Function Syntax
The following is the syntax for creating a handler function in Java:
Scope Return parameter Function name (User-defined parameter, Context)
- Scope: It must be defined as public for the function that FunctionGraph invokes to execute your code.
- Return parameter: user-defined output, which is converted into a character string and returned as an HTTP response. The HTTP response is a JSON string.
- Function name: user-defined function name.
- User-defined parameter: FunctionGraph supports only one user-defined parameter. For complex parameters, define them as an object and provide data through JSON strings. When invoking a function, FunctionGraph parses the JSON strings as an object.
- Context: runtime information provided for executing the function. For details, see SDK APIs.
When creating a function in Java, define a handler in the format of [Package name].[Class name].[Function name].
Java Initializer
FunctionGraph supports the following Java runtime:
- Java 8
- Java 11
- Java 17
- Java 21
Initializer syntax:
[Package name].[Class name].[Execution function name]
For example, if the initializer is named com.Demo.my_initializer, FunctionGraph loads the my_initializer function defined in the com.Demo file.
To use Java to build initialization logic, define a Java function as the initializer. The following is a simple initializer:
public void my_initializer(Context context)
{
RuntimeLogger log = context.getLogger();
log.log(String.format("ak:%s", context.getAccessKey()));
}
- Function name
The function name my_initializer must be the initializer function name specified for a function.
For example, if the initializer is named com.Demo.my_initializer, FunctionGraph loads the my_initializer function defined in the com.Demo file.
- context
The context parameter contains the runtime information about a function. For example, request ID, temporary AK, and function metadata.
SDK APIs
The Java SDK provides context, and logging APIs.
- Context APIs
The context APIs are used to obtain the context, such as agency AK/SK, current request ID, allocated memory space, and number of CPUs, required for executing a function.
Table 1 describes the context APIs provided by FunctionGraph.
Table 1 Context methods Method
Description
getRequestID( )
Obtains a request ID.
getRemainingTimeInMilligetRunningTimeInSecondsSeconds ( )
Obtains the remaining running time of a function.
getAccessKey( )
Obtains the AK (valid for 24 hours) of an agency. If you use this method, you need to configure an agency for the function.
NOTE:FunctionGraph has stopped maintaining the getAccessKey API in the Runtime SDK. You cannot use this API to obtain a temporary AK.
getSecretKey( )
Obtains the SK (valid for 24 hours) of an agency. If you use this method, you need to configure an agency for the function.
NOTE:FunctionGraph has stopped maintaining the getSecretKey API in the Runtime SDK. You cannot use this API to obtain a temporary SK.
getSecurityAccessKey( )
Obtains the SecurityAccessKey (valid for 24 hours) with an agency. If you use this method, you need to configure an agency for the function.
getSecuritySecretKey( )
Obtains the SecuritySecretKey (valid for 24 hours) with an agency. If you use this method, you need to configure an agency for the function.
getSecurityToken( )
Obtains the SecurityToken (valid for 24 hours) with an agency. If you use this method, you need to configure an agency for the function.
getUserData(string key)
Uses keys to obtain the values passed by environment variables.
getFunctionName( )
Obtains the name of a function.
getRunningTimeInSeconds ( )
Obtains the timeout of a function.
getVersion( )
Obtains the version of a function.
getMemorySize( )
Obtains the allocated memory.
getCPUNumber( )
Obtains CPU usage of a function.
getProjectID( )
Obtains a project ID.
getPackage( )
Obtains a function group, that is, an app.
getToken( )
Obtains the token (valid for 24 hours) of an agency. If you use this method, you need to configure an agency for the function.
getLogger( )
Obtains the logger method provided by the context. By default, information such as the time and request ID is output.
NoticeResults returned by using the getToken(), getAccessKey(), and getSecretKey() methods contain sensitive information. Exercise caution when using these methods.
- Logging API
Table 2 describes the logging API provided in the Java SDK.
Table 2 Logging API Method
Description
RuntimeLogger()
Records user input logs using the method log(String string).
Developing a Java Function
Perform the following procedure to develop a Java function:
- Create a function project.
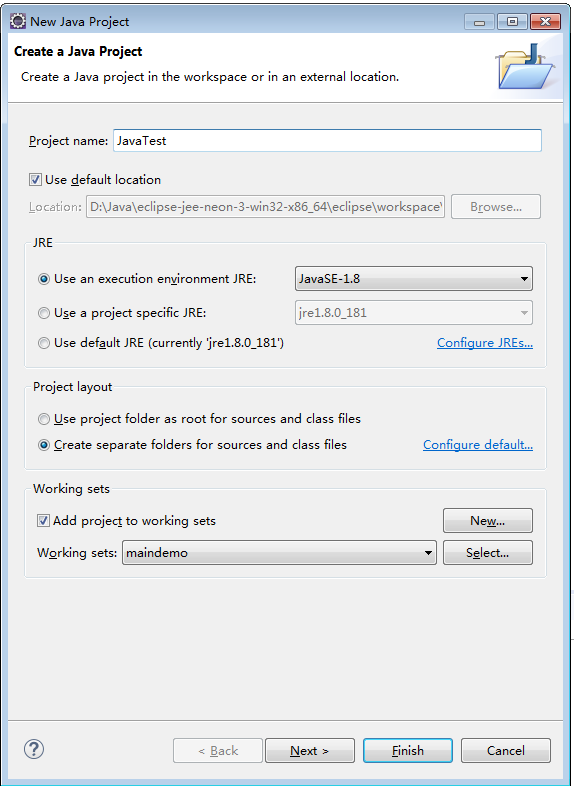
- Configure Eclipse and create a Java project named JavaTest, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Creating a project
- Add a dependency to the project.
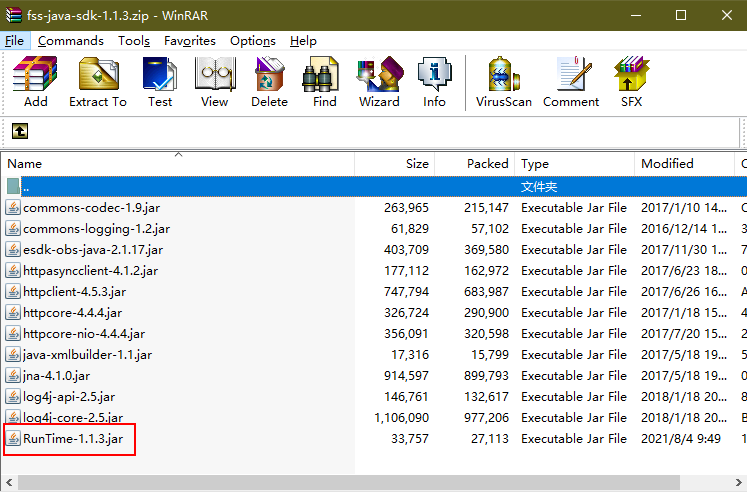
Download the to a local development environment, and decompress the SDK package, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Decompressing the downloaded SDK
- Configure the dependency.
Create a folder named lib in the project directory, copy the Runtime-1.1.3.jar file in the SDK package to the lib folder, and add the JAR file as a dependency of the project, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Configuring the dependency

- Configure Eclipse and create a Java project named JavaTest, as shown in Figure 1.
- Create a function.
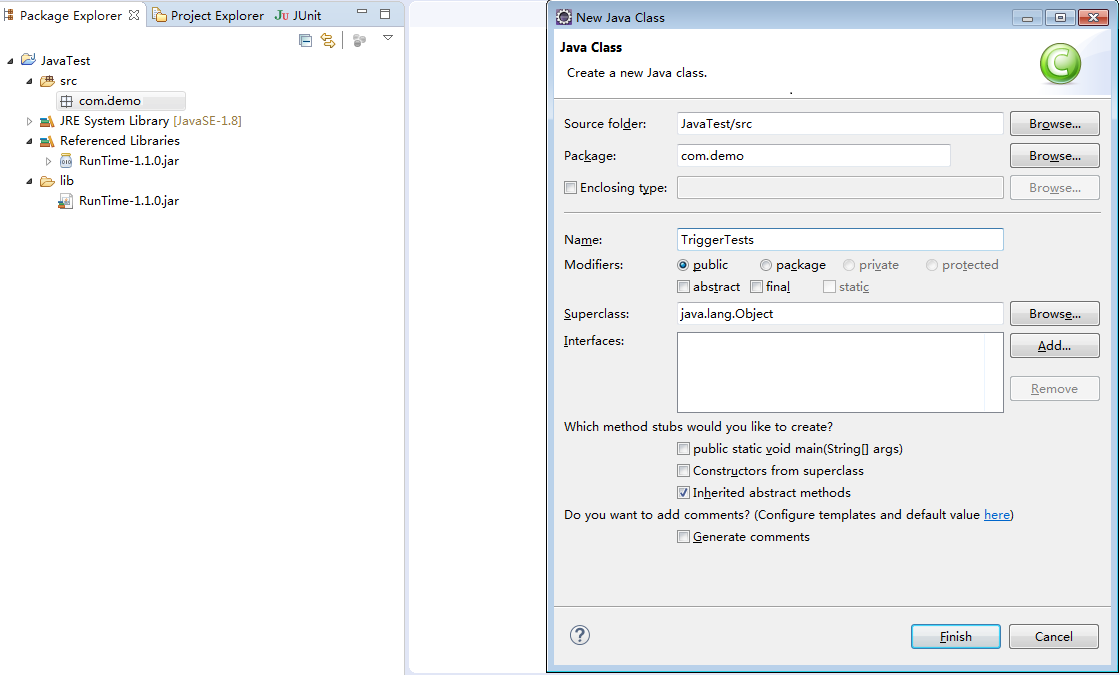
- Create a package named com.demo, and then create a class named TriggerTests under the package, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 Creating a package named com.demo
- Define the function handler in TriggerTests.java.1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526package com.demo;import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import com.services.runtime.Context;import com.services.runtime.entity.smn.SMNTriggerEvent;import com.services.runtime.entity.timer.TimerTriggerEvent;public class TriggerTests {public String smnTest(SMNTriggerEvent event, Context context){System.out.println(event);return "ok";}}public String timerTest(TimerTriggerEvent event, Context context){System.out.println(event);return "ok";}}
- Create a package named com.demo, and then create a class named TriggerTests under the package, as shown in Figure 4.
- Package the project files.
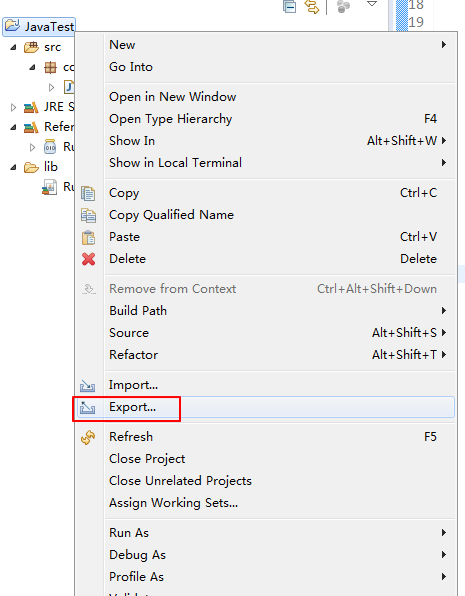
- Right-click the JavaTest project and choose Export, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Packaging the project files
- Export the project to a directory as a JAR file, as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
Figure 6 Selecting a format
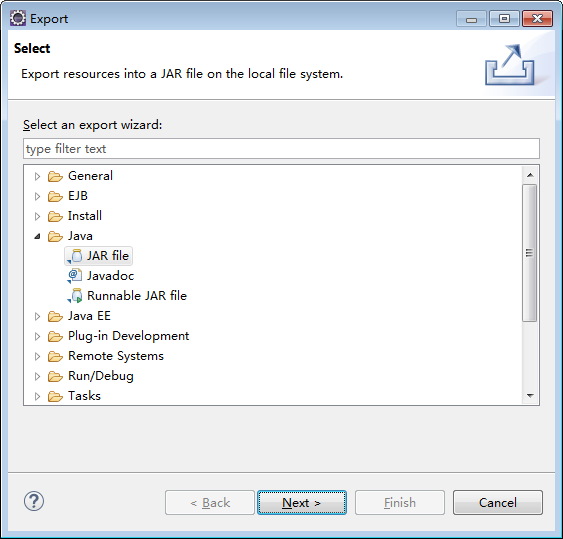
Figure 7 Specifying the destination path

- Right-click the JavaTest project and choose Export, as shown in Figure 5.
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console, create a Java function, and upload the code package.
- Test the function.
- Create a test event.
Select Timer and click Save.
- Click Test.
The function execution result consists of three parts: function output (returned by callback), summary, and logs (output by using the console.log or getLogger() method).
- Create a timer trigger.
- Access the API URL.
Change the handler to com.demo.TriggerTests.smnTest and change the event template to smn-event-template, and execute the function.
- Create a test event.
- Use a user-defined parameter in the Java code.
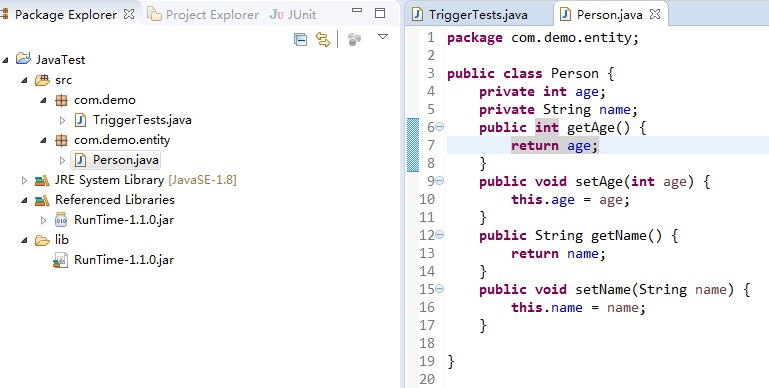
Create a Person class in the project, as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8 Creating a Person class
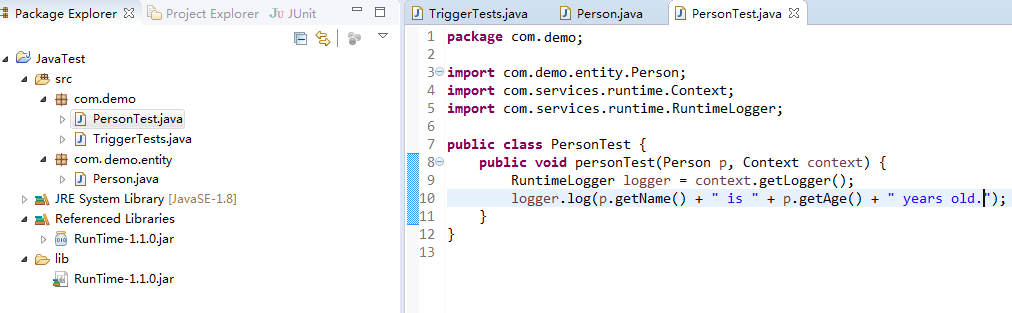
Create a class named PersonTest.java, and add a handler function to the class, as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9 Creating a class named PersonTest.java
After exporting the new package, upload it to the function, change the function handler to com.demo.PersonTest.personTest, and click Save.
In the Configure Test Event dialog box, select blank-template, enter a test event, and click Save.
Click Create, and then click Test.
Execution Result
The execution result consists of the function output, summary, and log output.
Parameter | Successful Execution | Failed Execution |
|---|---|---|
Function Output | The defined function output information is returned. | A JSON file that contains errorMessage and stackTrace is returned. The format is as follows:
errorMessage: Error message returned by the runtime. stackTrace: Stack error information returned by the runtime. |
Summary | Request ID, Memory Configured, Execution Duration, Memory Used, and Billed Duration are displayed. | Request ID, Memory Configured, Execution Duration, Memory Used, and Billed Duration are displayed. |
Log Output | Function logs are printed. A maximum of 4 KB logs can be displayed. | Error information is printed. A maximum of 4 KB logs can be displayed. |