the forwarding policy priority (a smaller value indicates a higher priority). Once a forwarding policy is matched, the request is forwarded based on this forwarding policy.
- If multiple conditions are configured for a forwarding policy, the request can match this forwarding policy only when all the conditions are met.
- If the request is matched with any forwarding policy of the listener, it is forwarded based on this forwarding policy.
- If the request is not matched with any forwarding policy, it is forwarded based on the default forwarding policy.
Forwarding Rule
Advanced forwarding policies support the following types of forwarding rules: domain name, path, HTTP request method, HTTP header, query string, and CIDR block.
Forwarding Rule | Description |
|---|---|
Domain name |
|
Path |
For more information about path matching rules, see Path Matching.
|
Query string | Route requests based on the query string. A query string consists of a key and one or more values. You need to set the key and values separately.
|
HTTP request method | Route requests based on the HTTP method.
|
HTTP header | Route requests based on the HTTP header. An HTTP header consists of a key and one or more values. You need to configure the key and values separately.
|
CIDR block | Route requests based on the source IP addresses from where requests originate.
|
Action Types
Advanced forwarding policies support the following actions: forward to a backend server group, redirect to another listener, redirect to another URL, and return a specific response body.
If you set Action to Forward to backend server group or Return a specific response body, you can add additional actions. ELB first performs additional actions and then forwards requests to the specified backend server group or returns a specific response body. Among all the additional actions, Limit request has the highest priority.
Action | Description |
|---|---|
Forward to a backend server group | Requests are forwarded to the specified backend server group. |
Redirect to another listener | Requests are redirected to another listener, which then routes the requests to its associated backend server group. NOTE: For example, if you configure a redirect for an HTTP listener, HTTP requests to access a web page will be redirected to the HTTPS listener you select and handled by the backend servers associated with the HTTPS listener. As a result, the clients access the web page over HTTPS. |
Redirect to another URL | Requests are redirected to the configured URL. When clients access website A, the load balancer returns 302 or any other 3xx status code and automatically redirects the clients to website B. You can customize the redirection URL that will be returned to the clients. Configure at least one of the following components:
|
Return a specific response body | Load balancers return a fixed response to the clients. You can custom the status code and response body that load balancers directly return to the clients without the need to route the requests to backend servers. Configure the following components:
Example text/plain
text/css
text/html
application/javascript
application/json
NOTE: Ensure that the response body does not contain carriage return characters. Otherwise, it cannot be saved. |
Action | Description |
|---|---|
Rewrite | Rewrites the request URL before forwarding requests to the specified backend server group. Configure the following parameters:
NOTE: The domain name, path, and query string cannot be left blank or made default. |
Path Matching
Table 5 shows how paths configured in the forwarding policies match those in the requests.
Request Path | Forwarding Policy | Specified Path | Matching Mode | Forwarding Policy Priority | Destination Backend Server Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
/elb/abc.html | Forwarding policy 01 | /elb/abc.html | Prefix match | 1 | Backend server group 01 |
Forwarding policy 02 | /elb | Prefix match | 2 | Backend server group 02 | |
/exa/index.html | Forwarding policy 03 | /exa[^\s]* | Regular expression match | 3 | Backend server group 03 |
Forwarding policy 04 | /exa/index.html | Regular expression match | 4 | Backend server group 04 | |
/mpl/index.html | Forwarding policy 05 | /mpl/index.html | Exact match | 5 | Backend server group 05 |
URLs are matched as follows:
- When the request path is /elb/abc.html, it matches both forwarding policy 01 and forwarding policy 02. However, the priority of forwarding policy 01 is higher than that of forwarding policy 02. Forwarding policy 01 is used, and requests are forwarded to backend server group 01.
- When the request path is /exa/index.html, it matches both forwarding policy 03 and forwarding policy 04. However, the priority of forwarding policy 03 is higher than that of forwarding policy 04. Forwarding policy 03 is used, and requests are forwarded to backend server group 03.
- If the request path is /mpl/index.html, it matches forwarding policy 05 exactly, and requests are forwarded to backend server group 05.
Path Matching Based on Regular Expressions
A path can contain letters, digits, and special characters: _~';@^-%#&$.*+?,=!:|\/()[]{} and must start with a slash (/). ${path} retains the path of the request.
If you select regular expression match, the request path will be overwritten by the variables that match the regular expressions.
How Request Paths Are Overwritten
- Path matching: The client sends a request, and the request matches a regular expression in the forwarding rule. You can specify one or more regular expressions as the match conditions and set multiple capture groups represented by parentheses ( ) for one regular expression.
- Extraction and replacement: extracts the content from the capture groups.
- Destination path: writes them to $1, $2, all the way to $9 configured for the path.
Example
When a client requests to access /test/ELB/elb/index, which matches the regular expression /test/(.*)/(.*)/index, $1 will be replaced by ELB and $2 by elb, and then the request will be redirected to /ELB/elb.
Matching Step | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Forwarding rule: path | Regular expression match |
| |
Action: rewrite or redirect to another URL | Path |
| |
- Overview
- How Requests Are Matched
- Forwarding Rule
- Action Types
- Path Matching
- Path Matching Based on Regular Expressions