In an Elasticsearch cluster, switching between hot and cold data storage means to allocate data to nodes of different performance standards based on data temperature (that is, how often data is accessed). The goal is to achieve optimal storage costs and query performance.
- Hot data: frequently accessed data, low latency required, stored using high-performance hardware (such as SSDs) to ensure fast write and query performance.
- Cold data: rarely accessed data, cost-optimized storage (such as HDDs).
If your cluster stores data used for different purposes, such as real-time analytics, log analytics, and monitoring data archives, you can switch between hot and cold storage for specified indexes to balance performance and costs.
How the Feature Works
Figure 1 How cold/hot storage switchover works
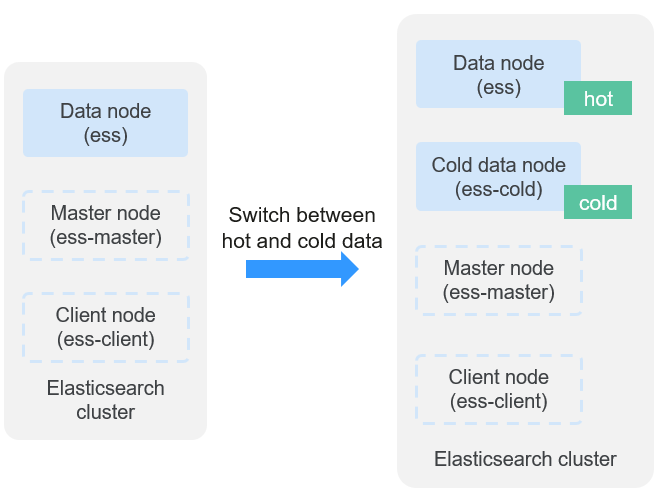
The key is to allocate index data storage by node labels and index allocation policies.
- Node labels:
- Data node (hot): Stores real-time data by default and supports high-concurrency read/write requests.
- Cold data node (cold): Stores historical data. Cold data nodes use less expensive hardware and deliver lower query performance than data nodes.
- Data allocation:
You can configure an index template or directly configure specific indexes to allocate data to data nodes or cold data nodes.
Procedure: Enable cold data nodes when creating a cluster, and configure an index template or specific index settings to allocate index data storage. The cluster automatically allocates data based on your settings.
Constraints
- You cannot add cold data nodes to existing clusters that did not have such nodes enabled upon cluster creation.
- In comparison with data nodes, cold data nodes deliver lower query performance. Determine which type of node to use based on service needs.
Switching Over Between Hot and Cold Storage
- Check whether cold data nodes are enabled in the target cluster.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Elasticsearch.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- On the Overview tab, check whether the Node Information area contains cold data node information.
Figure 2 Cold data node information
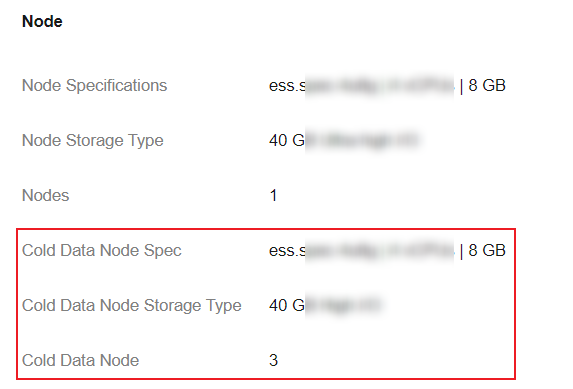
- If there is information about cold data nodes, the cluster has cold data nodes. Go to the next step.
- Otherwise, the cluster does not have cold data nodes, in which case, you cannot switch between cold and hot data storage.
- Log in to the Kibana console.
- On the cluster information page, click Kibana in the upper-right corner to log in to Kibana.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
The left part of the console is the command input box, and the triangle icon in its upper-right corner is the execution button. The right part shows the execution result.
- On the Kibana page, configure index allocation policies.
You can configure an index template or directly configure specific indexes to allocate data to data nodes or cold data nodes.
- Configuring an index template
Configure an index template to allocate indexes to cold or hot data nodes. For example, run the following command to store indexes whose name starts with myindex to cold data nodes. (The command varies slightly depending on the Elasticsearch version.)
- For Elasticsearch 6.x or later:PUT _template/test{"order": 1,"index_patterns": "myindex*","settings": {"refresh_interval": "30s","number_of_shards": "3","number_of_replicas": "0","routing.allocation.require.box_type": "cold"}}
- For Elasticsearch earlier than 6.x:PUT _template/test{"order": 1,"template": "myindex*","settings": {"index": {"refresh_interval": "30s","number_of_shards": "3","number_of_replicas": "0","routing.allocation.require.box_type": "cold"}}}
Parameter description:
- template or index_patterns: rule for matching index names (for example, myindex*).
- box_type: node type for matching indexes. cold indicates cold data nodes, and hot indicates regular data nodes.
- For Elasticsearch 6.x or later:
- Configuring specific indexes
To change the node type for an existing index, run the following command:
PUT myindex/_settings{"index.routing.allocation.require.box_type": "cold"}Parameter description:
- myindex: index name.
- box_type: node type for matching indexes. cold indicates cold data nodes, and hot indicates regular data nodes.
- Configuring an index template
- Verify the switchover between hot and cold storage.
Run the following command to check the distribution of index shards:
GET _cat/shards/myindex?vWhen the data volume is large, the switchover may take a long time. There may be an intermediate state where the data of an index resides on both cold data nodes and data nodes.
As shown in the following figure, all shards of the myindex index are stored on the cold data node css-e668-ess-cold-esn-1-1.
index shard prirep state docs store ip nodemyindex 1 p STARTED 14085446 17.8gb 192.168.91.188 css-e668-ess-coldcold-esn-1-1myindex 2 p STARTED 14094005 17.9gb 192.168.91.188 css-e668-ess-coldcold-esn-1-1myindex 0 p STARTED 14094742 17.8gb 192.168.91.188 css-e668-ess-coldcold-esn-1-1 - Roll back the cold-hot switchover configuration.
To cancel the cold-hot switchover configuration, run the following command:
PUT myindex/_settings{"index.routing.allocation.require.box_type": null}After the rollback, index data will be evenly and randomly allocated to both cold data nodes and data nodes.
Related Operations
- You can scale cold data nodes by adding or reducing nodes or their storage capacity. For details, see Scaling an Elasticsearch Cluster.
- If your cluster does not have cold data nodes but you wish to cut storage costs, you can try using decoupled storage and compute. For details, see Configuring Decoupled Storage and Compute for an Elasticsearch Cluster.