Introduction
CoreDNS is a DNS server that provides domain name resolution for Kubernetes clusters through chained plugins.
CoreDNS is an open-source software and has been a part of CNCF. It provides a means for cloud services to discover each other in cloud native deployments. Each of the plugins chained by CoreDNS provides a particular DNS function. You can integrate CoreDNS with only the plugins you need to make it fast, efficient, and flexible. When used in a Kubernetes cluster, CoreDNS can automatically discover services in the cluster and provide domain name resolution for these services. By working with DNS servers, CoreDNS can resolve external domain names for workloads in a cluster.
This add-on is installed by default during cluster creation.
Kubernetes backs CoreDNS as the official default DNS for all clusters going forward.
CoreDNS official website: https://coredns.io/
Open-source community: https://github.com/coredns/coredns
For details, see DNS.
Notes and Constraints
To run CoreDNS properly or upgrade CoreDNS in a cluster, ensure the number of available nodes in the cluster is greater than or equal to the number of CoreDNS instances and all CoreDNS instances are running. Otherwise, the add-on will malfunction or the upgrade will fail.
Installing the Add-on
This add-on has been installed by default. If it is uninstalled due to some reasons, you can reinstall it by performing the following steps:
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons. Locate CoreDNS on the right and click Install.
- On the Install Add-on page, configure the specifications as needed.
- If you selected Preset, you can choose between Small qps, Medium qps, or Large qps as needed. The system will automatically set the number of add-on pods and resource quotas according to the preset specifications. You can see the configurations on the console.
The small one can handle up to 2500 external and 10,000 internal domain names QPS. The medium specification can handle up to 5000 external and 20,000 internal domain names QPS. The large specification can handle up to 10,000 external and 40,000 internal domain names QPS.
- If you selected Custom, you can adjust the number of pods and resource quotas as needed. QPS of the CoreDNS add-on is positively correlated with the CPU consumption. If the number of nodes or containers in the cluster grows, the CoreDNS pods will bear heavier workloads. It is recommended that you adjust the number of the CoreDNS pods and their CPU and memory quotas based on the cluster scale. For details, see Table 1.
Table 1 Recommended CoreDNS quotas Nodes
Recommended QPS
Pods
Requested vCPUs
vCPU Limit
Requested Memory
Memory Limit
50
2500
2
500m
500m
512 MiB
512 MiB
200
5000
2
1000m
1000m
1024 MiB
1024 MiB
1000
10000
2
2000m
2000m
2048 MiB
2048 MiB
2000
20000
4
2000m
2000m
2048 MiB
2048 MiB
- If you selected Preset, you can choose between Small qps, Medium qps, or Large qps as needed. The system will automatically set the number of add-on pods and resource quotas according to the preset specifications. You can see the configurations on the console.
- Configure the add-on parameters.
Table 2 Add-on parameters Parameter
Description
Stub Domain
A domain name server for a custom domain name. The format is a key-value pair. The key is a domain name suffix, and the value is one or more DNS IP addresses, for example, acme.local -- 1.2.3.4,6.7.8.9.
For details, see Configuring the Stub Domain for CoreDNS.
CAUTION:Uppercase letters are not allowed in custom domain names.
Extended Parameter Settings
- parameterSyncStrategy: indicates whether to configure consistency check when the add-on is upgraded.
- ensureConsistent: indicates that the configuration consistency check is enabled. If the delivered configuration differs from the current effective configuration, the current effective configuration will be replaced. However, if the delivered configuration is the same as the current effective configuration, the current effective configuration will be preserved. The ensureConsistent parameter ensures the configuration consistency. If a ConfigMap is modified manually, the add-on cannot be upgraded. In such cases, you will need to use the force or inherit policy to upgrade the add-on.
- force: indicates that the configuration consistency check is ignored during an upgrade. The configuration provided during the add-on upgrade will be used, so it is important to make sure that it matches the current effective configuration. After the add-on is upgraded, you need to restore the value of parameterSyncStrategy to ensureConsistent to enable the configuration consistency check again.
- inherit: If the configuration provided during the add-on upgrade differs from the current effective configuration, the current effective configuration will be used instead. After the add-on is upgraded, you need to restore the value of parameterSyncStrategy to ensureConsistent to enable the configuration consistency check again.CAUTION:
After the automatic inheritance of parameter settings (parameterSyncStrategy=inherit) is enabled, stub domain settings will be cleared and merged into the extended parameter settings. The original stub domain settings remain unchanged and can still be viewed under Extended Parameter Settings.
- servers: nameservers, which are available in CoreDNS v1.23.1 and later versions. You can customize nameservers. For details, see dns-custom-nameservers.
plugins indicates the configuration of each component in CoreDNS. Retain the default settings typically to prevent CoreDNS from being unavailable due to configuration errors. Each plugin component contains name, parameters (optional), and configBlock (optional). The format of the generated Corefile is as follows:
$name $parameters {$configBlock} - upstream_nameservers: specifies the IP address of the upstream DNS server.
Example:
{"annotations": {},"parameterSyncStrategy": "ensureConsistent","servers": [{"plugins": [{"name": "bind","parameters": "{$POD_IP}"},{"name": "cache","parameters": 30},{"name": "errors"},{"name": "health","parameters": "{$POD_IP}:8080"},{"name": "ready","parameters": "{$POD_IP}:8081"},{"configBlock": "pods insecure\nfallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa","name": "kubernetes","parameters": "cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa"},{"name": "loadbalance","parameters": "round_robin"},{"name": "prometheus","parameters": "{$POD_IP}:9153"},{"configBlock": "policy random","name": "forward","parameters": ". /etc/resolv.conf"},{"name": "reload"}],"port": 5353,"zones": [{"zone": "."}]}],"upstream_nameservers": ["8.8.8.8", "8.8.4.4"]}Table 3 Default CoreDNS configurations Plugin Name
Type
Description
bind
Default configuration
Host IP address listened by CoreDNS. Retain the default value {$POD_IP}. For details, see bind.
cache
Default configuration
Enables DNS cache. For details, see cache.
If the add-on version is 1.25.10 or later, the servfail cache can be disabled. To disable the servfail cache, set configBlock to servfail 0. Otherwise, the unit of the servfail cache is second and cannot be omitted.
errors
Default configuration
Errors are logged to stdout. For details, see errors.
health
Default configuration
Health check for CoreDNS. {$POD_IP}:8080 is listened to. Retain the default setting. Otherwise, the CoreDNS health check will fail and the add-on will restart repeatedly. For details, see health.
ready
Default configuration
Whether the backend server is ready to receive traffic. {$POD_IP}:8081 is listened to. If the backend server is not ready, CoreDNS will suspend DNS resolution until the backend server is ready. For details, see ready.
kubernetes
Default configuration
CoreDNS Kubernetes plugin, which provides the service parsing capability in a cluster. For details, see kubernetes.
loadbalance
Default configuration
Round-robin DNS load balancer that randomizes the order of A, AAAA, and MX records in an answer. For details, see loadbalance.
prometheus
Default configuration
API for obtaining CoreDNS metrics. {$POD_IP}:9153 is listened to by default. Retain the default setting. Otherwise, Prometheus cannot collect CoreDNS metrics. For details, see Prometheus.
forward
Default configuration
Forwards any queries that are not within the cluster domain of Kubernetes to predefined resolvers (/etc/resolv.conf). For details, see forward.
reload
Default configuration
Automatically reloads modified Corefiles. After you modify a ConfigMap, wait for two minutes for the modification to take effect. For details, see reload.
log
Extended configuration
Enables CoreDNS logging. For details, see log.
The following is an example:
{"name": "log"}template
Extended configuration
A quick response template, where AAAA indicates an IPv6 request. If NXDOMAIN is returned in an rcode response, no IPv6 resolution result is returned. For details, see template.
The following is an example:
{"configBlock": "rcode NXDOMAIN","name": "template","parameters": "ANY AAAA"} - parameterSyncStrategy: indicates whether to configure consistency check when the add-on is upgraded.
- Configure deployment policies for the add-on pods.Note
- Scheduling policies do not take effect on add-on pods of the DaemonSet type.
- When configuring multi-AZ deployment or node affinity, ensure that there are nodes meeting the scheduling policy and that resources are sufficient in the cluster. Otherwise, the add-on cannot run.
Table 4 Configurations for add-on scheduling Parameter
Description
Multi-AZ Deployment
- Preferred: Deployment pods of the add-on will be preferentially scheduled to nodes in different AZs. If all the nodes in the cluster are deployed in the same AZ, the pods will be scheduled to different nodes in that AZ.
- Equivalent mode: Deployment pods of the add-on are evenly scheduled to the nodes in the cluster in each AZ. If a new AZ is added, you are advised to increase add-on pods for cross-AZ HA deployment. With the Equivalent multi-AZ deployment, the difference between the number of add-on pods in different AZs will be less than or equal to 1. If resources in one of the AZs are insufficient, pods cannot be scheduled to that AZ.
- Forcible: Deployment pods of the add-on are forcibly scheduled to nodes in different AZs. There can be at most one pod in each AZ. If nodes in a cluster are not in different AZs, some add-on pods cannot run properly. If a node is faulty, add-on pods on it may fail to be migrated.
Node Affinity
- Not configured: Node affinity is disabled for the add-on.
- Specify node: Specify the nodes where the add-on is deployed. If you do not specify the nodes, the add-on will be randomly scheduled based on the default cluster scheduling policy.
- Specify node pool: Specify the node pool where the add-on is deployed. If you do not specify the node pools, the add-on will be randomly scheduled based on the default cluster scheduling policy.
- Customize affinity: Enter the labels of the nodes where the add-on is to be deployed for more flexible scheduling policies. If you do not specify node labels, the add-on will be randomly scheduled based on the default cluster scheduling policy.
If multiple custom affinity policies are configured, ensure that there are nodes that meet all the affinity policies in the cluster. Otherwise, the add-on cannot run.
Toleration
Using both taints and tolerations allows (not forcibly) the add-on Deployment to be scheduled to a node with the matching taints, and controls the Deployment eviction policies after the node where the Deployment is located is tainted.
The add-on adds the default tolerance policy for the node.kubernetes.io/not-ready and node.kubernetes.io/unreachable taints, respectively. The tolerance time window is 60s.
For details, see Configuring Tolerance Policies.
- Click Install.
Components
Component | Description | Resource Type |
|---|---|---|
CoreDNS | DNS server for clusters | Deployment |
Configure CoreDNS Using Corefile
If you install the CoreDNS add-on, the Corefile view configuration is not available. This configuration is supported only when you are editing or upgrading the add-on.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons. Locate CoreDNS on the right and click Edit.
- In the Parameters area, select whether to switch to the Corefile View (supported by add-on 1.30.3 and later versions).
Once the function is enabled, the ConfigMap of CoreDNS in the kube-system namespace will be directly configured in the Corefile format. Any existing stub domain configurations and parameters such as parameterSyncStrategy, servers, and upstream_nameservers in the advanced configuration will no longer be in effect. It is important to verify that the Corefile configuration is accurate.
For description of the Corefile format, see Configuration.
Note- Once the Corefile view is disabled, the ConfigMap of CoreDNS will continue to be configured based on to the stub domain configurations and parameters such as parameterSyncStrategy, servers, and upstream_nameservers in the advanced configuration. It is important to verify that the configuration is correct during the function switchover.
- Once the Corefile view is enabled, the add-on can be upgraded. However, if the Corefile view is disabled again, the add-on upgrade will override the current configurations. To complete the upgrade, parameterSyncStrategy must be set to either force or inherit.
- Once the Corefile configuration is modified, simply wait for CoreDNS' reload mechanism to automatically update the configuration. This typically takes about 10 seconds for the changes to take effect.
- After editing the Corefile, click OK.
How Does Domain Name Resolution Work in Kubernetes?
DNS policies can be configured for each pod. Kubernetes supports DNS policies Default, ClusterFirst, ClusterFirstWithHostNet, and None. For details, see DNS for Services and Pods. These policies are specified in the dnsPolicy field in the pod-specific.
- Default: Pods inherit the name resolution configuration from the node that the pods run on. The custom upstream DNS server and the stub domain cannot be used together with this policy.
- ClusterFirst: Any DNS query that does not match the configured cluster domain suffix, such as www.kubernetes.io, is forwarded to the upstream name server inherited from the node. Cluster administrators may have extra stub domains and upstream DNS servers configured.
- ClusterFirstWithHostNet: For pods running with hostNetwork, set its DNS policy ClusterFirstWithHostNet.
- None: It allows a pod to ignore DNS settings from the Kubernetes environment. All DNS settings should be provided using the dnsPolicy field in dnsConfigPod.
- Clusters of Kubernetes v1.10 and later support Default, ClusterFirst, ClusterFirstWithHostNet, and None. Clusters earlier than Kubernetes v1.10 support only Default, ClusterFirst, and ClusterFirstWithHostNet.
- Default is not the default DNS policy. If dnsPolicy is not explicitly specified, ClusterFirst is used.
Routing
Without stub domain configurations: Any query that does not match the configured cluster domain suffix, such as www.kubernetes.io, is forwarded to the upstream DNS server inherited from the node.
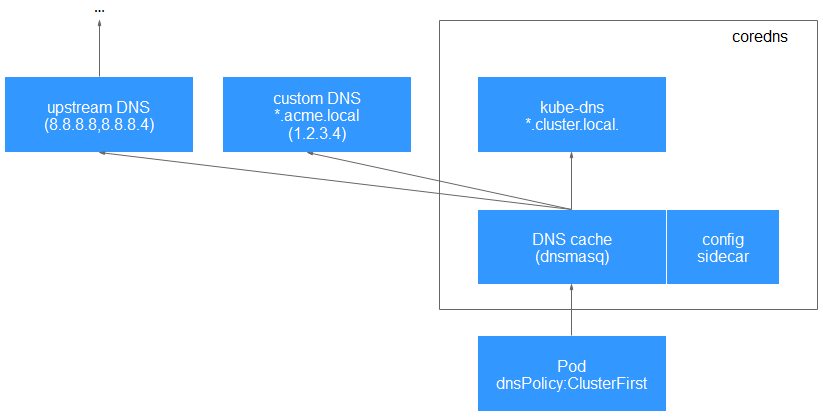
With stub domain configurations: If stub domains and upstream DNS servers are configured, DNS queries are routed according to the following flow:
- The query is first sent to the DNS caching layer in CoreDNS.
- From the caching layer, the suffix of the request is examined and then the request is forwarded to the corresponding DNS:
- Names with the cluster suffix, for example, .cluster.local: The request is sent to CoreDNS.
- Names with the stub domain suffix, for example, .acme.local: The request is sent to the configured custom DNS resolver that listens, for example, on 1.2.3.4.
- Names that do not match the suffix (for example, widget.com): The request is forwarded to the upstream DNS.
Figure 1 Routing