DCS for Redis provides Proxy Cluster instances, which use Linux Virtual Server (LVS) and proxies to achieve high availability. Proxy Cluster instances have the following features:
- The client is decoupled from the cloud service.
- They support millions of concurrent requests, equivalent to Redis Cluster instances.
- A wide range of memory specifications adapt to different scenarios.
- A Proxy Cluster instance can be connected in the same way that a single-node or master/standby instance is connected, without any special settings on the client. You can use the IP address or domain name of the instance, and do not need to know or use the proxy or shard addresses.
- The major version of a DCS Redis 4.0 or later instance cannot be upgraded. For example, a Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 4.0 instance cannot be upgraded to a Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 5.0 one. If your service requires the features of higher Redis versions, create a DCS Redis instance of a higher version and then migrate data from the old instance to the new one.
Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 3.0 Instances
Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 3.0 instances are compatible with codis. The specifications range from 64 GB to 1024 GB, meeting requirements for millions of concurrent connections and massive data cache. Distributed data storage and access is implemented by DCS, without requiring development or maintenance.
Each Proxy Cluster instance consists of load balancers, proxies, cluster managers, and shards.
Total Memory | Proxies | Shards |
|---|---|---|
64 GB | 3 | 8 |
128 GB | 6 | 16 |
256 GB | 8 | 32 |
Figure 1 Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 3.0 instance architecture
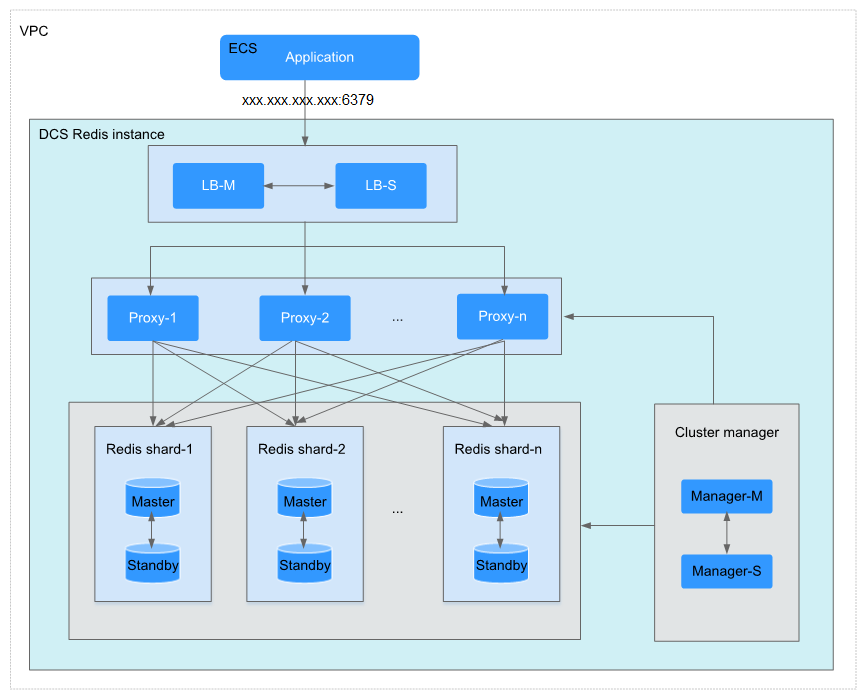
Architecture description:
- VPC
All server nodes of the cluster instance run in the same VPC.
NoteFor intra-VPC access, the client and the instance must be in the same VPC. For a Redis 3.0 instance, security group rules are required.
A DCS Redis 3.0 instance can be accessed from a VPC or over public networks. The client can be deployed outside the VPC and access the instance through the elastic IP address (EIP) bound to the instance. Public access is not supported by DCS Redis 4.0, 5.0, and 6.0 instances.
For details, see Security Group ConfigurationsPublic Access to a DCS Redis 3.0 Instance.
- Application
The client used to access the instance.
DCS Redis instances can be accessed through open-source clients. For details about accessing DCS instances, see Accessing an Instance.
- LB-M/LB-S
The load balancers, which are deployed in master/standby HA mode. The connection addresses (IP address:Port) of the cluster DCS Redis instance are the addresses of the load balancers.
- Proxy
The proxy server used to achieve high availability and process high-concurrency client requests.
You can connect to a Proxy Cluster instance at the IP addresses of its proxies.
- Redis shard
A shard of the cluster.
Each shard consists of a pair of master/standby nodes. If the master node becomes faulty, the standby node automatically takes over cluster services.
If both the master and standby nodes of a shard are faulty, the cluster can still provide services but the data on the faulty shard is inaccessible.
- Cluster manager
The cluster configuration managers, which store configurations and partitioning policies of the cluster. You cannot modify the information about the configuration managers.
Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 Instances
Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instances are built based on open-source Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 and compatible with open source codis. They provide multiple large-capacity specifications ranging from 4 GB to 1024 GB and .
Table 2 lists the number of shards corresponding to different specifications. You can customize the shard size when creating an instance. Currently, the number of shards and replicas cannot be customized. By default, each shard has two replicas.
Memory per shard = Instance specification/Number of shards. For example, if a 48 GB instance has 6 shards, the size of each shard is 48 GB/6 = 8 GB.
Total Memory | Proxies | Shards | Memory per Shard (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
4 GB | 3 | 3 | 1.33 |
8 GB | 3 | 3 | 2.67 |
16 GB | 3 | 3 | 5.33 |
24 GB | 3 | 3 | 8 |
32 GB | 3 | 3 | 10.67 |
48 GB | 6 | 6 | 8 |
64 GB | 8 | 8 | 8 |
96 GB | 12 | 12 | 8 |
128 GB | 16 | 16 | 8 |
192 GB | 24 | 24 | 8 |
256 GB | 32 | 32 | 8 |
384 GB | 48 | 48 | 8 |
512 GB | 64 | 64 | 8 |
768 GB | 96 | 96 | 8 |
1024 GB | 128 | 128 | 8 |
Figure 2 Architecture of a Proxy Cluster DCS Redis 4.0/5.0/6.0 instance
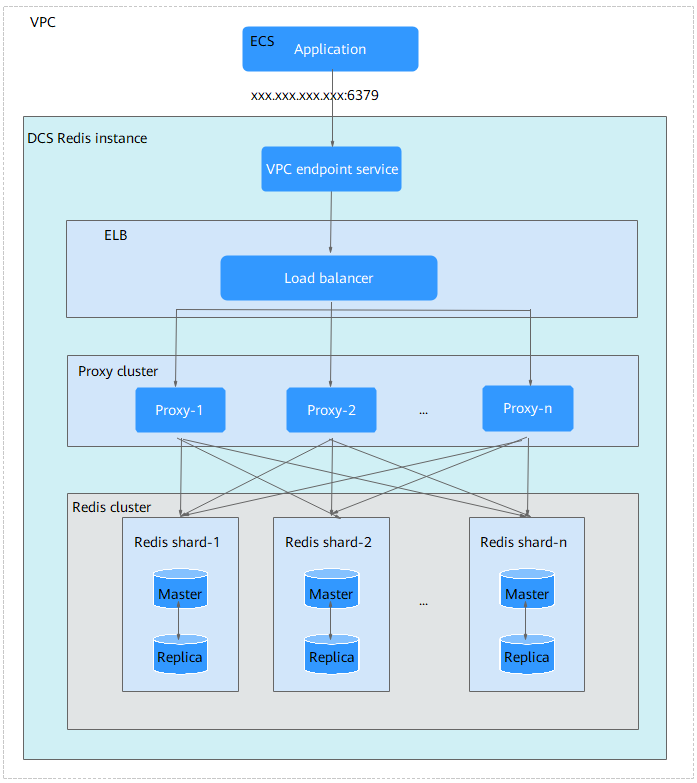
Architecture description:
- VPC
All server nodes of the cluster instance run in the same VPC.
NoteThe client and the cluster instance must be in the same VPC, and the instance whitelist must allow access from the client IP address.
- Application
The client used to access the instance.
DCS Redis instances can be accessed through open-source clients. For details about accessing DCS instances in different languages, see Accessing an Instance.
- VPC endpoint service
You can configure your DCS Redis instance as a VPC endpoint service and access the instance at the VPC endpoint service address.
The IP address of the Proxy Cluster DCS Redis instance is the address of the VPC endpoint service.
- ELB
The load balancers, which are deployed in cluster HA mode.
- Proxy
The proxy server used to achieve high availability and process high-concurrency client requests.
You cannot connect to a Proxy Cluster instance at the IP addresses of its proxies.
- Redis cluster
A shard of the cluster.
By default, each shard is a master/standby dual-replica Redis instance. When the master instance is faulty, the standby node will be switched to the master one after 15 to 30 seconds. Access to the shard will fail until the switchover is complete.
If both the master and standby nodes of a shard are faulty, the cluster can still provide services but the data on the faulty shard is inaccessible.