Before You Start
FunctionGraph hosts event-driven functions in a serverless context while ensuring high availability, high scalability, and zero maintenance. All you need to do is write your code and set the conditions.
This document describes how to use application programming interfaces (APIs) to perform operations on FunctionGraph resources, such as creating, deleting, query, and executing functions. For details about all supported operations, see API Overview.
FunctionGraph supports Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs, allowing you to call APIs using HTTPS. For details about API calling, see Calling APIs.
Notes and Constraints
- The number of functions that you can create is determined by your quota. For details, see Quotas.
- For more constraints, see API description.
Endpoints
An endpoint is the request address for calling an API. Endpoints vary depending on services and regions. For the endpoints of all services, see Regions and Endpoints.
Concepts
- Account
An account is created upon successful registration with the cloud system. The account has full access permissions for all of its cloud services and resources. It can be used to reset user passwords and grant user permissions. The account is a payment entity and should not be used directly to perform routine management. For security purposes, create Identity and Access Management (IAM) users and grant them permissions for routine management.
- IAM user
An IAM user is created using an account to use cloud services. Each IAM user has its own identity credentials (password and access keys).
The account name, username, and password will be required for API authentication.
- Region
Regions are geographic areas isolated from each other. Resources are region-specific and cannot be used across regions through internal network connections. For low network latency and quick resource access, select the nearest region.
- AZ
An AZ comprises of one or more physical data centers equipped with independent ventilation, fire, water, and electricity facilities. Computing, network, storage, and other resources in an AZ are logically divided into multiple clusters. AZs within a region are interconnected using high-speed optical fibers to support cross-AZ high-availability systems.
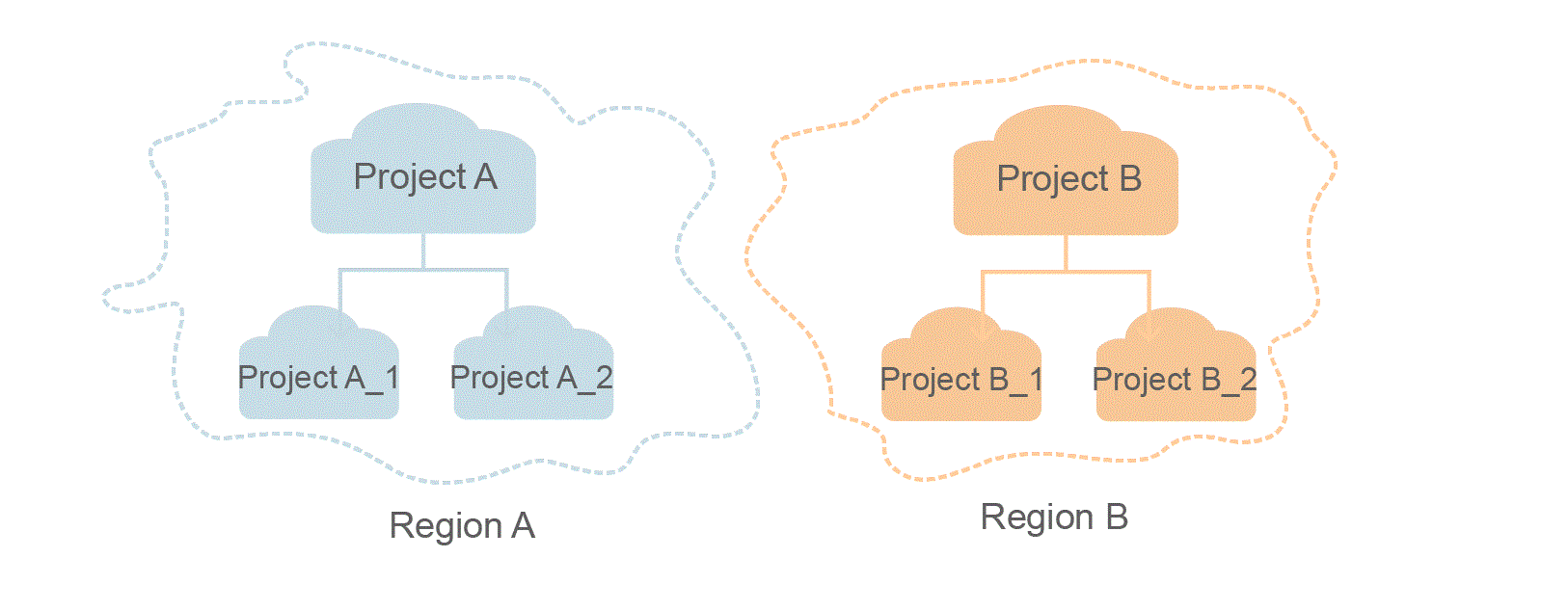
- Project
Projects group and isolate resources (including compute, storage, and network resources) across physical regions. A default project is provided for each region, and subprojects can be created under each default project. Users can be granted permissions to access all resources in a specific project. For more refined access control, create subprojects under a project and purchase resources in the subprojects. Users can then be assigned permissions to access only specific resources in the subprojects.
Figure 1 Project isolating model
- Enterprise project
Enterprise projects group and manage resources across regions. Resources in enterprise projects are logically isolated. An enterprise project can contain resources of multiple regions, and resources can be added to or removed from enterprise projects. For details about how to obtain enterprise project IDs and features, see the Enterprise Management Service User Guide.
- Notes and Constraints
- Endpoints
- Concepts