How Can I Clear and Reclaim the GaussDB(DWS) Storage Space?
After you delete data stored in GaussDB(DWS) data warehouses, dirty data may be generated possibly because the disk space is not released. This results in disk space waste and deteriorates snapshot creation and restoration performance. The following describes the impact on the system and subsequent operation to clear the disk space:
Points worth mentioning during clearing and reclaiming storage space:
- Unnecessary data needs to be deleted to release the storage space.
- Frequent read and write operations may affect proper database use. Therefore, it is good practice to clear and reclaim the storage space when not in peak hours.
- The data clearing time depends on the data stored in the database.
Periodically clear dirty data to clean up and reclaim storage space. The procedure varies depending on the cluster version. The details are as follows:
Version 8.1.3 or Later: Automatically Cleaning Using the Intelligent O&M Function on the Management Console
- Log in to the GaussDB(DWS) console.
- Click the name of the target cluster.
- In the navigation pane, choose Intelligent O&M.
- Click the O&M Plan tab. Click Add O&M Task.
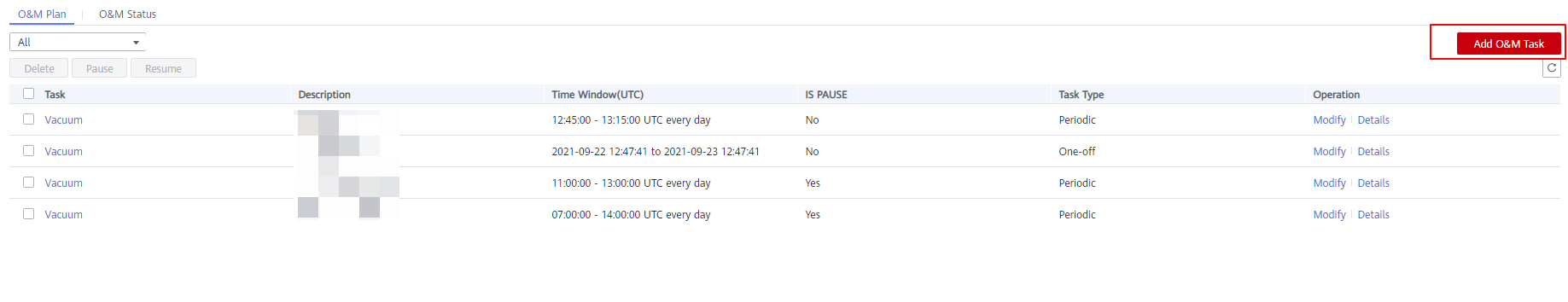
- The Add O&M Task page is displayed.
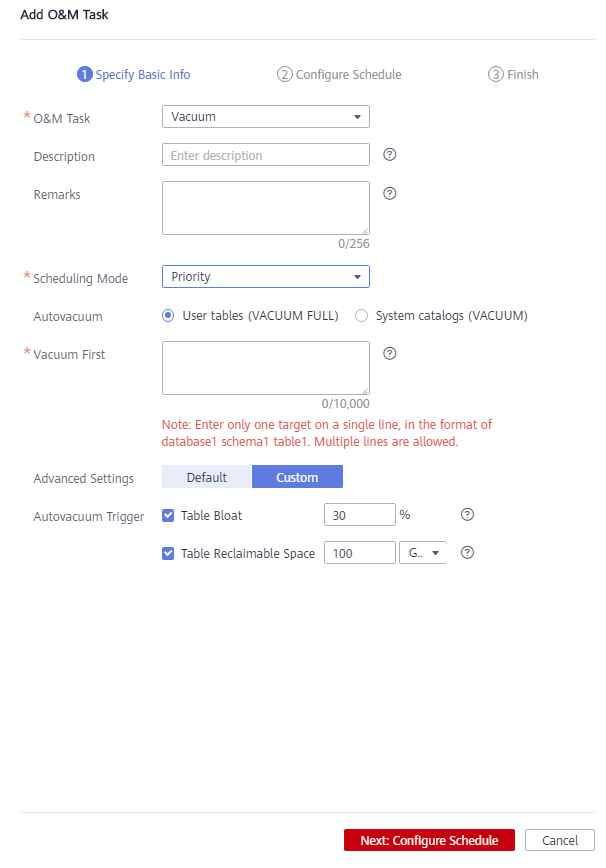
- Select Vacuum for O&M Task.
- Set Scheduling Mode to Auto. GaussDB(DWS) automatically scans tables that require VACUUM operation.
- Select System catalogs or User tables for Autovacuum.
- If there are a large number of UPDATE and DELETE operations, select the User tables.
- If there are a large number of CREATE and DELETE operations, select System catalogs.
- Click Next: Configure Schedule to configure the schedule and Vacuum type. You are advised to select Periodic for Task Type. The GaussDB(DWS) automatically executes VACUUM in your selected time windows.
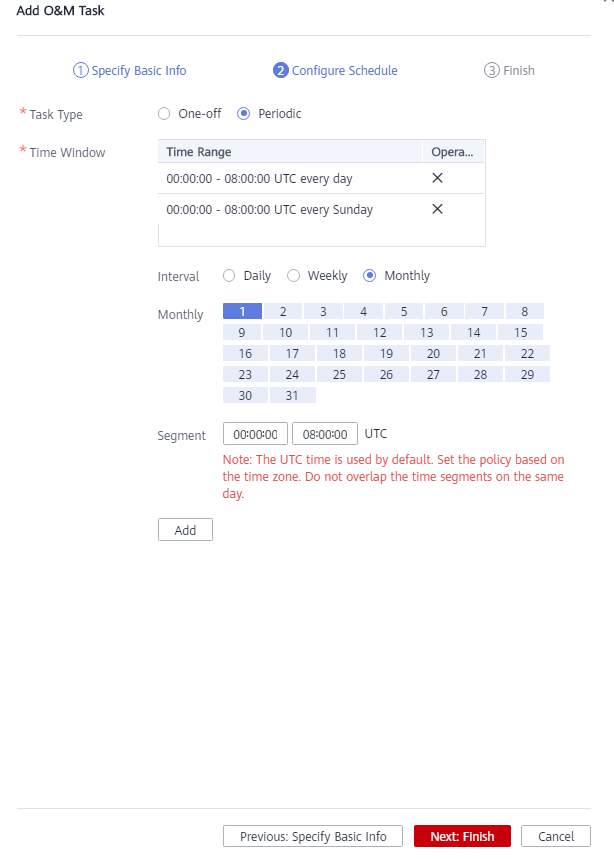 Note
NoteFor automatic Vacuum O&M tasks, the system uses the VACUUM FULL operation to process user tables. VACUUM FULL holds a level 8 lock, which blocks other transactions. Other transactions will be in lock waiting during VACUUM FULL execution. After 20 minutes, a timeout error is reported. Therefore, do not perform other transactions in the configured time window.
- After confirming that the information is correct, click Next to complete the configuration.
Version 8.1.2 or Earlier: Manually Cleaning by Running the VACUUM FULL Command
- The VACUUM FULL operation locks a table, blocking all access to it during this period and waiting for its completion. To avoid impacting services due to table locking, schedule appropriately.
- VACUUM FULL extracts valid data from the current table, reorganizes it, and removes dirty data. This process temporarily requires additional space, which is released after the reorganization is complete. As a result, space initially increases before decreasing. Calculate the necessary space for VACUUM FULL in advance using the formula: Additional reorganization space = Table size x (1 – Dirty page rate).
- Connect to the database, run the following SQL statements to query large tables whose dirty page rate exceeds 30%, and sort the tables by size in descending order:SELECT schemaname AS schema, relname AS table_name, n_live_tup AS analyze_count, pg_size_pretty(pg_table_size(relid)) as table_size, dirty_page_rateFROM PGXC_GET_STAT_ALL_TABLESWHERE schemaName NOT IN ('pg_toast', 'pg_catalog', 'information_schema', 'cstore', 'pmk')AND dirty_page_rate > 30ORDER BY table_size DESC, dirty_page_rate DESC;
- Check whether any command output is displayed.
- If yes, perform 3 for tables larger than 10 GB.
- If no, no further action is required.
- Run the VACUUM FULL command to clear the top 5 tables with the most dirty pages. If the maximum disk space is greater than 70%, clear the tables one by one.VACUUM FULL ANALYZE schema.table_name;
- Version 8.1.3 or Later: Automatically Cleaning Using the Intelligent O&M Function on the Management Console
- Version 8.1.2 or Earlier: Manually Cleaning by Running the VACUUM FULL Command