When analyzing data, you can create data tables using custom SQL statements for complex logic or models. These statements can be customized with variable settings to accommodate more complex and dynamic analysis scenarios.
Notes and Constraints
- A dataset can contain only one SQL statement.
- The SQL syntax for creating a custom dataset supports only SELECT, FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, SET, and LIMIT.
Prerequisites
- You have subscribed to DataArts Insight.
- A project has been created by referring to Creating a Project.
- A data source has been connected by referring to Creating a Data Source.
Creating a Dataset Using SQL Statements
- Click
 in the upper left corner to select a region.
in the upper left corner to select a region. - In the lower left corner of the navigation pane, select an enterprise project from Enterprise Project.
- Click the name of the target project to access it.
- Click Dataset.
- Click Create Dataset in the upper right corner of the page.
- Click Edit SQL Statement in the upper right corner of the dataset creation page.
- Click
 on the SQL editing page to name the custom data table. If the custom data table is not named, the default data table name sql is used.
on the SQL editing page to name the custom data table. If the custom data table is not named, the default data table name sql is used. - Enter SQL statements based on service requirements. SQL parameters can be used for dynamic query. After the editing is complete, click Run.
Example: Sort data1, data2, and data3 in the data table into a dataset.
SELECT*FROMdataWHEREcity IN ('data1', 'data2', 'data3')and date > ${param} - After the running is successful, view the running result on the Running Results tab.
- Click Finish and Exit to save the custom dataset.
Setting SQL Parameters
During data analysis, if you need to upload parameters to SQL when viewing dashboards or large screens, you can set SQL parameters. This section describes how to set SQL parameters.
- Use SQL parameters to dynamically edit SQL statements in an SQL script.
- The parameter format is ${param}, in which param indicates the parameter name. You can obtain the value of a specified parameter by sequence number. Example: ${params[0]} can be used to obtain the first value in the params parameter list.
- If a parameter is left empty, the related condition is set to 1=1 by default when the SQL statement is executed. In this way, data can be queried properly. You can also use <if test="param != null">Dynamic statement</if> to control the final SQL statement when the parameter is empty.
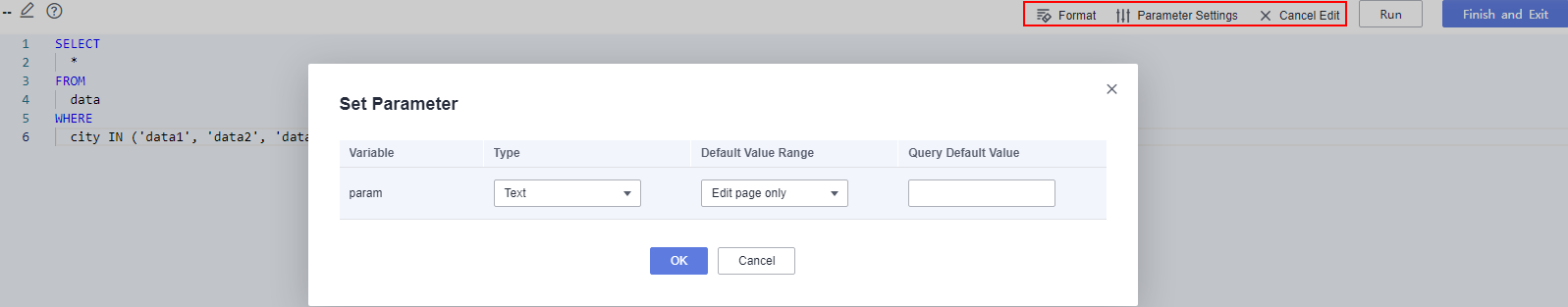
- On the SQL editing page, click Parameter Settings in the upper right corner.
Figure 1 Parameter setting page
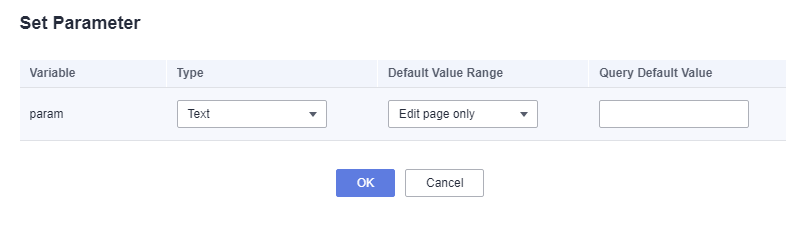
Table 1 Parameters Parameter
Description
Variable
Variable name.
Type
Three variable types are supported: text, number, and date.
Default Value Range
The value can take effect globally or only on the editing page.
- Global: The query default value takes effect on the dashboard, large screen, and SQL editing page.
- Edit page only: The query default value takes effect only on the SQL editing page.
Query Default Value
The parameter is optional. If the dataset is too large and cannot be saved, or if the dashboard query takes too long, it is recommended to adjust the default query value.
Modifying SQL Code
The SQL code needs to be modified for different analysis scenarios.
- Click
 in the upper left corner to select a region.
in the upper left corner to select a region. - In the lower left corner of the navigation pane, select an enterprise project from Enterprise Project.
- Click the name of the target project to access it.
- In the navigation pane, choose Datasets.
- In the dataset list, click the dataset created using custom SQL statements to go to the data editing page.Note
If a dataset is created using custom SQL statements, "SQL" is displayed next to the dataset name in the Name column on the Datasets page.
- Click Edit SQL Statement. On the displayed page, edit the SQL statement.
- The SQL editor provides a formatting tool to format the entered SQL statements.
- You can set SQL parameters by referring to Setting SQL Parameters.
Figure 2 Configuring fields
- Click Run. After the running is successful, view the running result on the Running Results tab.
- Click Finish and Exit to save the changes made to the dataset.