How Does GaussDB(DWS) Implement Row-to-Column and Column-to-Row Conversion?
This section describes how to use SQL statements to convert rows to columns and convert columns to rows in GaussDB(DWS).
Scenario
Use a student score table as an example:
Teachers record the score of each subject of each student in a table, but students care only bout their own scores. A student needs to use row-to-column conversion to view their scores of all subjects. If the teacher of a subject wants to view the sores of all students of that subject, the teacher needs to use the column-to-row conversion.
The following figure shows the row-to-column and column-to-row conversion.
Figure 1 Diagram
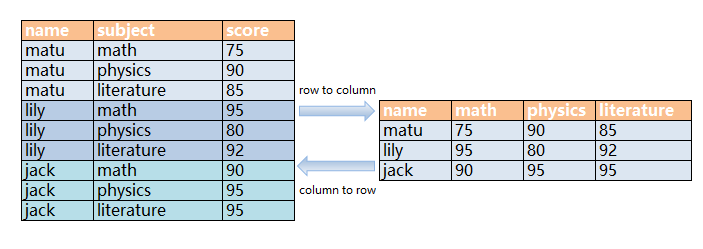
- Rows-to-column conversion
Convert multiple rows of data into one row, or convert one column of data into multiple columns.
- Column-to-row conversion
Convert a row of data into multiple rows, or convert multiple columns of data into one column.
Example
- Create a row-store table students_info, and insert data into the table.CREATE TABLE students_info(name varchar(20),subject varchar(100),score bigint) distribute by hash(name);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('lily','math',95);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('lily','physics',80);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('lily','literature',92);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('matu','math',75);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('matu','physics',90);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('matu','literature',85);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('jack','math',90);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('jack','physics',95);INSERT INTO students_info VALUES('jack','literature',95);
View information about the students_info table.
SELECT * FROM students_info;name | subject | score------+------------+-------matu | math | 75matu | physics | 90matu | literature | 85lily | math | 95lily | physics | 80lily | literature | 92jack | math | 90jack | physics | 95jack | literature | 95 - Create a column-store table students_info1, and insert data into the table.CREATE TABLE students_info1(name varchar(20), math bigint, physics bigint, literature bigint) with (orientation = column) distribute by hash(name);INSERT INTO students_info1 VALUES('lily',95,80,92);INSERT INTO students_info1 VALUES('matu',75,90,85);INSERT INTO students_info1 VALUES('jack',90,95,95);
View information about table students_info1.
SELECT * FROM students_info1;name | math | physics | literature------+------+---------+------------matu | 75 | 90 | 85lily | 95 | 80 | 92jack | 90 | 95 | 95(3 rows)
Static row-to-column conversion
Static row-to-column conversion requires you to manually specify the column names using the given values. If no value is given to a column, the default value 0 is assigned to the column.
SELECT name,sum(case when subject='math' then score else 0 end) as math,sum(case when subject='physics' then score else 0 end) as physics,sum(case when subject='literature' then score else 0 end) as literature FROM students_info GROUP BY name;name | math | physics | literature------+------+---------+------------matu | 75 | 90 | 85lily | 95 | 80 | 92jack | 90 | 95 | 95(3 rows)
Dynamic row-to-column conversion
For clusters of 8.1.2 or later, you can use GROUP_CONCAT to generate column-store statements.
SELECT group_concat(concat('sum(IF(subject = ''', subject, ''', score, 0)) AS "', name, '"'))FROM students_info;group_concat----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------sum(IF(subject = 'literature', score, 0)) AS "jack",sum(IF(subject = 'literature', score, 0)) AS "lily",sum(IF(subject = 'literature', score, 0)) AS "matu",sum(IF(subject = 'math', score, 0)) AS "jack",sum(IF(subject = 'math', score, 0)) AS "lily",sum(IF(subject = 'math', score, 0)) AS "matu",sum(IF(subject = 'physics', score, 0)) AS "jack",sum(IF(subject = 'physics', score, 0)) AS "lily",sum(IF(subject = 'physics', score, 0)) AS "matu"(1 row)
In 8.1.1 and earlier versions, you can use LISTAGG to generate column-store statements.
SELECT listagg(concat('sum(case when subject = ''', subject, ''' then score else 0 end) AS "', subject, '"'),',') within GROUP(ORDER BY 1)FROM (select distinct subject from students_info);listagg-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------sum(case when subject = 'literature' then score else 0 end) AS "literature",sum(case when subject = 'physics' then score else 0 end) AS "physics",sum(case when subject = 'math' then score else 0 end) AS "math"(1 row)
Dynamically rebuild the view:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION build_view()RETURNS VOIDLANGUAGE plpgsqlAS $$ DECLAREsql text;rec record;BEGINsql := 'select LISTAGG(CONCAT( ''sum(case when subject = '''''', subject, '''''' then score else 0 end) AS "'', subject, ''"'' ),'','' ) within group(order by 1) from (select distinct subject from students_info);';EXECUTE sql INTO rec;sql := 'drop view if exists get_score';EXECUTE sql;sql := 'create view get_score as select name, ' || rec.LISTAGG || ' from students_info group by name';EXECUTE sql;END$$;
Rebuild the database:
CALL build_view();
Query view:
SELECT * FROM get_score;name | literature | physics | math------+------------+---------+------matu | 85 | 90 | 75lily | 92 | 80 | 95jack | 95 | 95 | 90(3 rows)
Column-to-Row Conversion
Use UNION ALL to merge subjects (math, physics, and literature) into one column. The following is an example:
SELECT * FROM(SELECT name, 'math' AS subject, math AS score FROM students_info1union allSELECT name, 'physics' AS subject, physics AS score FROM students_info1union allSELECT name, 'literature' AS subject, literature AS score FROM students_info1)order by name;name | subject | score------+------------+-------jack | math | 90jack | physics | 95jack | literature | 95lily | math | 95lily | physics | 80lily | literature | 92matu | math | 75matu | physics | 90matu | literature | 85(9 rows)
- Scenario
- Example
- Static row-to-column conversion
- Dynamic row-to-column conversion
- Column-to-Row Conversion