EVS disks are classified based on the disk I/O performance. EVS disks differ in performance and price. You can choose whichever disk type that is the best fit for your applications.
EVS Performance
EVS performance metrics include:
- IOPS: The number of read/write operations performed by an EVS disk per second.
- Throughput: The amount of data read from and written into an EVS disk per second.
- Read/write I/O latency: The minimum interval between two consecutive read/write operations on an EVS disk.
Parameter | Extreme SSD | Ultra-high I/O | High I/O |
|---|---|---|---|
IOPS per GiB/EVS disk | 50 | 50 | 8 |
Max. IOPS/EVS disk | 128,000 | 50,000 | 5,000 |
Baseline IOPS/EVS disk | 1,800 | 1,800 | 1,800 |
IOPS burst limit/EVS disk | 64,000 | 16,000 | 5,000 |
Disk IOPS calculation formula | IOPS limit = Min. [128,000, 1,800 + 50 × Capacity (GiB)] | IOPS limit = Min. (50,000, 1,800 + 50 × Capacity) | IOPS limit = Min. (5,000, 1,800 + 8 × Capacity) |
Max. throughput | 1,000 MiB/s | 350 MiB/s | 150 MiB/s |
Disk throughput calculation formula | Throughput limit = Min. [1,000, 120 + 0.5 × Capacity (GiB)] MiB/s | Throughput limit = Min. (350, 120 + 0.5 × Capacity) MiB/s | Throughput limit = Min. (150, 100 + 0.15 × Capacity) MiB/s |
Single-queue access latency | Sub-milliseconds | 1 ms | 1–3 ms |
API name NOTE: This API name is the value of the volume_type parameter in the EVS API. It does not represent the type of the underlying hardware device. | ESSD | SSD | SAS |
Typical use cases |
| Read/write-intensive workloads that demand ultra-high I/O and throughput, such as distributed file systems used in HPC scenarios or NoSQL and relational databases used in I/O-intensive scenarios. Typical databases include MongoDB, Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, and PostgreSQL. | Mainstream applications requiring high performance and high reliability, such as large-scale development and test environments, web server logs, and enterprise applications. Typical enterprise applications include SAP applications, Microsoft Exchange, and Microsoft SharePoint. |
EVS disk performance is closely related with the data block size:
- If data blocks are all the same size, a disk can achieve either the maximum IOPS or maximum throughput depending on which one is reached first.
- If data blocks are of different sizes, the maximum performance metric that a disk can achieve varies:
- For small data blocks, such as 4 KiB or 8 KiB, a disk can reach the maximum IOPS.
- For data blocks of a large size, 16 KiB or greater, a disk can reach the maximum throughput.
Table 2 uses an ultra-high I/O disk as an example. In theory, when the size of an ultra-high I/O disk is at least 964 GiB, the disk theoretically can reach either the maximum IOPS 50,000 or the maximum throughput 350 MiB/s. However, this is not the case in practice. The maximum IOPS and maximum throughput that a disk can reach also vary with the data block size.
Data Block Size (KiB) | Max. IOPS | Max. Throughput (MiB/s) |
|---|---|---|
4 | About 50,000 | About 195 |
8 | About 44,800 | About 350 |
16 | About 22,400 | About 350 |
32 | About 11,200 | About 350 |
Disk IOPS Calculation Formula
Disk IOPS limit = Min. (Maximum IOPS, Baseline IOPS + IOPS per GiB × Capacity)
Take an ultra-high I/O EVS disk with a maximum IOPS of 50,000 for example.
If the disk capacity is 100 GiB, the disk IOPS limit is calculated as follows: Disk IOPS limit = Min. (50,000, 1,800 + 50 × 100)
The disk IOPS limit is 6,800, the smaller of the two values (50,000 and 6,800).
If the disk capacity is 1,000 GiB, the disk IOPS limit is calculated as follows: Disk IOPS limit = Min. (50,000, 1,800 + 50 × 1,000)
The disk IOPS limit is 50,000, the smaller of the two values (50,000 and 51,800).
Disk Burst Capability and Principles
EVS disks have a burst capability. A small-capacity disk can surpass its official maximum IOPS for a short period of time. This IOPS applies to each disk individually.
Disks with burst capability are well-suited for speeding up server startup. In most cases, system disks are fairly small, so their basic IOPS is fairly low. For example, the IOPS of a 50-GiB ultra-high I/O disk without burst can only reach up to 4,300 IOPS (Min. (50,000, 1,800 + 50 × Capacity)). But with burst capability, its IOPS can burst up to 16,000.
The following example uses an ultra-high I/O EVS disk with the IOPS burst limit of 16,000.
- If the disk capacity is 100 GiB, the disk has a maximum IOPS of 6,800, but it can temporarily burst to 16,000 IOPS.
- If the disk capacity is 1,000 GiB, the disk has a maximum IOPS of 50,000. The disk maximum IOPS already exceeds its burst IOPS 16,000, and the disk does not use the burst capability.
The following describes the burst IOPS consumption and reservation.
A token bucket is used to handle burst I/O operations. The number of initial tokens in the bucket is calculated as follows:
Number of initial tokens = Burst duration × IOPS burst limit
In the following example, a 100-GiB ultra-high I/O EVS disk is used, and the fixed burst duration is 1800 seconds. Therefore, the number of initial tokens is 28,800,000 (1,800 × 16,000).
- Token production rate: This rate equals the disk maximum IOPS, which is 6,800 tokens/s.
- Token consumption rate: This rate is based on the I/O usage. Each I/O request consumes a token. The maximum consumption rate is 16,000 tokens/s, which is the larger value of the disk burst IOPS and the maximum IOPS.
Consumption principles
When tokens are consumed faster than they are produced, the number of tokens decreases accordingly, and eventually the disk IOPS will be consistent with the token production rate (the maximum IOPS). In this example, the disk can burst for approximately 3,130 seconds (28,800,000/(16,000 - 6,800)).
Reservation principles
When tokens are consumed more slowly than they are produced, the number of tokens increases accordingly, and the disk regains burst capability. In this example, if the disk is suspended for approximately 4,235 seconds (28,800,000/6,800), the token bucket will be filled up with tokens.
As long as there are tokens in the token bucket, the disk has the burst capability.
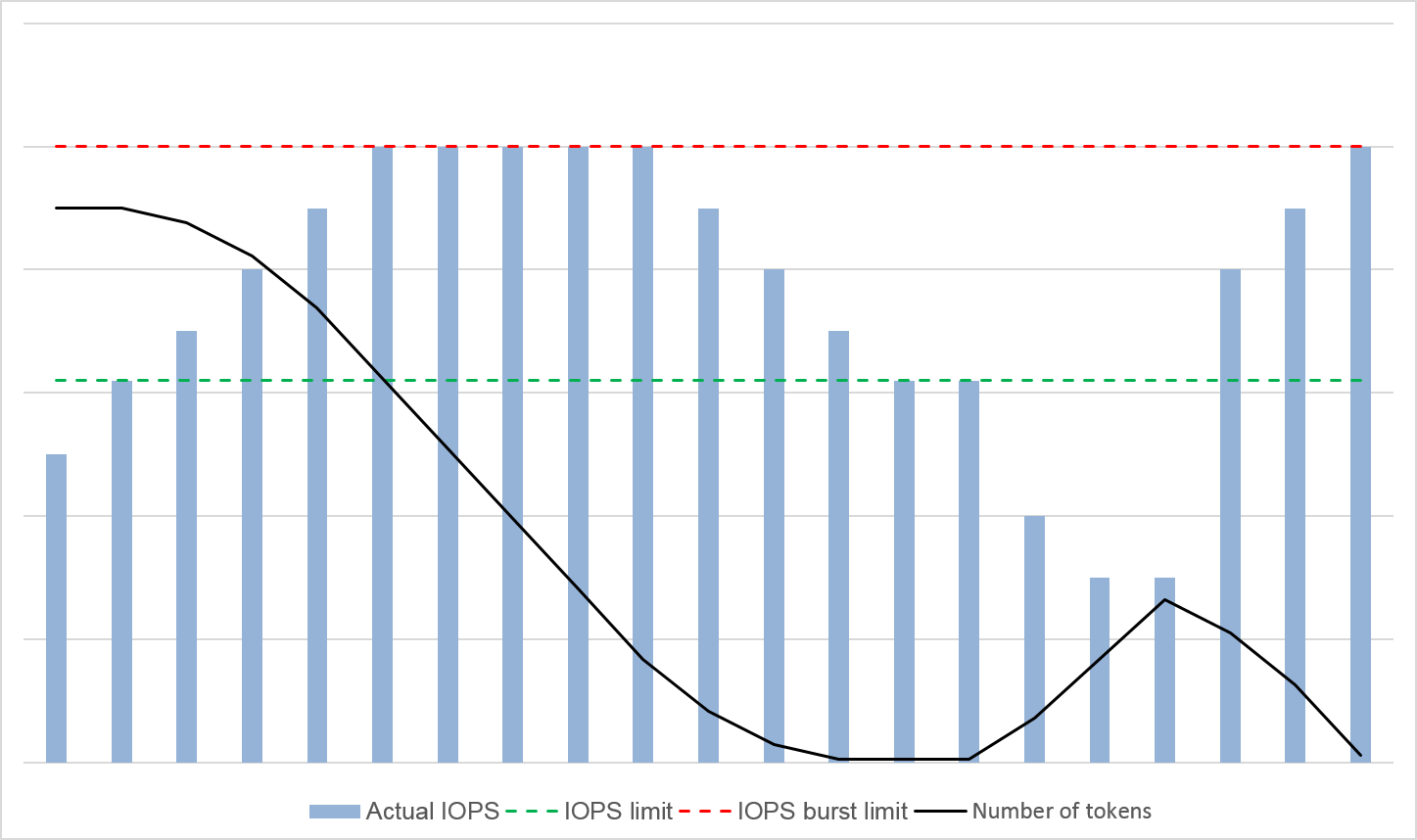
Figure 1 shows the token consumption and reservation principles. The blue bars indicate the disk IOPS usage, the green dashed line represents the maximum IOPS, the red dashed line indicates the IOPS burst limit, and the black curve indicates the changes of the number of tokens.
- As long as there are tokens, the disk IOPS can exceed 6,800 and can burst up to 16,000, the IOPS burst limit.
- When there are no more tokens, the disk loses the burst capability, and the disk IOPS can reach up to 6,800.
- Anytime the disk IOPS is less than 6,800, the number of tokens starts to increase, and the disk regains the burst capability.
Figure 1 Burst capability diagram
Instance QoS
ECSs support instance-level storage I/O isolation. Each instance (ECS) enjoys their storage bandwidth and IOPS exclusively. This prevents resource contention between the ECSs during peak hours.
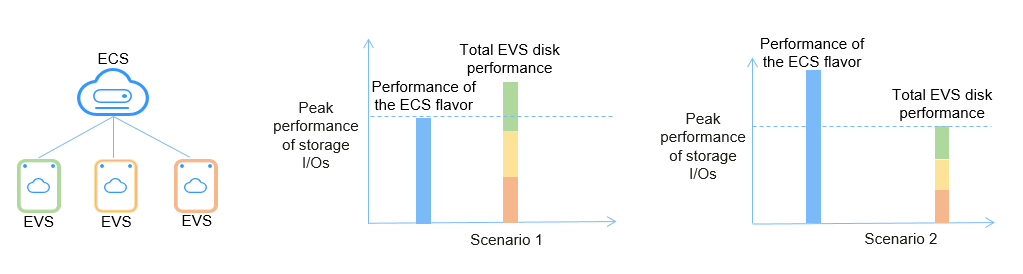
Scenario 1: If the total performance of EVS disks on an instance exceeds the storage I/O capabilities of the instance flavor, the instance flavor's storage I/O capabilities are used. If the instance has multiple EVS disks, the storage I/O performance is dynamically allocated to the EVS disks based on a contention mechanism.
Example 1: A customer purchases an ECS that offers up to 2,688 MiB/s (21 Gbit/s) storage bandwidth. The ECS has ten 1,000 GiB Ultra-high I/O EVS disks, each of which offers a maximum bandwidth of 350 MiB/s. So, the total maximum bandwidth of the ten disks is 3,500 MiB/s, which already exceeds the maximum storage bandwidth of the instance (2,688 MiB/s). In this case, the 3,500 MiB/s bandwidth cannot be reached.
Example 2: A customer purchases an ECS that offers up to 130,000 IOPS. The ECS has three 8 TiB Ultra-high I/O EVS disks, each of which offers a maximum IOPS of 50,000. So, the total maximum IOPS of the three disks is 150,000, which already exceeds the maximum IOPS of the instance (130,000). In this case, the maximum storage IOPS of the disks can only reach 130,000, not 150,000.
Scenario 2: If the total performance of EVS disks on an instance is less than the storage I/O capabilities of the instance flavor, the disks' storage performance is used.
Example: A customer purchases an ECS that offers up to 2,688 MiB/s (21 Gbit/s) storage bandwidth. The ECS has three 100 GiB Ultra-high I/O EVS disks, each of which offers a maximum bandwidth of 170 MiB/s. So, the total maximum bandwidth of the three disks is 510 MiB/s, which is less than the maximum storage bandwidth of the instance (2,688 MiB/s). In this case, the 2,688 MiB/s bandwidth cannot be reached.
Performance Testing
For details about how to test the EVS disk performance, see How Do I Test My Disk Performance?