With CSS, you can use in-house developed Logstash to ingest data into OpenSearch for efficient search and exploration. Supported data formats include JSON and CSV.
Logstash is an open-source, server-side data processing pipeline that ingests data from multiple sources simultaneously, processes and transforms the data, and then sends it to OpenSearch. For more information about Logstash, visit https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/getting-started-with-logstash.html
Depending on where Logstash is deployed, there are two data ingestion scenarios:
- Ingesting Data When Logstash Is Deployed on an External Network
- Ingesting Data When Logstash Is Deployed Using an ECS
Prerequisites
- To facilitate operations, you are advised to deploy Logstash on a host that runs a Linux operating system (OS).
- Logstash must use an OSS version that is consistent with that of the CSS cluster. To download Logstash, go to https://www.elastic.co/downloads/logstash-oss.
- The JDK must be installed before Logstash is installed. In a Linux OS, you can run the yum -y install java-1.8.0 command to install JDK 1.8.0. In a Windows OS, you can download the required JDK version from the official website of JDK, and install it by following the installation guide.
- After installing Logstash, perform the steps below to ingest data. For details about how to install Logstash, visit the following website: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/installing-logstash.html
- In the Ingesting Data When Logstash Is Deployed Using an ECS scenario, ensure that the ECS and the destination Elasticsearch cluster are in the same VPC.
Ingesting Data When Logstash Is Deployed on an External Network
Figure 1 illustrates the data ingestion process when Logstash is deployed on an external network.
Figure 1 Data ingestion process when Logstash is deployed on an external network
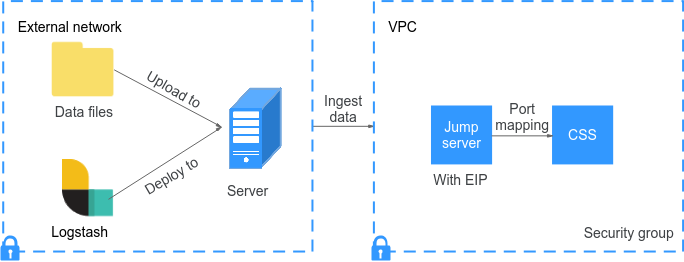
- Create a jump host and configure it as follows:
- The jump host is an ECS running a Linux OS and an EIP has been associated with it.
- The jump host resides in the same VPC as the destination cluster.
- SSH local port forwarding is configured for the jump host to forward requests from a chosen local port to port 9200 on one node of the CSS cluster.
- Refer to SSH documentation for the local port forwarding configuration.
- Use PuTTY to log in to the jump host via its EIP.
- Run the following command to configure port mapping to forward requests sent to the opened port on the jump host to the destination cluster:ssh -g -L <Local port of the jump host:Private network address and port number of a node> -N -f root@<Private IP address of the jump host>
- In the preceding command, <Local port of the jump host> refers to the jump host port configured in 1.
- In the preceding command, <Private network address and port number of a node> refers to the private network address and port number of a node in the cluster. If the node is faulty, command execution will fail. If the cluster contains multiple nodes, you can replace the value of <private network address and port number of a node> with the private network address and port number of any available node in the cluster. If the cluster contains only one node, restore the node and execute the command again.
- Replace <Private IP address of the jump host> in the preceding command with the IP address (with Private IP) of the created jump host in the IP Address column in the ECS list on the ECS management console.
For example, port 9200 on the jump host is accessible from the public network, the private network address and port number of the node are 192.168.0.81 and 9200, respectively, and the private IP address of the jump host is 192.168.0.227. You need to run the following command to perform port mapping:
ssh -g -L 9200:192.168.0.81:9200 -N -f root@192.168.0.227 - Log in to the server where Logstash is deployed and store the files to be ingested on this server.
For example, data file access_20181029_log needs to be ingested, the file storage path is /tmp/access_log/ (create the access_log folder if it does not already exist), and the data file contains the following data:
| All | Heap used for segments | | 18.6403 | MB || All | Heap used for doc values | | 0.119289 | MB || All | Heap used for terms | | 17.4095 | MB || All | Heap used for norms | | 0.0767822 | MB || All | Heap used for points | | 0.225246 | MB || All | Heap used for stored fields | | 0.809448 | MB || All | Segment count | | 101 | || All | Min Throughput | index-append | 66232.6 | docs/s || All | Median Throughput | index-append | 66735.3 | docs/s || All | Max Throughput | index-append | 67745.6 | docs/s || All | 50th percentile latency | index-append | 510.261 | ms | - On the server where Logstash is deployed, run the following command to create configuration file logstash-simple.conf in the Logstash installation directory:cd /<Logstash installation directory>/vi logstash-simple.conf
- Enter the following content in logstash-simple.conf:input {Location of data}filter {Related data processing}output {elasticsearch {hosts => "<EIP of the jump host>:<Number of the port assigned external network access permissions on the jump host>"}}
- The input parameter indicates the data source. Set this parameter based on the actual conditions. For details about the input parameter and its usage, visit the following website: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/input-plugins.html
- The filter parameter specifies the data processing method. For example, extract and process logs to convert unstructured information into structured information. For details about the filter parameter and its usage, visit the following website: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/filter-plugins.html
- The output parameter indicates the destination address of the data. For details about the output parameter and its usage, visit https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/output-plugins.html. Replace <EIP address of the jump host> with the IP address (with EIP) of the created jump host in the IP Address column in the ECS list on the ECS management console. <The port accessible from the public network on the jump host> is the port number obtained in 1, for example, 9200.
Consider the data files in the /tmp/access_log/ path mentioned in 4 as an example. Assume that data ingestion starts from the first row of the file, the filtering condition is left unspecified (indicating no data processing operations are performed), the public IP address and port number of the jump host are 192.168.0.227 and 9200, respectively, and the name of the destination index is myindex. Edit the configuration file as follows, and enter :wq to save the change and exit.
input {file{path => "/tmp/access_log/*"start_position => "beginning"}}filter {}output {elasticsearch {hosts => "192.168.0.227:9200"index => "myindex"}}NoteIf a license error is reported, set ilm_enabled to false to try and rectify the error.
If the cluster has the security mode enabled, you need to download a certificate first.
- Obtaining the Security Certificate.
- Store the downloaded certificate to the server where Logstash is deployed.
- Modify the logstash-simple.conf configuration file.
Consider the data files in the /tmp/access_log/ path mentioned in 4 as an example. Assume that data ingestion starts from the first row of the file, the filtering condition is left unspecified (indicating no data processing operations are performed), the public IP address and port number of the jump host are 192.168.0.227 and 9200, respectively, The name of the index for importing data is myindex, and the certificate is stored in /logstash/config/CloudSearchService.cer. Edit the configuration file as follows, and enter :wq to save the change and exit.
input{file {path => "/tmp/access_log/*"start_position => "beginning"}}filter {}output{elasticsearch{hosts => ["https://192.168.0.227:9200"]index => "myindex"user => "admin" # Username for accessing the security-mode clusterpassword => "******" # Password for accessing the security-mode clustercacert => "/logstash/config/CloudSearchService.cer"manager_template => falseilm_enabled => falsessl => truessl_certificate_verification => false}}
- Run the following command to import the data collected by Logstash to the cluster:./bin/logstash -f logstash-simple.conf
This command must be executed in the directory where the logstash-simple.conf file is located. For example, if the logstash-simple.conf file is stored in /root/logstash-7.1.1/, navigate to this directory before executing the command.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, find the destination cluster, and click Dashboards in the Operation column to log in to OpenSearch Dashboards.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
- On the Console page of OpenSearch Dashboards, search for the ingested data.
Run the following command to search for data. Check the search results. If they are consistent with the ingested data, data ingestion has been successful.
GET myindex/_search
Ingesting Data When Logstash Is Deployed Using an ECS
Figure 2 illustrates the data ingestion process when Logstash is deployed on an ECS that resides in the same VPC as the destination cluster.
Figure 2 Data ingestion process when Logstash is deployed on an ECS
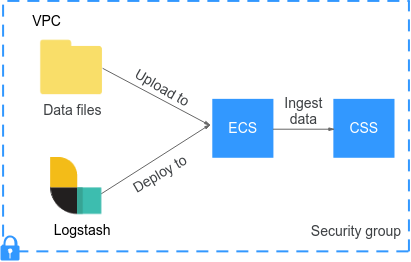
- Make sure the ECS where Logstash is deployed and the destination cluster reside in the same VPC, port 9200 is opened in the ECS's security group to allow external network access, and an EIP has been associated with the ECS.
- If there are multiple servers in a VPC, you only need to associate an EIP with one of these servers. Switch to the node where Logstash is deployed from the node with which the EIP is associated.
- If a private line or VPN is available, there is no need for an EIP.
- Use PuTTY to log in to the ECS.
For example, the file access_20181029_log is stored in the /tmp/access_log/ path of the ECS, and the file contains the following data:
| All | Heap used for segments | | 18.6403 | MB || All | Heap used for doc values | | 0.119289 | MB || All | Heap used for terms | | 17.4095 | MB || All | Heap used for norms | | 0.0767822 | MB || All | Heap used for points | | 0.225246 | MB || All | Heap used for stored fields | | 0.809448 | MB || All | Segment count | | 101 | || All | Min Throughput | index-append | 66232.6 | docs/s || All | Median Throughput | index-append | 66735.3 | docs/s || All | Max Throughput | index-append | 67745.6 | docs/s || All | 50th percentile latency | index-append | 510.261 | ms | - Run the following command to create configuration file logstash-simple.conf in the Logstash installation directory:cd /<Logstash installation directory>/vi logstash-simple.conf
Enter the following content in logstash-simple.conf:
input {Location of data}filter {Related data processing}output {elasticsearch{hosts => "<Private network address and port number of the node>"}}- The input parameter indicates the data source. Set this parameter based on the actual conditions. For details about the input parameter and its usage, visit the following website: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/input-plugins.html
- The filter parameter specifies the data processing method. For example, extract and process logs to convert unstructured information into structured information. For details about the filter parameter and its usage, visit the following website: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/filter-plugins.html
- The output parameter indicates the destination address of the data. For details about the output parameter and its usage, visit https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/output-plugins.html. <private network address and port number of a node> refers to the private network address and port number of a node in the cluster.
If the cluster contains multiple nodes, you are advised to replace the value of <Private network address and port number of a node> with the private network addresses and port numbers of all nodes in the cluster to prevent node faults. Use commas (,) to separate the nodes' private network addresses and port numbers. The following is an example:
hosts => ["192.168.0.81:9200","192.168.0.24:9200"]If the cluster contains only one node, the format is as follows:
hosts => "192.168.0.81:9200"
Consider the data files in the /tmp/access_log/ path mentioned in 2 as an example. Assume that data ingestion starts from the first row of the file, the filtering condition is left unspecified (indicating no data processing operations are performed), the private network address and port number of the node in the destination cluster are 192.168.0.81 and 9200, respectively, and the name of the destination index is myindex. Edit the configuration file as follows, and enter :wq to save the change and exit.
input {file{path => "/tmp/access_log/*"start_position => "beginning"}}filter {}output {elasticsearch {hosts => "192.168.0.81:9200"index => "myindex"}}If the cluster has the security mode enabled, you need to download a certificate first.
- Obtaining the Security Certificate.
- Store the downloaded certificate to the server where Logstash is deployed.
- Modify the logstash-simple.conf configuration file.
Consider the data files in the /tmp/access_log/ path mentioned in step 2 as an example. Assume that data ingestion starts from the first row of the file, the filtering condition is left unspecified (indicating no data processing operations are performed), the public IP address and port number of the jump host are 192.168.0.227 and 9200, respectively, The name of the index for importing data is myindex, and the certificate is stored in /logstash/config/CloudSearchService.cer. Edit the configuration file as follows, and enter :wq to save the change and exit.
input{file {path => "/tmp/access_log/*"start_position => "beginning"}}filter {}output{elasticsearch{hosts => ["https://192.168.0.227:9200"]index => "myindex"user => "admin" # Username for accessing the security-mode clusterpassword => "******" # Password for accessing the security-mode clustercacert => "/logstash/config/CloudSearchService.cer"manager_template => falseilm_enabled => falsessl => truessl_certificate_verification => false}}
- Run the following command to import the ECS data collected by Logstash to the cluster:./bin/logstash -f logstash-simple.conf
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and click Dashboards in the Operation column to log in to OpenSearch Dashboards.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
- On the Console page of OpenSearch Dashboards, search for the ingested data.
Run the following command to search for data. Check the search results. If they are consistent with the ingested data, data ingestion has been successful.
GET myindex/_search
Obtaining the Security Certificate
To access a security-mode OpenSearch cluster that uses HTTPS, a security certificate must be loaded. To obtain this security certificate (CloudSearchService.cer), follow these steps:
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Click the Overview tab. In the Configuration area, click Download Certificate next to HTTPS Access.